Integer 클래스는 int 값을 문자열 표현으로 변환하거나 그 반대로 변환하는 것과 같이 효과적으로 int 값을 처리하는 여러 메서드를 포함하는 기본 유형 int에 대한 래퍼 클래스입니다. Integer 클래스의 객체는 단일 int 값을 보유할 수 있습니다.
생성자:
- 정수(int b): 제공된 값으로 초기화된 Integer 객체를 생성합니다.
통사론:
public Integer(int b)>
매개변수:
b : value with which to initialize>
- 정수(문자열): 문자열 표현에서 제공하는 int 값으로 초기화된 Integer 개체를 만듭니다. 기본 기수는 10으로 간주됩니다.
통사론:
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
s : string representation of the int value>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : If the string provided does not represent any int value.>
행동 양식:
1. toString() : int 값에 해당하는 문자열을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public String toString(int b)>
매개변수:
b : int value for which string representation required.>
2. toHexString() : int 값에 해당하는 문자열을 16진수 형식으로 반환합니다. 즉, int 값을 16진수 문자-[0-9][a-f]로 나타내는 문자열을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public String toHexString(int b)>
매개변수:
b : int value for which hex string representation required.>
삼. toOctalString() : int 값에 해당하는 문자열을 8진수 형식으로 반환합니다. 즉, int 값을 8진수 문자-[0-7]로 나타내는 문자열을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public String toOctalString(int b)>
매개변수:
b : int value for which octal string representation required.>
4. toBinaryString() : int 값에 해당하는 문자열을 이진수로 반환합니다. 즉, int 값을 16진수 문자로 나타내는 문자열을 반환합니다.-[0/1]
통사론:
public String toBinaryString(int b)>
매개변수:
b : int value for which binary string representation required.>
5. 가치() : 제공된 값으로 초기화된 Integer 객체를 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static Integer valueOf(int b)>
매개변수:
b : a int value>
- valueOf(문자열 값, 정수 기수) : new Integer(Integer.parseInteger(val,radix)) 와 유사한 기능을 제공하는 또 다른 오버로드된 함수
통사론:
public static Integer valueOf(String val, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
val : String to be parsed into int value radix : radix to be used while parsing>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
- valueOf(문자열 값) : new Integer(Integer.parseInt(val,10)) 와 유사한 기능을 제공하는 또 다른 오버로드된 함수
통사론:
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
s : a String object to be parsed as int>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
6. 파싱인트() : 제공된 기수로 문자열을 구문 분석하여 int 값을 반환합니다. 기본 int 값을 반환하고 valueOf()는 Integer 객체를 반환하므로 valueOf()와 다릅니다.
통사론:
public static int parseInt(String val, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
val : String representation of int radix : radix to be used while parsing>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
- String만 매개 변수로 포함하는 또 다른 오버로드된 메서드인 radix는 기본적으로 10으로 설정됩니다.
통사론:
public static int parseInt(String val) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
val : String representation of int>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
7. getInteger(): 주어진 시스템 속성과 연관된 값을 나타내는 Integer 객체를 반환하거나, 존재하지 않는 경우 null을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static Integer getInteger(String prop)>
매개변수:
prop : System property>
- 속성이 존재하지 않는 경우 두 번째 인수를 반환하는 또 다른 오버로드된 메서드, 즉 null을 반환하지 않고 사용자가 제공한 기본값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static Integer getInteger(String prop, int val)>
매개변수:
prop : System property val : value to return if property does not exist.>
- 반환된 값에 따라 값을 구문 분석하는 또 다른 오버로드된 메서드입니다. 즉, 반환된 값이 #으로 시작하면 16진수로 구문 분석되고, 0으로 시작하면 8진수로 구문 분석되고, 그렇지 않으면 10진수로 구문 분석됩니다.
통사론:
public static Integer getInteger(String prop, Integer val)>
매개변수:
prop : System property val : value to return if property does not exist.>
8. 디코드() : 제공된 문자열의 디코딩된 값을 보유하는 Integer 객체를 반환합니다. 제공된 문자열은 다음 형식이어야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 NumberFormatException이 발생합니다.
Decimal- (부호)Decimal_Number
Hex-(부호)0xHex_Digits
Hex- (부호)0XHex_Digits
8진수-(부호)0″Octal_Digits
통사론:
public static Integer decode(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
매개변수:
s : encoded string to be parsed into int val>
던지기:
NumberFormatException : If the string cannot be decoded into a int value>
9. 회전왼쪽() : 주어진 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 주어진 거리만큼 왼쪽 비트를 회전하여 기본 int를 반환합니다. 왼쪽으로 회전하면 최상위 비트가 오른쪽으로 이동하거나 최하위 위치로 이동합니다. 즉, 비트의 순환 이동이 발생합니다. 음의 거리는 오른쪽 회전을 의미합니다.
통사론:
public static int rotateLeft(int val, int dist)>
매개변수:
val : int value to be rotated dist : distance to rotate>
10. 회전오른쪽() : 주어진 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 주어진 거리만큼 오른쪽으로 비트를 회전하여 기본 int를 반환합니다. 오른쪽으로 회전하면 최하위 비트가 왼쪽으로 이동하거나 최상위 위치, 즉 비트의 순환 이동이 발생합니다. 음의 거리는 왼쪽 회전을 나타냅니다.
통사론:
public static int rotateRight(int val, int dist)>
매개변수:
val : int value to be rotated dist : distance to rotate>
자바
// Java program to illustrate> // various Integer methods> public> class> Integer_test {> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >int> b =>55>;> >String bb =>'45'>;> >// Construct two Integer objects> >Integer x =>new> Integer(b);> >Integer y =>new> Integer(bb);> >// toString()> >System.out.println(>'toString(b) = '> >+ Integer.toString(b));> >// toHexString(),toOctalString(),toBinaryString()> >// converts into hexadecimal, octal and binary> >// forms.> >System.out.println(>'toHexString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toHexString(b));> >System.out.println(>'toOctalString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toOctalString(b));> >System.out.println(>'toBinaryString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toBinaryString(b));> >// valueOf(): return Integer object> >// an overloaded method takes radix as well.> >Integer z = Integer.valueOf(b);> >System.out.println(>'valueOf(b) = '> + z);> >z = Integer.valueOf(bb);> >System.out.println(>'ValueOf(bb) = '> + z);> >z = Integer.valueOf(bb,>6>);> >System.out.println(>'ValueOf(bb,6) = '> + z);> >// parseInt(): return primitive int value> >// an overloaded method takes radix as well> >int> zz = Integer.parseInt(bb);> >System.out.println(>'parseInt(bb) = '> + zz);> >zz = Integer.parseInt(bb,>6>);> >System.out.println(>'parseInt(bb,6) = '> + zz);> >// getInteger(): can be used to retrieve> >// int value of system property> >int> prop> >= Integer.getInteger(>'sun.arch.data.model'>);> >System.out.println(> >'getInteger(sun.arch.data.model) = '> + prop);> >System.out.println(>'getInteger(abcd) ='> >+ Integer.getInteger(>'abcd'>));> >// an overloaded getInteger() method> >// which return default value if property not found.> >System.out.println(> >'getInteger(abcd,10) ='> >+ Integer.getInteger(>'abcd'>,>10>));> >// decode() : decodes the hex,octal and decimal> >// string to corresponding int values.> >String decimal =>'45'>;> >String octal =>'005'>;> >String hex =>'0x0f'>;> >Integer dec = Integer.decode(decimal);> >System.out.println(>'decode(45) = '> + dec);> >dec = Integer.decode(octal);> >System.out.println(>'decode(005) = '> + dec);> >dec = Integer.decode(hex);> >System.out.println(>'decode(0x0f) = '> + dec);> >// rotateLeft and rotateRight can be used> >// to rotate bits by specified distance> >int> valrot =>2>;> >System.out.println(> >'rotateLeft(0000 0000 0000 0010 , 2) ='> >+ Integer.rotateLeft(valrot,>2>));> >System.out.println(> >'rotateRight(0000 0000 0000 0010,3) ='> >+ Integer.rotateRight(valrot,>3>));> >}> }> |
>
>
산출:
toString(b) = 55 toHexString(b) =37 toOctalString(b) =67 toBinaryString(b) =110111 valueOf(b) = 55 ValueOf(bb) = 45 ValueOf(bb,6) = 29 parseInt(bb) = 45 parseInt(bb,6) = 29 getInteger(sun.arch.data.model) = 64 getInteger(abcd) =null getInteger(abcd,10) =10 decode(45) = 45 decode(005) = 5 decode(0x0f) = 15 rotateLeft(0000 0000 0000 0010 , 2) =8 rotateRight(0000 0000 0000 0010,3) =1073741824>
11. 바이트값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 바이트 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public byte byteValue()>
12. 짧은값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 짧은 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public short shortValue()>
13. 정수값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 int 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public int intValue()>
13. 긴값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 긴 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public long longValue()>
14. 더블값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 double 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public double doubleValue()>
15. 플로트값() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 부동 소수점 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public float floatValue()>
16. 해시코드() : 이 정수 객체에 해당하는 해시코드를 반환합니다.
통사론:
public int hashCode()>
17. 비트카운트() : 주어진 정수의 2의 보수로 설정된 비트 수를 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int bitCount(int i)>
매개변수:
i : int value whose set bits to count>
18. NumberOfLeadingZeroes() : 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 가장 높은 1비트보다 앞선 0비트의 수를 반환합니다. 즉, 2의 보수 형식의 숫자가 0000 1010 0000 0000인 경우 이 함수는 4를 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int numberofLeadingZeroes(int i)>
매개변수:
i : int value whose leading zeroes to count in twos complement form>
19. 숫자OfTrailingZeroes() : 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 마지막 1비트 뒤에 오는 0비트의 수를 반환합니다. 즉, 2의 보수 형식의 숫자가 0000 1010 0000 0000인 경우 이 함수는 9를 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int numberofTrailingZeroes(int i)>
매개변수:
i : int value whose trailing zeroes to count in twos complement form>
20. 최고원비트() : 주어진 값에서 가장 높은 1비트 위치에 있는 최대 1비트의 값을 반환합니다. 주어진 값이 0이면 0을 반환합니다. 즉, 숫자가 0000 0000 0000 1111이면 이 함수는 0000 0000 0000 1000(주어진 숫자에서 가장 높은 1비트에 1)을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int highestOneBit(int i)>
매개변수:
i : int value>
21. 최저원비트() : 주어진 값에서 가장 낮은 1비트 위치에서 최대 1비트의 값을 반환합니다. 주어진 값이 0이면 0을 반환합니다. 즉, 숫자가 0000 0000 0000 1111이면 이 함수는 0000 0000 0000 0001(주어진 숫자에서 가장 높은 1비트에 1)을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int LowestOneBit(int i)>
매개변수:
i : int value>
22. 같음() : 두 Integer 객체의 동등성을 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 메서드는 두 객체 모두 동일한 int 값을 포함하는 경우 true를 반환합니다. 동등성을 확인하는 경우에만 사용해야 합니다. 다른 모든 경우에는 CompareTo 메서드가 선호됩니다.
통사론:
public boolean equals(Object obj)>
매개변수:
obj : object to compare with>
23. 비교() : 수치적 동등성을 위해 두 Integer 객체를 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 더 작은 값과 더 큰 값을 구별하므로 수치 동등성을 위해 두 정수 값을 비교할 때 사용해야 합니다. 0,0보다 작은 값을 반환하고, 보다 작음, 같음, 보다 큰 경우 0보다 큰 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public int compareTo(Integer b)>
매개변수:
숫자의 알파벳
b : Integer object to compare with>
24. 비교() : 수치적 동등성을 위해 두 개의 기본 int 값을 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. 정적 메소드이므로 Integer 객체를 생성하지 않고도 사용할 수 있습니다.
통사론:
public static int compare(int x,int y)>
매개변수:
x : int value y : another int value>
25. 사인() : 음수 값의 경우 -1, 0의 경우 0, 0보다 큰 값의 경우 +1을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int signum(int val)>
매개변수:
val : int value for which signum is required.>
26. 역방향() : 주어진 int 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 비트 순서를 반대로 하는 기본 int 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int reverseBytes(int val)>
매개변수:
val : int value whose bits to reverse in order.>
27. 역방향바이트() : 주어진 int 값의 2의 보수 형식으로 바이트 순서를 반대로 하는 기본 int 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int reverseBytes(int val)>
매개변수:
val : int value whose bits to reverse in order.>
28. static int CompareUnsigned(int x, int y) : 이 방법은 값을 부호 없는 값으로 처리하여 두 개의 int 값을 비교합니다.
통사론:
public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y)>
29. static int DivideUnsigned(int 배당금, int 제수) : 이 메서드는 첫 번째 인수를 두 번째 인수로 나눈 부호 없는 몫을 반환하며, 여기서 각 인수와 결과는 부호 없는 값으로 해석됩니다.
통사론:
public static int divideUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor)>
30. static int max(int a, int b) : 이 메서드는 Math.max를 호출하는 것처럼 두 int 값 중 더 큰 값을 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static int max(int a, int b)>
31. static int min(int a, int b) : Math.min을 호출한 것처럼 두 개의 int 값 중 더 작은 값을 반환하는 메서드입니다.
통사론:
public static int min(int a, int b)>
32. static int parseUnsignedInt(CharSequence s, int startIndex, int endIndex, int radix) : 이 메서드는 지정된 BeginIndex에서 시작하여 endIndex – 1까지 확장되는 지정된 기수의 부호 없는 int로 CharSequence 인수를 구문 분석합니다.
통사론:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
33. static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) : 이 메서드는 문자열 인수를 부호 없는 10진수 정수로 구문 분석합니다.
통사론:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
34. static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix) : 이 메서드는 문자열 인수를 두 번째 인수로 지정된 기수의 부호 없는 정수로 구문 분석합니다.
통사론:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
35. static int 나머지Unsigned(int 배당금, int 제수) : 이 메서드는 첫 번째 인수를 두 번째 인수로 나눈 부호 없는 나머지를 반환하며, 여기서 각 인수와 결과는 부호 없는 값으로 해석됩니다.
통사론:
public static int remainderUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor)>
36. static int sum(int a, int b) : 이 방법은 + 연산자에 따라 두 개의 정수를 더합니다.
통사론:
public static int sum(int a, int b)>
37. static long toUnsignedLong(int x) : 이 메서드는 부호 없는 변환을 통해 인수를 long으로 변환합니다.
통사론:
public static long toUnsignedLong(int x)>
38. 정적 문자열 toUnsignedString(int i) : 이 메서드는 인수의 문자열 표현을 부호 없는 10진수 값으로 반환합니다.
통사론:
public static String toUnsignedString(int i, int radix)>
자바
// Java program to illustrate> // various Integer class methods> public> class> Integer_test {> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >int> b =>55>;> >String bb =>'45'>;> >// Construct two Integer objects> >Integer x =>new> Integer(b);> >Integer y =>new> Integer(bb);> >// xxxValue can be used to retrieve> >// xxx type value from int value.> >// xxx can be int,byte,short,long,double,float> >System.out.println(>'bytevalue(x) = '> >+ x.byteValue());> >System.out.println(>'shortvalue(x) = '> >+ x.shortValue());> >System.out.println(>'intvalue(x) = '> + x.intValue());> >System.out.println(>'longvalue(x) = '> >+ x.longValue());> >System.out.println(>'doublevalue(x) = '> >+ x.doubleValue());> >System.out.println(>'floatvalue(x) = '> >+ x.floatValue());> >int> value =>45>;> >// bitcount() : can be used to count set bits> >// in twos complement form of the number> >System.out.println(>'Integer.bitcount(value)='> >+ Integer.bitCount(value));> >// numberOfTrailingZeroes and numberOfLeadingZeroes> >// can be used to count prefix and postfix sequence> >// of 0> >System.out.println(> >'Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value)='> >+ Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value));> >System.out.println(> >'Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value)='> >+ Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value));> >// highestOneBit returns a value with one on highest> >// set bit position> >System.out.println(>'Integer.highestOneBit(value)='> >+ Integer.highestOneBit(value));> >// highestOneBit returns a value with one on lowest> >// set bit position> >System.out.println(>'Integer.lowestOneBit(value)='> >+ Integer.lowestOneBit(value));> >// reverse() can be used to reverse order of bits> >// reverseBytes() can be used to reverse order of> >// bytes> >System.out.println(>'Integer.reverse(value)='> >+ Integer.reverse(value));> >System.out.println(>'Integer.reverseBytes(value)='> >+ Integer.reverseBytes(value));> >// signum() returns -1,0,1 for negative,0 and> >// positive values> >System.out.println(>'Integer.signum(value)='> >+ Integer.signum(value));> >// hashcode() returns hashcode of the object> >int> hash = x.hashCode();> >System.out.println(>'hashcode(x) = '> + hash);> >// equals returns boolean value representing> >// equality> >boolean> eq = x.equals(y);> >System.out.println(>'x.equals(y) = '> + eq);> >// compare() used for comparing two int values> >int> e = Integer.compare(x, y);> >System.out.println(>'compare(x,y) = '> + e);> >// compareTo() used for comparing this value with> >// some other value> >int> f = x.compareTo(y);> >System.out.println(>'x.compareTo(y) = '> + f);> >}> }> |
>
>
출력 :
bytevalue(x) = 55 shortvalue(x) = 55 intvalue(x) = 55 longvalue(x) = 55 doublevalue(x) = 55.0 floatvalue(x) = 55.0 Integer.bitcount(value)=4 Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value)=0 Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value)=26 Integer.highestOneBit(value)=32 Integer.lowestOneBit(value)=1 Integer.reverse(value)=-1275068416 Integer.reverseBytes(value)=754974720 Integer.signum(value)=1 hashcode(x) = 55 x.equals(y) = false compare(x,y) = 1 x.compareTo(y) = 1>
Java에서 정수 래퍼 클래스 초기화:
유형 1: 직접 초기화:
Integer 클래스의 상수 객체는 힙 메모리의 상수 공간 내부에 생성됩니다. 상수 공간: 힙 메모리에 상수를 위한 공간이 있다는 것을 더 잘 이해하기 위해 상상하기 위한 것입니다.
예:
Integer x = 200; //initializing directly x = 300; //modifying x x = 10; //modifying x again>
정수 x = 200
- 컴파일러는 위의 명령문을 다음과 같이 변환합니다. 정수 x=Integer.valueOf(200) . 이것은 다음과 같이 알려져 있습니다. 오토박싱 . 기본 정수 값 200이 객체로 변환됩니다.
( Autoboxing 및 Unboxing을 이해하려면 여기를 확인하세요. )
- x는 상수 공간에 존재하는 200을 가리킵니다. 그림 1을 참조하십시오.
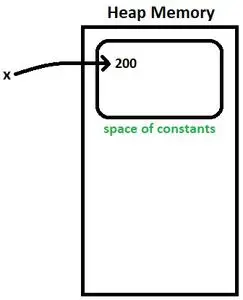
그림 1
엑스 = 300
- x는 직접 초기화되는 Integer 클래스 객체이기 때문에 오토박싱이 다시 수행됩니다.
- 메모: 직접 초기화된 객체(x)는 상수이므로 수정할 수 없습니다. 새 상수(300)를 가리켜 객체를 수정하려고 하면 이전 상수(200)가 힙 메모리에 있지만 객체는 새 상수를 가리키게 됩니다.
- x는 상수 공간에 존재하는 300을 가리킨다. 그림 2를 참조하세요.
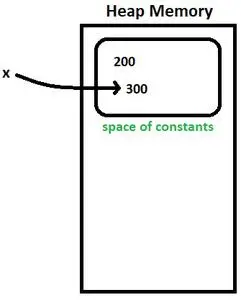
그림 2
엑스 = 10
- 메모: 기본적으로 -128 ~ 127 값의 경우 Integer.valueOf() 메서드는 Integer의 새 인스턴스를 생성하지 않습니다. 캐시에서 값을 반환합니다.
- x 캐시에 존재하는 포인트 10입니다.
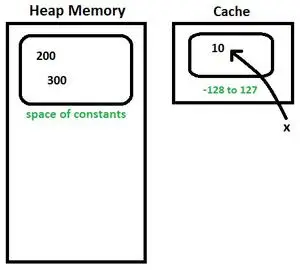
그림 3
다음에 x = 200 또는 x=300을 할당하면 이미 상수 공간에 존재하는 값 200 또는 300을 가리킬 것입니다. x에 이 두 값 이외의 값을 할당하면 새로운 상수가 생성됩니다.
(더 나은 이해를 위해 정수 래퍼 클래스 비교 항목을 확인하세요.)
유형 2: 동적으로 초기화:
상수가 아닌 Integer 클래스 객체는 상수 공간 외부에 생성됩니다. 또한 상수 공간 내부에 정수 상수를 생성합니다. 변수는 Integer 상수가 아닌 Integer 객체를 가리킵니다.
예:
Integer a = new Integer(250); //Initializing dynamically a = 350; //Type 1 initialization>
정수 a = 새로운 정수(250)
- 250은 상수 공간의 내부와 외부에 생성됩니다. 변수 'a'는 상수 공간 외부의 값을 가리킵니다. 그림 4를 참조하십시오.
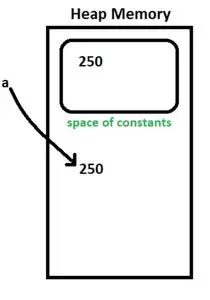
그림 4
a = 350;
- 오토박싱 후 'a'는 350을 가리키게 됩니다. 그림 5를 참조하세요.
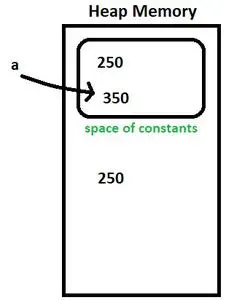
그림 5
다음에 a = 250을 할당하면 이미 동일한 값으로 존재하는 개체를 가리키지 않고 새 개체가 생성됩니다.
참고자료: 공식 Java 문서
