표준::shared_ptr C++11에 도입된 스마트 포인터 중 하나입니다. 단순 포인터와는 달리 관리 개체의 참조 횟수를 추적하는 관련 제어 블록이 있습니다. 이 참조 횟수는 동일한 객체를 가리키는 shared_ptr 인스턴스의 모든 복사본에서 공유되므로 적절한 메모리 관리 및 삭제가 보장됩니다.
전제 조건: C++의 포인터 , C++의 스마트 포인터 .
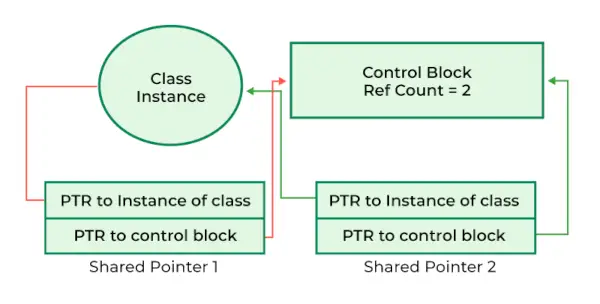
C++의 공유 포인터
std::shared_ptr 구문
T 유형의 shared_ptr은 다음과 같이 선언될 수 있습니다.
std::shared_ptr ptr_name;>
shared_ptr 객체 초기화
다음 방법을 사용하여 shared_ptr을 초기화할 수 있습니다.
1. 새로운 포인터를 이용한 초기화
shared_ptr ptr (new T()); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared (new T());>
2. 기존 포인터를 이용한 초기화
shared_ptr ptr(already_existing_pointer); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared(already_existing_pointer);>
shared_ptr의 멤버 메소드
다음은 shared_ptr과 관련된 일부 멤버입니다.
| 방법 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 초기화() | std::shared_ptr을 빈 상태로 재설정하여 관리 개체의 소유권을 해제합니다. |
| use_count() | 소유권을 공유하는 std::shared_ptr 인스턴스 수를 나타내는 현재 참조 횟수를 반환합니다. |
| 고유한() | 객체를 소유하는 std::shared_ptr이 하나만 있는지 확인합니다(참조 횟수는 1). |
| 얻다() | 관리 객체에 대한 원시 포인터를 반환합니다. 이 방법을 사용할 때는 주의하세요. |
| 스왑(shr_ptr2) | 두 std::shared_ptr 인스턴스의 내용(소유권)을 교환합니다. |
std::shared_ptr의 예
예시 1:
C++
>
>산출
0x1365c20 A::show() A::show() 0x1365c20 0x1365c20 2 2 0 1 0x1365c20>
예 2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of make_shared> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >// Creating shared pointers using std::make_shared> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr1 = make_shared<>int>>(42);> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr2 = make_shared<>int>>(24);> >// Accessing the values using the dereference operator> >// (*)> >cout << 'Value 1: ' << *shr_ptr1 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 2: ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >// Using the assignment operator (=) to share ownership> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr3 = shr_ptr1;> >// Checking if shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3> >// point to the same object> >if> (shr_ptr1 == shr_ptr3) {> >cout << 'shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 '> >'point to the same object.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Swapping the contents of shared pointer 2 and shared> >// pointer 3> >shr_ptr2.swap(shr_ptr3);> >// Checking the values after the swap> >cout << 'Value 2 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 3 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr3 << endl;> >// Using logical operators to check if shared pointers> >// are valid> >if> (shr_ptr1 && shr_ptr2) {> >cout << 'Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer '> >'2 are valid.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Resetting a shared pointer> >shr_ptr1.reset();> }> |
>
>산출
Value 1: 42 Value 2: 24 shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 point to the same object. Value 2 (after swap): 42 Value 3 (after swap): 24 Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 2 are valid.>
예제 3: std::shared_ptr을 사용하여 연결 목록 구현
C++
#include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Define a singly linked list node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >shared_ptr next;> >Node(>int> val)> >: data(val)> >, next(NULL)> >{> >}> };> class> LinkedList {> public>:> >LinkedList()> >: head(NULL)> >{> >}> >// Insert a new node at the end of the linked list> >void> insert(>int> val)> >{> >shared_ptr newNode = make_shared(val);> >if> (!head) {> >head = newNode;> >}> >else> {> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->다음) {> >current = current->다음;> >}> >current->다음 = newNode;> >}> >}> >// Delete a node with a given value from the linked list> >void> del(>int> val)> >{> >if> (!head) {> >return>;> >}> >if> (head->데이터 == 발) {> >head = head->다음;> >return>;> >}> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->다음> >&& current->다음->데이터 != val) {> >current = current->다음;> >}> >if> (current->다음 && 현재->다음->데이터 == val) {> >current->다음 = 현재->다음->다음;> >}> >}> >// Traverse and print the linked list> >void> Print()> >{> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current) {> >cout current = current->다음; } cout<< 'NULL' << endl; } private: shared_ptr head; }; int main() { LinkedList linkedList; // Insert nodes into the linked list linkedList.insert(1); linkedList.insert(2); linkedList.insert(3); // Print the linked list cout << 'Linked List: '; linkedList.Print(); // Delete a node and print the updated linked list linkedList.del(2); cout << 'Linked List after deleting 2: '; linkedList.Print(); return 0; }> |
>
문자열 C++에서 찾기
>산출
Linked List: 1 ->2 -> 3 -> NULL 2 삭제 후 연결리스트: 1 -> 3 -> NULL>
