런타임 오류:
- 프로그램의 런타임 오류는 프로그램이 성공적으로 컴파일된 후 실행되는 동안 발생하는 오류입니다.
- 런타임 오류는 일반적으로 다음과 같이 불립니다. 버그 소프트웨어가 출시되기 전 디버깅 과정에서 종종 발견됩니다.
- 프로그램이 대중에게 배포된 후 런타임 오류가 발생하면 개발자는 오류를 수정하기 위해 고안된 패치나 작은 업데이트를 릴리스하는 경우가 많습니다.
- 초보자라면 누구나 직면할 수 있는 문제 목록을 찾을 수 있습니다. 이 기사 .
- 온라인 플랫폼에서 문제를 해결하는 동안 함께 제공되는 메시지에 명확하게 지정되지 않은 많은 런타임 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 다양한 런타임 오류가 발생합니다. 논리적 오류 , 입출력 오류 , 정의되지 않은 개체 오류 , 0으로 나누기 오류 , 그리고 더 많은.
런타임 오류 유형:
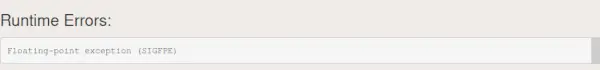
- 서명: SIGFPE는 부동 소수점 오류. 이는 거의 항상 다음으로 인해 발생합니다. 0으로 나누기 . SIGFPE 오류의 주요 원인은 주로 다음과 같이 세 가지입니다.
- 0으로 나누기.
- Zero에 의한 모듈로 연산.
- 정수 오버플로.
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGFPE error #include using namespace std; // Driver Code int main() { int a = 5; // Division by Zero cout << a / 0; return 0; }>public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 5; try { // Division by Zero System.out.println(a / 0); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { // Handle the ArithmeticException System.out.println('Error: Division by zero is not allowed.'); } } }># Python program to illustrate # the ZeroDivisionError # Driver Code def main(): a = 5 try: # Division by Zero print(a / 0) except ZeroDivisionError as e: print(f'Error: {e}') if __name__ == '__main__': main()>using System; class Program { static void Main() { int a = 5; try { // Division by Zero Console.WriteLine(a / 0); } catch (DivideByZeroException ex) { // Handling DivideByZeroException Console.WriteLine('Error: ' + ex.Message); } Console.ReadLine(); } }>// JavaScript program to demonstrate division by zero behavior // Perform division by zero let result = 5 / 0; // Print the result console.log(result);>
- SIGABRT: 프로그램에 의해 오류 자체가 감지되면 이 신호는 호출을 사용하여 생성됩니다. 중단() 기능. 이 신호는 표준 라이브러리에서 내부 오류를 보고하는 데에도 사용됩니다. 주장하다() 기능하다 C++ 또한 이 신호를 생성하기 위해 abort()를 사용합니다. 다음은 SIGBRT 오류를 설명하는 프로그램입니다.C++
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGBRT error #include using namespace std; // Driver Code int main() { // Assigning excessive memory int a = 100000000000; int* arr = new int[a]; return 0; }>public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Assigning excessive memory int a = 1000000000; int[] arr = new int[a]; } catch (OutOfMemoryError e) { // Catch the OutOfMemoryError System.err.println('Caught OutOfMemoryError: ' + e.getMessage()); } } } //This code is contributed by Adarsh># Python program to illustrate # the MemoryError # Driver Code def main(): try: # Attempting to allocate excessive memory a = 100000000000 arr = [0] * a except MemoryError as e: print(f'Error: {e}') if __name__ == '__main__': main()>// JavaScript program to illustrate the MemoryError // Driver Code function main() { try { // Attempting to allocate excessive memory const a = 100000000000; const arr = new Array(a).fill(0); } catch (e) { console.log('Error: ' + e.message); } } main();>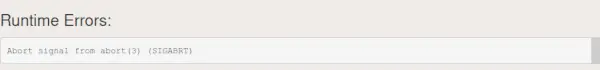
- NZEC: 이 오류는 다음을 나타냅니다. 0이 아닌 종료 코드 . 을 위한 씨 사용자가 다음과 같은 경우 이 오류가 생성됩니다. 메인() 메소드 반품이 없습니다 0 성명. 자바 /C++ 사용자는 예외가 발생하면 이 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다. NZEC 오류가 발생할 수 있는 이유는 다음과 같습니다.
- 무한 재귀 또는 스택 메모리가 부족한 경우.
- 음수 배열 인덱스에 액세스합니다.
- ArrayIndexOutOfBounds 예외.
- StringIndexOutOfBounds 예외.
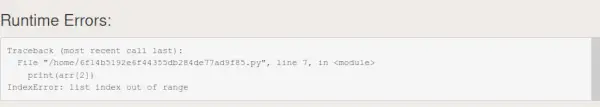
#include #include using namespace std; int main() { vector도착 = {1, 2}; try { // 의도적 오류: 범위를 벗어난 요소에 액세스하는 중 cout<< arr.at(2) << endl; // Accessing index 2 which is out of bounds } catch (const out_of_range& e) { cout << 'Error the index is out of bound'<< endl; // Handle the out_of_range exception } return 0; } //This code is contrbiuted by Adarsh> public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2}; // Intentional Error: Accessing an element out of bounds System.out.println(arr[2]); // Error: Accessing index 2 which is out of bounds } } //this code is contributed by Utkarsh.># Python program to illustrate # the NZEC Error # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [1, 2] # Runtime Error # Array Index out of Bounds print(arr[2])>
// JavaScript program to illustrate // the error similar to NZEC Error // Driver Code let arr = [1, 2]; // Runtime Error // Array Index out of Bounds console.log(arr[2]);>
- SIGSEGV: 이 오류는 가장 일반적인 오류이며 다음과 같이 알려져 있습니다. 세그멘테이션 오류 . 프로그램이 액세스가 허용되지 않는 메모리에 액세스하려고 하거나 허용되지 않는 방식으로 메모리 위치에 액세스하려고 시도할 때 생성됩니다. 분할 오류의 일반적인 원인 목록은 다음과 같습니다.
- 범위를 벗어난 배열에 액세스합니다.
- NULL 포인터 역참조.
- 해제된 메모리를 역참조합니다.
- 초기화되지 않은 포인터를 역참조합니다.
- 잘못된 사용 & (주소) 그리고 * (역참조) 연산자.
- printf 및 scanf 문의 형식 지정자가 잘못되었습니다.
- 스택 오버플로.
- 읽기 전용 메모리에 쓰기.
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGSEGV error #include using namespace std; // Function with infinite // Recursion void infiniteRecur(int a) { return infiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code int main() { // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); }>import java.util.*; public class Main { // Function with infinite Recursion static void infiniteRecur(int a) { // Recursively call the function without a base case infiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); } } //This code is contributed by Monu.># Python program to illustrate # the SIGSEGV error # Function with infinite # Recursion def infiniteRecur(a): return infiniteRecur(a) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5) #This code is contributed by Utkarsh.>
using System; class Program { // Function with infinite Recursion static void InfiniteRecur(int a) { // Recursively calling the function InfiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code static void Main() { // Infinite Recursion InfiniteRecur(5); } }>// Function with infinite Recursion function infiniteRecur(a) { // Recursively call the function without a base case infiniteRecur(a); } // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); // Note: JavaScript does not have tail-call optimization, // so running this code will eventually lead to a maximum call stack size exceeded error.>
런타임 오류를 방지하는 방법:
- 초기화되지 않은 변수를 사용하지 마십시오. 다음과 같이 설정할 수 있습니다. 0 시스템에는 있지만 코딩 플랫폼에는 없습니다.
- 배열 요소가 나타나는 모든 항목을 확인하고 범위를 벗어나지 않았는지 확인하세요.
- 너무 많은 메모리를 선언하지 마십시오. 질문에 지정된 메모리 제한을 확인하세요.
- 너무 많은 선언을 피하세요 스택 메모리 . 큰 배열은 함수 외부에서 전역적으로 선언되어야 합니다.
- return을 종료문으로 사용하세요.
- 참조를 피하세요 여유 메모리 또는 널 포인터 .




