맵에는 키를 기반으로 하는 값, 즉 키와 값 쌍이 포함됩니다. 각 키와 값 쌍을 항목이라고 합니다. 맵에는 고유 키가 포함되어 있습니다.
스크립트를 실행하는 방법
맵은 키를 기준으로 요소를 검색, 업데이트 또는 삭제해야 하는 경우 유용합니다.
Java 맵 계층
Java에는 Map을 구현하기 위한 두 가지 인터페이스(Map 및 SortedMap)와 세 가지 클래스(HashMap, LinkedHashMap 및 TreeMap)가 있습니다. Java Map의 계층 구조는 다음과 같습니다.
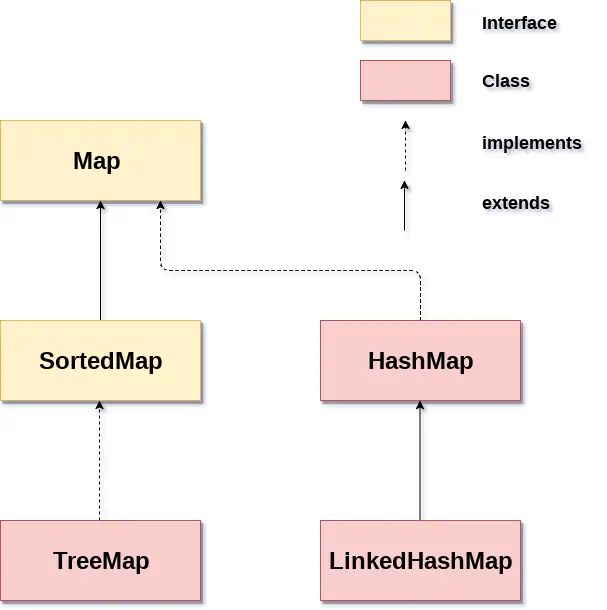
맵은 중복 키를 허용하지 않지만 중복 값을 가질 수 있습니다. HashMap과 LinkedHashMap은 null 키와 값을 허용하지만 TreeMap은 null 키나 값을 허용하지 않습니다.
Map은 순회할 수 없으므로 다음을 사용하여 Set으로 변환해야 합니다. 키세트() 또는 엔트리셋() 방법.
| 수업 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 해시맵 | HashMap은 Map의 구현이지만 순서를 유지하지 않습니다. |
| LinkedHashMap | LinkedHashMap은 Map의 구현입니다. HashMap 클래스를 상속받습니다. 삽입 순서를 유지합니다. |
| 트리맵 | TreeMap은 Map 및 SortedMap을 구현한 것입니다. 오름차순을 유지합니다. |
Map 인터페이스의 유용한 방법
| 방법 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| V put(객체 키, 객체 값) | 지도에 항목을 삽입하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| void putAll(지도 맵) | 지정된 지도를 지도에 삽입하는데 사용됩니다. |
| V putIfAbsent(K 키, V 값) | 아직 지정되지 않은 경우에만 지정된 키와 함께 지정된 값을 맵에 삽입합니다. |
| V 제거(객체 키) | 지정된 키에 대한 항목을 삭제하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 불리언 제거(객체 키, 객체 값) | 연관된 지정된 키와 함께 지정된 값을 맵에서 제거합니다. |
| 키세트() 설정 | 모든 키를 포함하는 Set 뷰를 반환합니다. |
| 세트 | 모든 키와 값을 포함하는 Set 뷰를 반환합니다. |
| 무효 클리어() | 지도를 재설정하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| V 계산(K 키, BiFunction remappingFunction) | 지정된 키와 현재 매핑된 값(또는 현재 매핑이 없는 경우 null)에 대한 매핑을 계산하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| V 계산IfAbsent(K 키, 함수 매핑함수) | 지정된 키가 아직 값과 연결되어 있지 않은 경우(또는 null에 매핑된 경우) 지정된 매핑 함수를 사용하여 해당 값을 계산하는 데 사용되며, null이 아닌 경우 해당 키를 이 맵에 입력합니다. |
| V 계산IfPresent(K 키, BiFunction remappingFunction) | 지정된 키의 값이 존재하고 null이 아닌 경우 키와 현재 매핑된 값이 주어지면 새 매핑을 계산하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| boolean containValue(객체 값) | 이 메서드는 해당 값과 동일한 값이 맵 내에 존재하면 true를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환합니다. |
| boolean containKey(객체 키) | 이 메서드는 키와 동일한 키가 맵 내에 있으면 true를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환합니다. |
| 부울 같음(객체 o) | 지정된 객체를 맵과 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| void forEach(BiConsumer 작업) | 모든 항목이 처리되거나 작업에서 예외가 발생할 때까지 맵의 각 항목에 대해 지정된 작업을 수행합니다. |
| V get(객체 키) | 이 메소드는 키와 연관된 값을 포함하는 객체를 반환합니다. |
| V getOrDefault(객체 키, V defaultValue) | 지정된 키가 매핑된 값을 반환하거나, 맵에 키에 대한 매핑이 포함되어 있지 않은 경우 defaultValue를 반환합니다. |
| 정수 해시코드() | 지도의 해시 코드 값을 반환합니다. |
| 부울 isEmpty() | 이 메서드는 지도가 비어 있으면 true를 반환합니다. 하나 이상의 키가 포함되어 있으면 false를 반환합니다. |
| V 병합(K 키, V 값, BiFunction remappingFunction) | 지정된 키가 아직 값과 연결되어 있지 않거나 null과 연결된 경우 해당 키를 지정된 null이 아닌 값과 연결합니다. |
| V 대체(K 키, V 값) | 지정된 키에 대해 지정된 값을 대체합니다. |
| 부울 교체(K 키, V oldValue, V newValue) | 지정된 키의 이전 값을 새 값으로 바꿉니다. |
| void replacementAll(BiFunction 함수) | 모든 항목이 처리되거나 함수에서 예외가 발생할 때까지 각 항목의 값을 해당 항목에 대해 지정된 함수를 호출한 결과로 바꿉니다. |
| 컬렉션 값() | 맵에 포함된 값의 컬렉션 뷰를 반환합니다. |
| 정수 크기() | 이 메소드는 지도의 항목 수를 반환합니다. |
지도.입력 인터페이스
Entry는 Map의 하위 인터페이스입니다. 따라서 Map.Entry 이름으로 액세스합니다. 요소가 이 클래스에 속하는 맵의 컬렉션 뷰를 반환합니다. 키와 값을 가져오는 방법을 제공합니다.
Map.Entry 인터페이스의 메소드
| 방법 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| K getKey() | 열쇠를 획득하는데 사용됩니다. |
| V getValue() | 가치를 얻기 위해 사용됩니다. |
| 정수 해시코드() | hashCode를 얻는 데 사용됩니다. |
| V setValue(V 값) | 이 항목에 해당하는 값을 지정된 값으로 바꾸는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 부울 같음(객체 o) | 지정된 개체를 기존의 다른 개체와 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 공전 | 키에 따라 객체를 자연 순서로 비교하는 비교기를 반환합니다. |
| 정적 비교기 | 주어진 Comparator를 사용하여 키별로 객체를 비교하는 비교기를 반환합니다. |
| 공전 | 값에 따라 객체를 자연 순서로 비교하는 비교기를 반환합니다. |
| 정적 비교기 | 주어진 Comparator를 사용하여 객체를 값으로 비교하는 비교기를 반환합니다. |
Java 맵 예: 비일반(이전 스타일)
//Non-generic import java.util.*; public class MapExample1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map=new HashMap(); //Adding elements to map map.put(1,'Amit'); map.put(5,'Rahul'); map.put(2,'Jai'); map.put(6,'Amit'); //Traversing Map Set set=map.entrySet();//Converting to Set so that we can traverse Iterator itr=set.iterator(); while(itr.hasNext()){ //Converting to Map.Entry so that we can get key and value separately Map.Entry entry=(Map.Entry)itr.next(); System.out.println(entry.getKey()+' '+entry.getValue()); } } } 산출:
1 Amit 2 Jai 5 Rahul 6 Amit
Java 맵 예: 일반(새 스타일)
import java.util.*; class MapExample2{ public static void main(String args[]){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put(100,'Amit'); map.put(101,'Vijay'); map.put(102,'Rahul'); //Elements can traverse in any order for(Map.Entry m:map.entrySet()){ System.out.println(m.getKey()+' '+m.getValue()); } } } 산출:
102 Rahul 100 Amit 101 Vijay
Java 맵 예제: CompareByKey()
import java.util.*; class MapExample3{ public static void main(String args[]){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put(100,'Amit'); map.put(101,'Vijay'); map.put(102,'Rahul'); //Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map map.entrySet() //Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source .stream() //Sorted according to the provided Comparator .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByKey()) //Performs an action for each element of this stream .forEach(System.out::println); } } 산출:
100=Amit 101=Vijay 102=Rahul
Java 맵 예: 내림차순 비교ByKey()
import java.util.*; class MapExample4{ public static void main(String args[]){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put(100,'Amit'); map.put(101,'Vijay'); map.put(102,'Rahul'); //Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map map.entrySet() //Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source .stream() //Sorted according to the provided Comparator .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByKey(Comparator.reverseOrder())) //Performs an action for each element of this stream .forEach(System.out::println); } } 산출:
102=Rahul 101=Vijay 100=Amit
Java 맵 예제: CompareByValue()
import java.util.*; class MapExample5{ public static void main(String args[]){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put(100,'Amit'); map.put(101,'Vijay'); map.put(102,'Rahul'); //Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map map.entrySet() //Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source .stream() //Sorted according to the provided Comparator .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()) //Performs an action for each element of this stream .forEach(System.out::println); } } 산출:
향상된 for 루프 자바
100=Amit 102=Rahul 101=Vijay
Java 맵 예: 내림차순 비교ByValue()
import java.util.*; class MapExample6{ public static void main(String args[]){ Map map=new HashMap(); map.put(100,'Amit'); map.put(101,'Vijay'); map.put(102,'Rahul'); //Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map map.entrySet() //Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source .stream() //Sorted according to the provided Comparator .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue(Comparator.reverseOrder())) //Performs an action for each element of this stream .forEach(System.out::println); } } 산출:
101=Vijay 102=Rahul 100=Amit
