숫자 n이 주어지면 처음 n 비트의 합이 마지막 n 비트의 합과 같도록 길이가 2n인 모든 이진 시퀀스를 찾습니다.
예:
리눅스에서 커맨드 터치
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
아이디어는 첫 번째와 마지막 비트를 수정한 다음 나머지 2*(n-1) 비트에 대해 반복하는 것입니다. 첫 번째 비트와 마지막 비트를 수정할 때 네 가지 가능성이 있습니다.
- 첫 번째와 마지막 비트는 1이고 나머지 n - 1비트도 양쪽의 합이 동일해야 합니다.
- 첫 번째와 마지막 비트는 0이고 나머지 n - 1 비트는 양쪽 모두 동일한 합계를 가져야 합니다.
- 첫 번째 비트는 1이고 마지막 비트는 0입니다. 왼쪽에 남아 있는 n - 1비트의 합은 오른쪽에 있는 n-1비트의 합보다 1 작아야 합니다.
- 첫 번째 비트는 0이고 마지막 비트는 1입니다. 왼쪽에 남아 있는 n - 1비트의 합은 오른쪽에 있는 n-1비트의 합보다 1 커야 합니다.
아래는 위의 아이디어를 구현한 것입니다.
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include
// Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char out[] int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { System.out.print(out); System.out.print(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void main (String[] args) { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char[] out = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array out[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
# Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences(diff out start end): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) // 2): return; # if all bits are filled if (start > end): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if (diff == 0): print(''.join(list(out))end=' '); return; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out[start] = '0'; out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 1 out[start] = out[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first and last bits as 0 out[start] = out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff out start + 1 end - 1); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out[start] = '1'; out[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1); # Driver program # input number n = 2; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out=['']*(2*n); findAllSequences(0 out 0 2*n - 1); # This code is contributed by mits
// C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences(int diff char []outt int start int end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.Abs(diff) > (end - start + 1) / 2) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { Console.Write(outt); Console.Write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char []outt = new char[2 * n + 1]; // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
// PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences($diff $out $start $end) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if (abs($diff) > (int)(($end - $start + 1) / 2)) return; // if all bits are filled if ($start > $end) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ($diff == 0) print(implode(''$out).' '); return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out[$start] = '0'; $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '1'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out[$start] = $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out[$start] = '1'; $out[$end] = '0'; findAllSequences($diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out=array_fill(02*$n''); findAllSequences(0 $out 0 2*$n - 1); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?> <script> // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences(diff outt start end) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if (Math.abs(diff) > parseInt((end - start + 1) / 2 10)) return; // if all bits are filled if (start > end) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if (diff == 0) { document.write(outt.join('')); document.write(' '); } return; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt[start] = '0'; outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt[start] = outt[end] = '1'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt[start] = outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff outt start + 1 end - 1); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt[start] = '1'; outt[end] = '0'; findAllSequences(diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1); } // input number let n = 2; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array(2 * n + 1); // null terminate output array outt[2 * n] = '�'; findAllSequences(0 outt 0 2*n - 1); </script>
산출
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
시간 복잡도: O((4 ^ N )* N)
4번의 재귀 호출로 인해 4^N, 크기가 2N인 문자열을 인쇄하는 데 소요된 시간으로 인해 N(2N에서 단순화됨)
보조 공간: 에)
길이 n의 가능한 모든 문자열을 생성하고 해당 문자열의 합계를 나타내는 인덱스에 있는 목록에 저장하는 또 다른 접근 방식이 있습니다. 그런 다음 각 목록을 반복하고 각 문자열을 목록의 다른 모든 문자열과 합산하여 동일한 값을 인쇄하여 크기 2n의 문자열을 생성합니다.
C++// C++ program to implement the approach #include
// Java program to implement the approach import java.util.*; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences(int n) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.add( new ArrayList<String>()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum( n sumToString new ArrayList<String>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum( int n ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString ArrayList<String> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if (n == 0) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = ''; for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++) { seq = seq + sequence.get(i); } ArrayList<String> x = sumToString.get(sumSoFar); x.add(seq); sumToString.set(sumSoFar x); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.remove(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1); sequence.remove(0); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences( ArrayList<ArrayList<String> > sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for (int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.size(); sumIndexArr++) { // Append for (int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence1++) { for (int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString.get(sumIndexArr).size(); sequence2++) { if (sumIndexArr == sumToString.size() - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString .get(sumIndexArr) .size() - 1) { System.out.print('1111'); } else { System.out.println( sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence1) + sumToString.get(sumIndexArr) .get(sequence2)); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Function Call findAllSequences(2); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
def findAllSequences(n): sumToString = [[] for x in range(n+1)] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0) permuteSequences(sumToString) def generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0: sumToString[sumSoFar].append(''.join(sequence)) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence.append('0') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar) sequence.pop() #Generate sequence +1 sequence.append('1') generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1) sequence.pop() def permuteSequences(sumToString): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString: # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr: for sequence2 in sumIndexArr: print(sequence1 + sequence2) findAllSequences(2) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { static void findAllSequences(int n) { List<List<string>> sumToString = new List<List<string>>(); for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.Add(new List<string>()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString new List<string>() 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } static void generateSequencesWithSum(int n List<List<string>> sumToString List<string> sequence int sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = ''; for(int i = 0; i < sequence.Count; i++) { seq = seq + sequence[i]; } sumToString[sumSoFar].Add(seq); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.Add('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.RemoveAt(0); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.Add('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.RemoveAt(0); } static void permuteSequences(List<List<string>> sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(int sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.Count; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(int sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence1++) { for(int sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.Count-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].Count-1) { Console.Write('1111'); } else { Console.WriteLine(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2]); } } } } } static void Main() { findAllSequences(2); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
<script> function findAllSequences(n) { let sumToString = []; for(let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { sumToString.push([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString [] 0); permuteSequences(sumToString); } function generateSequencesWithSum(n sumToString sequence sumSoFar) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if(n == 0) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString[sumSoFar].push(sequence.join('')); return; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence.push('0'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar); sequence.shift(); // Generate sequence +1 sequence.push('1'); generateSequencesWithSum(n-1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar+1); sequence.shift(); } function permuteSequences(sumToString) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for(let sumIndexArr = 0; sumIndexArr < sumToString.length; sumIndexArr++) { // Append for(let sequence1 = 0; sequence1 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence1++) { for(let sequence2 = 0; sequence2 < sumToString[sumIndexArr].length; sequence2++) { if(sumIndexArr == sumToString.length-1 && sequence1 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1 && sequence2 == sumToString[sumIndexArr].length-1) { document.write('1111'); } else { document.write(sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence1] + sumToString[sumIndexArr][sequence2] + ''); } } } } } findAllSequences(2); // This code is contributed by decode2207. </script>
산출
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
시간 복잡도 분석:
generateSequencesWithSum =O((2N)*N)
- 2N: 크기 N의 이진 문자열의 모든 순열을 생성합니다.
- N: 문자 목록을 문자열로 변환하고 배열에 저장합니다. 이는 기본 사례에서 수행됩니다.
순열순서 =O((2N) * N!/(N/2)!2* N)
- 2N: 크기 n으로 생성된 모든 문자열을 반복합니다.
- N!/(N/2)!2: 이건 설명하기가 좀 어렵네요
N = 2를 예로 들어보겠습니다. 크기 n의 가능한 시퀀스 배열은 다음과 같습니다.
| 배열 인덱스 | 1 | 2 | |
| 문자열 목록 | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
인덱스가 합계를 나타내는 문자열 목록에서 'n choose k' 공식을 사용하여 크기 2n의 문자열 개수를 얻습니다. 우리의 경우에는 nCk *nCk가 됩니다. 여기서 k는 크기가 2n인 문자열의 각 절반에 있는 1의 수를 나타냅니다.
k = 0 (2C0)^2 = 1 문자열 (0000)
k = 1 (2C1)^2 문자열 = 4 문자열(0101 0110 1001 1010)
k = 2 (2c2)^2 = 1 문자열 (1111)
타이프스크립트 화살표 기능
k = N/2일 때 가장 긴 문자열 목록을 얻습니다.N기음N/2= N!/[(N/2)! * (N - N/2)!] 간단히 말하면N기음N/2= N!/(N/2)!2
따라서 각 요소에 대해 최대한 반복해야 합니다.N기음N/2길이 2N의 스트링 형성용
정식 증명 없이 2^N과 N!/(N/2)을 그래프로 나타내면!2우리는 그것을 본다 2N후자보다 성장 속도가 빠릅니다. 그러므로 O(2N* N!/(N/2)2)< O(2N*2N) = O(22n) = O(4N)
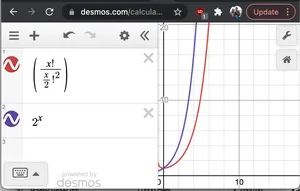 2^x와 nC(n/2)의 그래프
2^x와 nC(n/2)의 그래프- N: 크기가 2N인 각 문자열을 인쇄해야 합니다.
마지막으로 permuteSequence가 주요 용어이기 때문에 generateSequencesWithSum의 시간 복잡도를 무시할 수 있습니다.
시간 복잡도: 오(2N* N!/(N/2)!2* N) (O((4^N) * N의 첫 번째 솔루션보다 더 자세한 내용은 위 설명 참조)
보조 공간 : 오(2N) 크기 N의 모든 이진 문자열 순열을 저장하기 때문입니다.
파이썬 경로 설정
#include
import java.util.*; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data; int sum; FirstHalf(String data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map<Integer ArrayList<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); //first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new ArrayList<>(); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString(String s) { int sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(char c: s.toCharArray()) { sum += c - '0'; } return sum; } public static void perm(String p char[] bin int level int n) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if(level == 0) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map.putIfAbsent(sum new ArrayList<String>()); map.get(sum).add(p); return; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(char c: bin) { perm(p+c bin level-1 n); } } public static void result() { int i = 0; for(FirstHalf first: firstHalf) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList<String> secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(String second: secondHalf) { //append first and second half and print System.out.print(first.data+second+' '); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) System.out.println(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { char[] up = {'0' '1'}; int n = 2; perm('' up n n); result(); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
# Python code implementation class FirstHalf: def __init__(self data sum): self.data = data self.sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString(s): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range(len(s)): sum += ord(s[i]) - ord('0') return sum def perm(p bin level n): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0: # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString(p) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.append(FirstHalf(p sum)) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map: map[sum] = [] map[sum].append(p) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range(len(bin)): perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n) def result(): i = 0 for j in range(len(firstHalf)): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf[j].sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map[sum] for k in range(len(secondHalf)): # append first and second half and print print(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' ' end='') # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if(i % 6 == 0): print('n') up = ['0' '1'] n = 2 perm('' up n n) result() # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class FirstHalf { public string data; public int sum; public FirstHalf(string data int sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary<int List<string>> mp = new Dictionary<int List<string>>(); // first N-half bits static List<FirstHalf> firstHalf = new List<FirstHalf>(); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString(string s) { int sum = 0; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach (char c in s) { sum += (c - '0'); } return sum; } static void perm(string p char[] bin int level int n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if (level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.Add(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if (mp.ContainsKey(sum)) { mp[sum].Add(p); } else { mp.Add(sum new List<string> { p }); } return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = bin[i]; perm(p + c bin level - 1 n); } } static void result() { int i = 0; foreach (FirstHalf first in firstHalf) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first.sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List<string> secondHalf = mp[sum]; foreach (string second in secondHalf) { // append first and second half and print Console.Write(first.data + second + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if (i % 6 == 0) Console.WriteLine(); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { char[] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2; string x = ''; perm(x up n n); result(); } }
class FirstHalf { constructor(data sum) { this.data = data; this.sum = sum; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map(); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString(s) { let sum = 0; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { sum += s.charCodeAt(i) - '0'.charCodeAt(0); } return sum; } function perm(p bin level n) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if(level == 0) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString(p); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf.push(new FirstHalf(p sum)); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if(!map.has(sum)) map.set(sum []); map.get(sum).push(p); return; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for(let i = 0; i < bin.length; i++) { perm(p+bin[i] bin level-1 n); } } function result() { let i = 0; for(let j = 0; j < firstHalf.length; j++) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf[j].sum; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map.get(sum); for(let k = 0; k < secondHalf.length; k++) { // append first and second half and print process.stdout.write(firstHalf[j].data + secondHalf[k] + ' '); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i++; if(i % 6 == 0) process.stdout.write('n'); } } } const up = ['0' '1']; const n = 2; perm('' up n n); result();
산출
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
연산:
1. 크기 n의 모든 이진 순열을 생성합니다.
2. 각 순열의 비트 합계를 계산하고 후반부에 기억합니다.
[예: n=2의 경우 sum = 1인 두 개의 문자열, 즉 '01' '10'이 있다는 것을 기억하세요.]
3. 생성된 모든 순열을 반복하고 각 순열에 대해 비트 합계에 따라 후반부를 추가합니다.
시간 복잡도 분석:
에디스 맥 허쉬
문자열합계() = O(N) : 각 비트를 순회하여 합계에 추가합니다.
파마() =O(2N* N)
2N * N : 크기 N의 이진 비트의 모든 순열을 생성하고 각 순열에 대한 비트의 합을 찾습니다.
결과() =O((2N) * (N!/(N/2)!)2)
2N: 크기 N(전반)의 가능한 모든 순열을 반복합니다.
NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!2: (하반기 최대 크기) : 아래 설명:
N = 4를 예로 들어보겠습니다.:
//해시맵은 다음과 같습니다.
0 -> [0000] .....................(목록 크기: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] .....................(목록 크기: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] .....................(목록 크기: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] .....................(목록 크기: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] .....................(목록 크기: 4C4 = 1)
우리는 여기서 각 목록의 크기가 N 선택 키를 가지며 N 선택 N/2에서 최대가 된다는 것을 관찰합니다.
우리는 2를 모두 반복하고 있기 때문에N순열과 지도에서 후반부를 추가합니다. 지도의 N/2 위치에는 최대 크기 목록이 있습니다.
최악의 경우는 NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)!를 통과해야 하는 N/2 위치에서 발생합니다.2순열.
스리 라마누잔
시간 복잡도: O(2N* N!/(N/2)!2)
보조공간 : O(2N) 왜냐하면 우리는 N 크기의 모든 이진 문자열 순열을 저장하기 때문입니다.
