C++에서 상속은 한 개체가 상위 개체의 모든 속성과 동작을 자동으로 획득하는 프로세스입니다. 이러한 방식으로 다른 클래스에 정의된 속성과 동작을 재사용, 확장 또는 수정할 수 있습니다.
C++에서는 다른 클래스의 멤버를 상속하는 클래스를 파생 클래스라고 하고, 멤버를 상속받은 클래스를 기본 클래스라고 합니다. 파생 클래스는 기본 클래스에 대한 특수 클래스입니다.
C++ 상속의 장점
코드 재사용성: 이제 상위 클래스의 멤버를 재사용할 수 있습니다. 따라서 멤버를 다시 정의할 필요가 없습니다. 따라서 수업에 필요한 코드가 줄어듭니다.
자바 수면
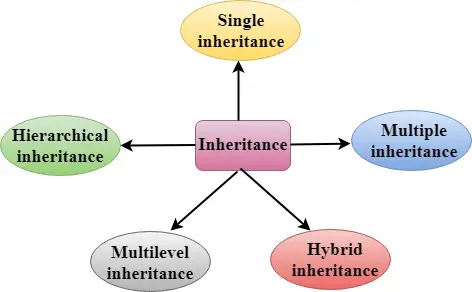
상속 유형
C++는 다섯 가지 유형의 상속을 지원합니다.
- 단일 상속
- 다중 상속
- 계층적 상속
- 다단계 상속
- 하이브리드 상속
파생 클래스
파생 클래스는 기본 클래스에서 파생된 클래스로 정의됩니다.
단어 빠른 액세스 도구 모음
파생 클래스의 구문:
|_+_|위의 경우 파생 클래스의 함수가 기본 클래스의 메서드를 재정의합니다. 따라서 display() 함수를 호출하면 파생 클래스에 정의된 함수가 호출됩니다. 기본 클래스 함수를 호출하려면 클래스 확인 연산자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } C++ 하이브리드 상속
하이브리드 상속은 두 가지 이상의 상속 유형을 조합한 것입니다.

간단한 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> C++ 계층적 상속
계층적 상속은 기본 클래스에서 둘 이상의 클래스를 파생시키는 프로세스로 정의됩니다.

계층적 상속의 구문:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } 간단한 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
타이프스크립트 화살표 기능
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>