객체지향 프로그래밍에서는 수업 기본 빌딩 블록입니다. 클래스 인스턴스화와 관련된 데이터 및 동작을 설명하는 템플릿으로 정의할 수 있습니다. 인스턴스화는 클래스의 멤버 변수 및 메소드에 액세스하는 데 사용할 수 있는 해당 클래스의 객체(변수)를 생성하는 것입니다.
클래스는 공통 속성과 메서드를 공유하는 객체를 생성하기 위한 논리적 템플릿이라고도 할 수 있습니다.
각도 cli 제거
예를 들어 Employee 클래스에는 변수 및 메서드 형식으로 모든 직원 세부 정보가 포함될 수 있습니다. 클래스가 인스턴스화되면, 즉 클래스의 객체가 생성되면(예: e1) 클래스의 모든 메서드나 속성에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
Java에서 클래스 정의
Java는 예약어를 제공합니다 수업 클래스를 정의합니다. 키워드 뒤에는 클래스 이름이 와야 합니다. 클래스 내부에는 메소드와 변수를 선언합니다.
일반적으로 클래스 선언에는 나타나는 순서대로 다음이 포함됩니다.
자바의 역사
통사론:
class class_name { // member variables // class methods } Java 클래스 예
예시 1:
Java에서 클래스를 정의하고 이를 클래스 객체로 구현하는 방법을 이해하기 위해 다음 예제를 살펴보겠습니다.
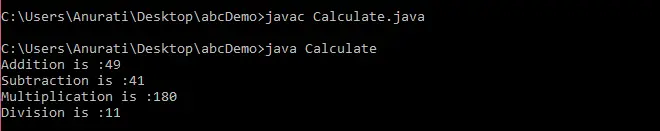
Calculate.java
// class definition public class Calculate { // instance variables int a; int b; // constructor to instantiate public Calculate (int x, int y) { this.a = x; this.b = y; } // method to add numbers public int add () { int res = a + b; return res; } // method to subtract numbers public int subtract () { int res = a - b; return res; } // method to multiply numbers public int multiply () { int res = a * b; return res; } // method to divide numbers public int divide () { int res = a / b; return res; } // main method public static void main(String[] args) { // creating object of Class Calculate c1 = new Calculate(45, 4); // calling the methods of Calculate class System.out.println('Addition is :' + c1.add()); System.out.println('Subtraction is :' + c1.subtract()); System.out.println('Multiplication is :' + c1.multiply()); System.out.println('Division is :' + c1.divide()); } 산출:
자바에서 메소드를 호출하는 방법
예 2:
다음 예제에서는 Employee와 EmployeeClass라는 두 개의 클래스를 생성합니다. Employee 클래스는 직원 세부 정보를 가져와 표시합니다. EmployeeClass에서는 Employee 클래스의 객체를 생성하고 해당 메서드를 사용합니다. 여기서는 클래스 생성자를 사용하여 객체를 초기화합니다.
EmployeeClass.java
// class to get the employee details class Employee { // declaring variables int emp_id; String name; String dept; float salary; // method to initialize the variables void add_info (int id, String n, String d, float sal) { this.emp_id = id; this.name = n; this.dept = d; this.salary = sal; } // method to display the employee details void display() { System.out.println('Employee id: ' + emp_id ); System.out.println('Employee name: ' + name ); System.out.println('Employee department: ' + dept ); System.out.println('Employee salary: ' + salary ); } } public class EmployeeClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // creating objects of class Employee Employee e1 = new Employee(); Employee e2 = new Employee(); Employee e3 = new Employee(); // calling the methods e1.add_info (101, 'Naman', 'Salesforce', 45000); e2.add_info (102, 'Riya', 'Tax', 25000); e3.add_info (103, 'Anu', 'Development', 55000); e1.display(); e2.display(); e3.display(); } } 산출:

