set 인터페이스는 java.util 패키지에 있으며 컬렉션 인터페이스 . 중복된 값을 저장할 수 없는 순서가 지정되지 않은 개체 컬렉션입니다. 수학적 집합을 구현하는 인터페이스입니다. 이 인터페이스에는 Collection 인터페이스에서 상속된 메소드가 포함되어 있으며 중복 요소 삽입을 제한하는 기능이 추가되어 있습니다. Set 구현을 확장하는 두 개의 인터페이스, 즉 SortedSet 및 NavigableSet이 있습니다.
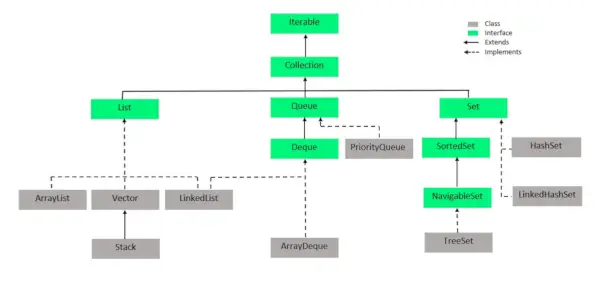
위 이미지에서 탐색 가능한 세트는 정렬된 세트 인터페이스를 확장합니다. 세트는 삽입 순서를 유지하지 않으므로 탐색 가능한 세트 인터페이스는 세트를 탐색하기 위한 구현을 제공합니다. 탐색 가능한 세트를 구현하는 클래스는 자체 균형 트리를 구현하는 TreeSet입니다. 따라서 이 인터페이스는 이 트리를 탐색하는 방법을 제공합니다.
선언: Set 인터페이스는 다음과 같이 선언됩니다.
public interface Set extends Collection>
세트 객체 생성
세트는 상호 작용 , 해당 조판으로 개체를 만들 수 없습니다. 객체를 생성하려면 항상 이 목록을 확장하는 클래스가 필요합니다. 또한, 도입 이후에는 제네릭 Java 1.5에서는 Set에 저장할 수 있는 객체 유형을 제한하는 것이 가능합니다. 이 유형 안전 세트는 다음과 같이 정의할 수 있습니다.
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Set Set set = new HashSet ();>
아래에 제공된 Set 인터페이스에 존재하는 메소드를 다음과 같이 표 형식으로 논의하겠습니다.
| 방법 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 추가(요소) | 이 방법은 세트에 특정 요소를 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 지정된 요소가 집합에 이미 존재하지 않는 경우에만 요소를 추가합니다. 그렇지 않으면 해당 요소가 집합에 이미 존재하는 경우 함수는 False를 반환합니다. |
| addAll(컬렉션) | 이 메소드는 언급된 컬렉션의 모든 요소를 기존 세트에 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. 요소는 특정 순서를 따르지 않고 무작위로 추가됩니다. |
| 분명한() | 이 방법은 세트에서 모든 요소를 제거하는 데 사용되지만 세트를 삭제하지는 않습니다. 세트에 대한 참조가 여전히 존재합니다. |
| 포함(요소) | 이 메소드는 Set에 특정 요소가 존재하는지 여부를 확인하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 모두 포함(컬렉션) | 이 메소드는 세트가 주어진 컬렉션에 존재하는 모든 요소를 포함하는지 여부를 확인하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 메서드는 집합에 모든 요소가 포함되어 있으면 true를 반환하고 요소 중 하나라도 누락되면 false를 반환합니다. |
| 해시 코드() | 이 메소드는 Set의 이 인스턴스에 대한 hashCode 값을 가져오는 데 사용됩니다. Set의 이 인스턴스에 대한 hashCode 값인 정수 값을 반환합니다. |
| 비었다() | 이 방법은 세트가 비어 있는지 여부를 확인하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 반복자() | 이 메소드는 다음을 반환하는 데 사용됩니다. 반복자 세트의. 세트의 요소는 무작위 순서로 반환됩니다. |
| 제거(요소) | 이 메소드는 세트에서 지정된 요소를 제거하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 메서드는 지정된 요소가 Set에 있으면 True를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 False를 반환합니다. |
| 모두 제거(컬렉션) | 이 메소드는 세트에 존재하는 컬렉션의 모든 요소를 제거하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 메서드는 호출의 결과로 이 집합이 변경된 경우 true를 반환합니다. |
| keepAll(컬렉션) | 이 방법은 주어진 컬렉션에 언급된 세트의 모든 요소를 유지하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 메서드는 호출의 결과로 이 집합이 변경된 경우 true를 반환합니다. |
| 크기() | 이 방법은 세트의 크기를 얻는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 요소 수를 나타내는 정수 값을 반환합니다. |
| toArray() | 이 메소드는 Set의 요소와 동일한 요소의 배열을 형성하는 데 사용됩니다. |
삽화: 세트 인터페이스를 설명하기 위한 샘플 프로그램
자바
// Java program Illustrating Set Interface> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Demonstrating Set using HashSet> >// Declaring object of type String> >Set hash_Set =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to the Set> >// using add() method> >hash_Set.add(>'Geeks'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'For'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Geeks'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Example'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Set'>);> > >// Printing elements of HashSet object> >System.out.println(hash_Set);> >}> }> |
>
>
리눅스 단축키산출
[Set, Example, Geeks, For]>
Set 인터페이스에서의 작업
세트 인터페이스를 통해 사용자는 세트에서 기본적인 수학 연산을 수행할 수 있습니다. 이러한 기본 작업을 이해하기 위해 두 개의 배열을 사용하겠습니다. set1 = [1, 3, 2, 4, 8, 9, 0] 및 set2 = [1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 0, 7, 5]라고 가정합니다. 그러면 세트에서 가능한 작업은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 교차점: 이 작업은 주어진 두 세트의 모든 공통 요소를 반환합니다. 위의 두 세트의 경우 교차점은 다음과 같습니다.
Intersection = [0, 1, 3, 4]>
2. 연합: 이 작업은 한 세트의 모든 요소를 다른 세트에 추가합니다. 위의 두 세트의 경우 합집합은 다음과 같습니다.
Union = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]>
3. 차이점: 이 작업은 한 세트에 있는 모든 값을 다른 세트에서 제거합니다. 위의 두 세트의 경우 차이점은 다음과 같습니다.
Difference = [2, 8, 9]>
이제 위에서 정의한 대로 다음 작업을 구현해 보겠습니다.
예:
자바
// Java Program Demonstrating Operations on the Set> // such as Union, Intersection and Difference operations> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> SetExample {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Creating an object of Set class> >// Declaring object of Integer type> >Set a =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding all elements to List> >a.addAll(Arrays.asList(> >new> Integer[] {>1>,>3>,>2>,>4>,>8>,>9>,>0> }));> > >// Again declaring object of Set class> >// with reference to HashSet> >Set b =>new> HashSet();> > >b.addAll(Arrays.asList(> >new> Integer[] {>1>,>3>,>7>,>5>,>4>,>0>,>7>,>5> }));> > > >// To find union> >Set union =>new> HashSet(a);> >union.addAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Union of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(union);> > >// To find intersection> >Set intersection =>new> HashSet(a);> >intersection.retainAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Intersection of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(intersection);> > >// To find the symmetric difference> >Set difference =>new> HashSet(a);> >difference.removeAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Difference of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(difference);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Union of the two Set[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9] Intersection of the two Set[0, 1, 3, 4] Difference of the two Set[2, 8, 9]>
SortedSet에서 다양한 작업 수행
도입 후 제네릭 Java 1.5에서는 Set에 저장할 수 있는 객체 유형을 제한하는 것이 가능합니다. Set은 인터페이스이므로 이 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스에서만 사용할 수 있습니다. HashSet은 Set 인터페이스를 구현하는 널리 사용되는 클래스 중 하나입니다. 이제 HashSet에서 자주 사용되는 몇 가지 작업을 수행하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다. 우리는 다음과 같은 작업을 수행할 예정입니다.
- 요소 추가
- 요소에 접근하기
- 요소 제거
- 요소 반복
- 세트 반복
이제 다음과 같이 이러한 작업을 개별적으로 논의하겠습니다.
작업 1: 요소 추가
Set에 요소를 추가하기 위해 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다. add() 메소드 . 그러나 삽입 순서는 세트에 유지되지 않습니다. 내부적으로 모든 요소에 대해 해시가 생성되고 생성된 해시와 관련하여 값이 저장됩니다. 값을 비교하고 오름차순으로 정렬합니다. 중복 요소는 허용되지 않으며 모든 중복 요소는 무시된다는 점을 기억해야 합니다. 또한 Set에서는 Null 값을 허용합니다.
예
자바
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Adding elements using add() method> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating an object of Set and> >// declaring object of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to above object> >// using add() method> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'A'>);> > >// Printing the elements inside the Set object> >System.out.println(hs);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
[A, B, C]>
작업 2: 요소에 접근하기
요소를 추가한 후 해당 요소에 액세스하려면 contain() 과 같은 내장 메서드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
예
자바
객관적인 자바
// Java code to demonstrate Working of Set by> // Accessing the Elements of the Set object> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating an object of Set and> >// declaring object of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Elements are added using add() method> >// Later onwards we will show accessing the same> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'A'>);> > >// Print the Set object elements> >System.out.println(>'Set is '> + hs);> > >// Declaring a string> >String check =>'D'>;> > >// Check if the above string exists in> >// the SortedSet or not> >// using contains() method> >System.out.println(>'Contains '> + check +>' '> >+ hs.contains(check));> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Set is [A, B, C] Contains D false>
작업 3: 값 제거
Remove() 메서드를 사용하여 Set에서 값을 제거할 수 있습니다.
예
자바
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Removing Element/s from the Set> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Declaring object of Set of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Elements are added> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'D'>);> >hs.add(>'E'>);> > >// Printing initial Set elements> >System.out.println(>'Initial HashSet '> + hs);> > >// Removing custom element> >// using remove() method> >hs.remove(>'B'>);> > >// Printing Set elements after removing an element> >// and printing updated Set elements> >System.out.println(>'After removing element '> + hs);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Initial HashSet [A, B, C, D, E] After removing element [A, C, D, E]>
작업 4: 세트 반복
Set을 반복하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다. 가장 유명한 것은 향상된 for 루프를 사용하는 것입니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of Set by> // Iterating through the Elements> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating object of Set and declaring String type> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to Set> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'D'>);> >hs.add(>'E'>);> > >// Iterating through the Set> >// via for-each loop> >for> (String value : hs)> > >// Printing all the values inside the object> >System.out.print(value +>', '>);> > >System.out.println();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
A, B, C, D, E,>
Java 컬렉션에서 Set 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스는 아래 이미지에서 쉽게 인식할 수 있으며 다음과 같이 나열됩니다.
- 해시세트
- EnumSet
- LinkedHashSet
- 트리세트

클래스 1: 해시세트
HashSet 클래스는 다음에서 구현됩니다. 수집 프레임워크 의 고유한 구현입니다. 예
자바
// Java program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the Hashset class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating object of Set of type String> >Set h =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements into the HashSet> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >h.add(>'India'>);> >h.add(>'Australia'>);> >h.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate element> >h.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the HashSet> >System.out.println(h);> > >// Removing items from HashSet> >// using remove() method> >h.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + h);> > >// Iterating over hash set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> > >// Iterating through iterators> >Iterator i = h.iterator();> > >// It holds true till there is a single element> >// remaining in the object> >while> (i.hasNext())> > >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>산출
[South Africa, Australia, India] Set after removing Australia:[South Africa, India] Iterating over set: South Africa India>
클래스 2: EnumSet
EnumSet 클래스는 다음에서 구현됩니다. 컬렉션 프레임워크 와 함께 사용하기 위한 Set 인터페이스의 특수 구현 중 하나입니다. 열거형 . HashSet보다 훨씬 빠른 고성능 세트 구현입니다. 열거형 세트의 모든 요소는 세트가 명시적으로 또는 암시적으로 생성될 때 지정되는 단일 열거 유형에서 나와야 합니다. 이 클래스를 사용하여 집합 개체를 만드는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
예
자바
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of the set object> // using the EnumSet class> import> java.util.*;> > enum> Gfg { CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ }> ;> > public> class> GFG {> > >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating a set> >Set set1;> > >// Adding the elements> >set1 = EnumSet.of(Gfg.QUIZ, Gfg.CONTRIBUTE,> >Gfg.LEARN, Gfg.CODE);> > >System.out.println(>'Set 1: '> + set1);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Set 1: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ]>
클래스 3: LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet 클래스는 다음에서 구현됩니다. 컬렉션 프레임워크 모든 요소에 걸쳐 이중 연결 목록을 유지 관리하는 HashSet의 정렬된 버전입니다. 반복 순서를 유지해야 할 때 이 클래스가 사용됩니다. HashSet을 반복할 때 순서는 예측할 수 없지만 LinkedHashSet을 사용하면 삽입된 순서대로 요소를 반복할 수 있습니다. 이 클래스를 사용하여 집합 개체를 만드는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
예
자바
뭐야?
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of Set object using> // the LinkedHashset class> import> java.util.*;> > class> GFG {> > >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >Set lh =>new> LinkedHashSet();> > >// Adding elements into the LinkedHashSet> >// using add()> >lh.add(>'India'>);> >lh.add(>'Australia'>);> >lh.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate> >// element> >lh.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the LinkedHashSet> >System.out.println(lh);> > >// Removing items from LinkedHashSet> >// using remove()> >lh.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + lh);> > >// Iterating over linked hash set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> >Iterator i = lh.iterator();> >while> (i.hasNext())> >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>산출
[India, Australia, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa>
클래스 4: 트리세트
구현된 TreeSet 클래스 컬렉션 프레임워크 SortedSet 인터페이스의 구현과 SortedSet은 Set 인터페이스를 확장합니다. 요소를 정렬된 형식으로 저장한다는 점을 제외하면 단순한 집합처럼 동작합니다. TreeSet은 저장을 위해 트리 데이터 구조를 사용합니다. 개체는 오름차순으로 정렬되어 저장됩니다. 그러나 TreeSet.descendingIterator() 메서드를 사용하면 내림차순으로 반복할 수 있습니다. 이 클래스를 사용하여 집합 개체를 만드는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
예
자바
// Java Program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the TreeSet class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating a Set object and declaring it of String> >// type> >// with reference to TreeSet> >Set ts =>new> TreeSet();> > >// Adding elements into the TreeSet> >// using add()> >ts.add(>'India'>);> >ts.add(>'Australia'>);> >ts.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate> >// element> >ts.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the TreeSet> >System.out.println(ts);> > >// Removing items from TreeSet> >// using remove()> >ts.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + ts);> > >// Iterating over Tree set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> >Iterator i = ts.iterator();> > >while> (i.hasNext())> >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>산출
[Australia, India, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa>
