Java 레이아웃 관리자
LayoutManager는 특정 방식으로 구성 요소를 정렬하는 데 사용됩니다. 그만큼 Java 레이아웃 관리자 GUI 형태로 구성 요소의 위치와 크기를 제어할 수 있습니다. LayoutManager는 레이아웃 관리자의 모든 클래스에 의해 구현되는 인터페이스입니다. 레이아웃 관리자를 나타내는 다음 클래스가 있습니다.
- java.awt.BorderLayout
- java.awt.FlowLayout
- java.awt.GridLayout
- java.awt.CardLayout
- java.awt.GridBagLayout
- javax.swing.BoxLayout
- javax.swing.GroupLayout
- javax.swing.ScrollPaneLayout
- javax.swing.SpringLayout 등
자바 테두리 레이아웃
BorderLayout은 북쪽, 남쪽, 동쪽, 서쪽, 중앙의 5개 지역에 구성 요소를 배열하는 데 사용됩니다. 각 지역(영역)에는 하나의 구성요소만 포함될 수 있습니다. 프레임이나 창의 기본 레이아웃입니다. BorderLayout은 각 영역에 대해 5개의 상수를 제공합니다.
BorderLayout 클래스의 생성자:
BorderLayout 클래스의 예: BorderLayout() 생성자 사용
파일 이름: Border.java
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Border { JFrame f; Border() { f = new JFrame(); // creating buttons JButton b1 = new JButton('NORTH');; // the button will be labeled as NORTH JButton b2 = new JButton('SOUTH');; // the button will be labeled as SOUTH JButton b3 = new JButton('EAST');; // the button will be labeled as EAST JButton b4 = new JButton('WEST');; // the button will be labeled as WEST JButton b5 = new JButton('CENTER');; // the button will be labeled as CENTER f.add(b1, BorderLayout.NORTH); // b1 will be placed in the North Direction f.add(b2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); // b2 will be placed in the South Direction f.add(b3, BorderLayout.EAST); // b2 will be placed in the East Direction f.add(b4, BorderLayout.WEST); // b2 will be placed in the West Direction f.add(b5, BorderLayout.CENTER); // b2 will be placed in the Center f.setSize(300, 300); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Border(); } } 산출:
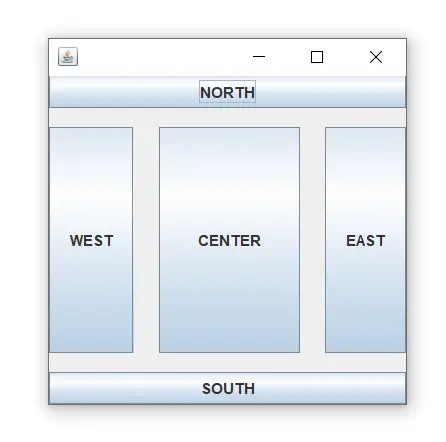 이 예제를 다운로드하세요
이 예제를 다운로드하세요BorderLayout 클래스의 예: BorderLayout(int hgap, int vgap) 생성자 사용
다음 예제에서는 매개변수화된 생성자 BorderLayout(int hgap, int gap)을 사용하여 버튼 사이에 가로 및 세로 간격을 삽입합니다.
파일 이름: BorderLayoutExample.java
// import statement import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BorderLayoutExample { JFrame jframe; // constructor BorderLayoutExample() { // creating a Frame jframe = new JFrame(); // create buttons JButton btn1 = new JButton('NORTH'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('SOUTH'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('EAST'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('WEST'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('CENTER'); // creating an object of the BorderLayout class using // the parameterized constructor where the horizontal gap is 20 // and vertical gap is 15. The gap will be evident when buttons are placed // in the frame jframe.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20, 15)); jframe.add(btn1, BorderLayout.NORTH); jframe.add(btn2, BorderLayout.SOUTH); jframe.add(btn3, BorderLayout.EAST); jframe.add(btn4, BorderLayout.WEST); jframe.add(btn5, BorderLayout.CENTER); jframe.setSize(300,300); jframe.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new BorderLayoutExample(); } } 산출:

Java BorderLayout: 지역을 지정하지 않음
JFrame 클래스의 add() 메서드는 영역을 지정하지 않은 경우에도 작동할 수 있습니다. 이러한 경우에는 가장 최근에 추가된 구성요소만 프레임에 표시되고 이전에 추가된 구성요소는 모두 삭제됩니다. 최신 구성 요소가 전체 영역을 포괄합니다. 다음 예에서는 동일한 내용을 보여줍니다.
파일 이름: BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample.java
// import statements import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample { JFrame jframe; // constructor BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample() { jframe = new JFrame(); JButton btn1 = new JButton('NORTH'); JButton btn2 = new JButton('SOUTH'); JButton btn3 = new JButton('EAST'); JButton btn4 = new JButton('WEST'); JButton btn5 = new JButton('CENTER'); // horizontal gap is 7, and the vertical gap is 7 // Since region is not specified, the gaps are of no use jframe.setLayout(new BorderLayout(7, 7)); // each button covers the whole area // however, the btn5 is the latest button // that is added to the frame; therefore, btn5 // is shown jframe.add(btn1); jframe.add(btn2); jframe.add(btn3); jframe.add(btn4); jframe.add(btn5); jframe.setSize(300,300); jframe.setVisible(true); } // main method public static void main(String argvs[]) { new BorderLayoutWithoutRegionExample(); } } 산출:

