토폴로지 정렬 방향성 비순환 그래프(DAG) 모든 방향 에지 u-v에 대해 정점이 되도록 정점의 선형 순서입니다. ~에 전에 온다 ~에 주문에.
메모: 그래프가 그래프가 아닌 경우 그래프에 대한 토폴로지 정렬이 불가능합니다. 낮 .
파워셸과 배쉬
예:
권장 실습위상 정렬을 찾는 DFS 기반 솔루션 이미 논의되었습니다.입력: 그래프 :
예
산출: 5 4 2 3 1 0
설명: 위상 정렬의 첫 번째 꼭짓점은 항상 in차수가 0인 꼭짓점(들어오는 가장자리가 없는 꼭짓점)입니다. 다음 그래프의 위상 정렬은 5 4 2 3 1 0입니다. 그래프에는 둘 이상의 위상 정렬이 있을 수 있습니다. 다음 그래프의 또 다른 위상 정렬은 4 5 2 3 1 0입니다.
토폴로지 순서는 고유하지 않을 수 있습니다.
위상 정렬 하나의 작업 완료가 순서가 달라질 수 있는 여러 다른 작업의 완료에 따라 달라지는 종속성 문제입니다. 예를 통해 이 개념을 이해해 보겠습니다.
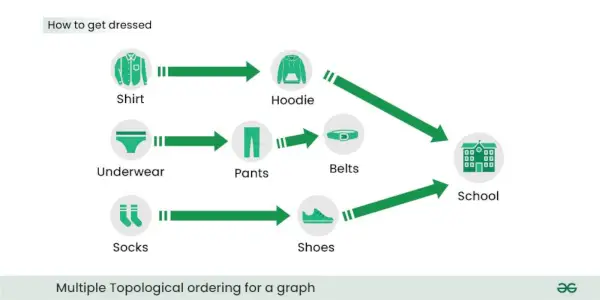
우리의 임무가 학교에 가는 것이고 거기에 가기 위해 먼저 옷을 입어야 한다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 옷을 입는 데 따른 종속성은 아래 종속성 그래프에 나와 있습니다. 예를 들어 양말을 신기 전에는 신발을 신을 수 없습니다.
위 이미지를 보면 옷을 입는 데 여러 가지 방법이 있다는 것을 이미 깨달았을 것입니다. 아래 이미지는 그러한 방법 중 일부를 보여줍니다.
나열할 수 있나요? 가능한 모든 위상 순서 위의 종속성 그래프에 맞게 옷을 입는 방법은 무엇입니까?
DFS를 사용한 위상 정렬 알고리즘:
다음은 깊이 우선 검색(DFS)을 사용하여 위상 정렬을 위한 단계별 알고리즘입니다.
- 다음을 사용하여 그래프를 만듭니다. N 정점과 중 -방향 가장자리.
- 스택 및 방문한 크기의 배열 초기화 N .
- 그래프의 방문하지 않은 각 정점에 대해 다음을 수행합니다.
- 정점을 매개변수로 사용하여 DFS 함수를 호출합니다.
- DFS 함수에서 정점을 방문한 것으로 표시하고 정점의 방문하지 않은 모든 이웃에 대해 DFS 함수를 재귀적으로 호출합니다.
- 모든 이웃을 방문하고 나면 정점을 스택에 밀어 넣습니다.
- 결국 정점을 방문하고 스택에서 요소를 팝하여 스택이 빌 때까지 출력 목록에 추가합니다.
- 결과 목록은 그래프의 위상적으로 정렬된 순서입니다.
그림 토폴로지 정렬 알고리즘:
아래 이미지는 위의 접근 방식을 보여줍니다.

위상 정렬의 전반적인 작업 흐름
1 단계:
- 들어오는 노드가 0이므로 노드 0에서 DFS를 시작합니다.
- 스택의 노드 0을 푸시하고 최소 인접 노드 수를 갖는 다음 노드, 즉 노드 1로 이동합니다.
2 단계:
- 이번 단계에서는 이 노드에 인접한 노드가 없으므로 스택에 있는 노드 1을 푸시하고 다음 노드로 이동합니다.
3단계:
- 이 단계에서는 0과 1 다음으로 인접한 노드 수가 최소이기 때문에 노드 2를 선택합니다.
- 노드 2에 대해 DFS를 호출하고 노드 2에서 순회하는 모든 노드를 역순으로 푸시합니다.
- 따라서 3을 누른 다음 2를 누르십시오.
4단계:
- 이제 노드 4에 대해 DFS를 호출합니다.
- 0과 1이 이미 스택에 있으므로 스택에 노드 4를 푸시하고 반환하기만 하면 됩니다.
5단계:
- 이 단계에서는 5의 모든 인접 노드가 이미 스택에 있으므로 스택에 노드 5를 푸시하고 반환합니다.
6단계: 이것은 스택에서 모든 요소를 팝하고 해당 순서대로 인쇄하는 토폴로지 정렬의 마지막 단계입니다.
행 대 열
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ #include using namespace std; // Function to perform DFS and topological sorting void topologicalSortUtil(int v, vector>& 조정, 벡터 & 방문, 스택 & Stack) { // 현재 노드를 방문한 것으로 표시 Visited[v] = true; // 모든 인접 정점에 대해 반복 for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, Visited, Stack); } // 결과를 저장하는 스택에 현재 정점을 푸시합니다. Stack.push(v); } // 위상 정렬을 수행하는 함수 void topologicalSort(벡터>& adj, int V) { 스택 스택; // 결과 벡터를 저장하기 위한 스택 방문함(V, 거짓); // 재귀 도우미 함수를 호출하여 저장합니다. // 모든 정점에서 하나씩 시작하여 // 하나씩 for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, Stack); } // Print contents of stack while (!Stack.empty()) { cout << Stack.top() << ' '; Stack.pop(); } } int main() { // Number of nodes int V = 4; // Edges vector> 가장자리 = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 }, { 3, 1 }, { 3, 2 } }; // 인접 목록 벡터로 표현된 그래프> 조정(V); for (auto i : edge) { adj[i[0]].push_back(i[1]); } cout<< 'Topological sorting of the graph: '; topologicalSort(adj, V); return 0; }>
자바 import java.util.*; public class TopologicalSort { // Function to perform DFS and topological sorting static void topologicalSortUtil(int v, List> adj, boolean[] 방문, 스택 stack) { // 현재 노드를 방문한 것으로 표시 Visited[v] = true; // 모든 인접 정점에 대해 반복 for (int i : adj.get(v)) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, Visited, stack); } // 현재 정점을 결과를 저장하는 // 스택으로 푸시합니다. stack.push(v); } // 위상 정렬을 수행하는 함수 static void topologicalSort(List> adj, int V) { // 결과를 저장할 스택 Stack 스택 = 새로운 스택(); boolean[] 방문함 = 새로운 boolean[V]; // 재귀 도우미 함수를 호출하여 저장합니다. // 모든 정점에서 하나씩 // 토폴로지 정렬을 시작합니다. for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack); } // Print contents of stack System.out.print( 'Topological sorting of the graph: '); while (!stack.empty()) { System.out.print(stack.pop() + ' '); } } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Number of nodes int V = 4; // Edges List> 가장자리 = 새로운 ArrayList(); edge.add(Arrays.asList(0, 1)); edge.add(Arrays.asList(1, 2)); edge.add(Arrays.asList(3, 1)); edge.add(Arrays.asList(3, 2)); // 인접 리스트로 표현된 그래프 List> 조정 = 새로운 ArrayList(V); for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) { adj.add(new ArrayList()); } for (List i : 가장자리) { adj.get(i.get(0)).add(i.get(1)); } topologicalSort(adj, V); } }>
파이썬3 def topologicalSortUtil(v, adj, visited, stack): # Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = True # Recur for all adjacent vertices for i in adj[v]: if not visited[i]: topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack) # Push current vertex to stack which stores the result stack.append(v) # Function to perform Topological Sort def topologicalSort(adj, V): # Stack to store the result stack = [] visited = [False] * V # Call the recursive helper function to store # Topological Sort starting from all vertices one by # one for i in range(V): if not visited[i]: topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack) # Print contents of stack print('Topological sorting of the graph:', end=' ') while stack: print(stack.pop(), end=' ') # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Number of nodes V = 4 # Edges edges = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [3, 1], [3, 2]] # Graph represented as an adjacency list adj = [[] for _ in range(V)] for i in edges: adj[i[0]].append(i[1]) topologicalSort(adj, V)> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Program { // Function to perform DFS and topological sorting static void TopologicalSortUtil(int v, List> adj, bool[] 방문, 스택 stack) { // 현재 노드를 방문한 것으로 표시 Visited[v] = true; // 모든 인접한 정점에 대해 반복 foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) TopologicalSortUtil(i, adj, Visited, stack); } // 결과를 저장하는 // 스택에 현재 정점을 푸시합니다. stack.Push(v); } // 위상 정렬을 수행하는 함수 static void TopologicalSort(List> adj, int V) { // 결과를 저장할 스택 Stack 스택 = 새 스택 (); bool[] 방문 = 새로운 bool[V]; // 재귀 도우미 함수를 호출하여 저장합니다. // 모든 정점에서 하나씩 // 토폴로지 정렬을 시작합니다. for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) TopologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack); } // Print contents of stack Console.Write('Topological sorting of the graph: '); while (stack.Count>0) { Console.Write(stack.Pop() + ' '); } } // 드라이버 코드 static void Main(string[] args) { // 노드 수 int V = 4; // 가장자리 목록> 가장자리 = 새 목록>{ 새 목록 { 0, 1 }, 새 목록 { 1, 2 }, 새 목록 { 3, 1 }, 새 목록 { 3, 2 } }; // 인접 리스트로 표현된 그래프 List> adj = 새 목록>(); for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) { adj.Add(new List ()); } foreach(목록 나는 가장자리에 있음) { adj[i[0]].Add(i[1]); } TopologicalSort(adj, V); } }>
자바스크립트 // Function to perform DFS and topological sorting function topologicalSortUtil(v, adj, visited, stack) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all adjacent vertices for (let i of adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack); } // Push current vertex to stack which stores the result stack.push(v); } // Function to perform Topological Sort function topologicalSort(adj, V) { // Stack to store the result let stack = []; let visited = new Array(V).fill(false); // Call the recursive helper function to store // Topological Sort starting from all vertices one by // one for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) topologicalSortUtil(i, adj, visited, stack); } // Print contents of stack console.log('Topological sorting of the graph: '); while (stack.length>0) { console.log(stack.pop() + ' '); } } // 드라이버 코드 (() => { // 노드 수 const V = 4; // 모서리 const edge = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [3, 1], [3, 2]]; // 인접 리스트로 표현된 그래프 const adj = Array.from({ length: V }, () => []) for (let i of edge) { adj[i[0]].push (i[1]); } topologicalSort(adj, V) })();> 산출
Topological sorting of the graph: 3 0 1 2>
시간 복잡도: O(V+E). 위의 알고리즘은 단순히 추가 스택이 있는 DFS입니다. 따라서 시간 복잡도는 DFS와 동일합니다.
보조 공간: 오(V). 스택에 추가 공간이 필요합니다.
BFS를 사용한 토폴로지 정렬:
C++ #include #include #include using namespace std; // Class to represent a graph class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices list * 조정; // 인접 목록을 포함하는 // 배열에 대한 포인터 public: Graph(int V); // 생성자 void addEdge(int v, int w); // 그래프에 간선을 추가하는 함수 void topologicalSort(); // 전체 그래프의 토폴로지 정렬을 인쇄합니다. }; Graph::Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = 새 목록 [V]; } void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); // v의 목록에 w를 추가합니다. } // 위상 정렬을 수행하는 함수 void Graph::topologicalSort() { // 모든 정점 벡터의 차수를 저장하는 벡터를 생성합니다. in_degree(V, 0); // in_degree of 정점을 채우기 위해 인접 목록을 탐색합니다. for (int v = 0; v< V; ++v) { for (auto const& w : adj[v]) in_degree[w]++; } // Create a queue and enqueue all vertices with // in-degree 0 queue 큐; for (int i = 0; i< V; ++i) { if (in_degree[i] == 0) q.push(i); } // Initialize count of visited vertices int count = 0; // Create a vector to store topological order vector 최고순서; // 큐에서 정점을 하나씩 dequeue하고 enqueue // 인접 차수가 0이 되면 인접한 정점 while (!q.empty()) { // 큐의 앞 부분을 추출(또는 dequeue 수행) // 추가합니다. 토폴로지 순서 int u = q.front(); q.pop(); top_order.push_back(u); // 큐에서 제거된 노드 u의 // 모든 이웃 노드를 반복하고 // 해당 노드의 차수를 1 리스트만큼 감소시킵니다. ::반복자 itr; for (itr = adj[u].begin(); itr != adj[u].end(); ++itr) // in-degree가 0이 되면 대기열에 추가합니다. if (--in_degree[*itr ] == 0) q.push(*itr); 카운트++; } // 사이클이 있었는지 확인합니다. if (count != V) { cout<< 'Graph contains cycle
'; return; } // Print topological order for (int i : top_order) cout << i << ' '; } // Driver code int main() { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g(6); g.addEdge(5, 2); g.addEdge(5, 0); g.addEdge(4, 0); g.addEdge(4, 1); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 1); cout << 'Following is a Topological Sort of the given ' 'graph
'; g.topologicalSort(); return 0; }> 자바 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent a graph class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private ArrayList [] 조정; // 인접 목록 // 그래프의 // 표현 // 생성자 Graph(int V) { this.V = V; adj = 새로운 ArrayList[V]; for (int i = 0; i< V; ++i) adj[i] = new ArrayList(); } // Function to add an edge to the graph void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v’s list. } // Function to perform Topological Sort void topologicalSort() { // Create an array to store in-degree of all // vertices int[] inDegree = new int[V]; // Calculate in-degree of each vertex for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) { for (int w : adj[v]) { inDegree[w]++; } } // Create a queue and enqueue all vertices with // in-degree 0 Queue q = 새로운 LinkedList(); for (int i = 0; i< V; ++i) { if (inDegree[i] == 0) q.add(i); } // Initialize count of visited vertices int count = 0; // Create an ArrayList to store topological order ArrayList topOrder = 새로운 ArrayList(); // 큐에서 정점을 하나씩 큐에서 빼내고 // 인접 차수가 0이 되면 인접한 정점을 큐에 넣습니다. while (!q.isEmpty()) { // 큐의 앞부분을 추출하여 // 토폴로지 순서 int에 추가합니다. u = q.poll(); topOrder.add(u); 카운트++; // 대기열에서 제거된 노드 u의 // 모든 이웃 노드를 반복하고 // 진입 차수를 1씩 줄입니다. for (int w : adj[u]) { // 진입 차수가 0이 되면 // 대기열에 추가합니다. if (--inDegree[w] == 0) q.add(w); } } // 주기가 있었는지 확인 if (count != V) { System.out.println('Graph Contains Cycle'); 반품; } // 위상 순서 인쇄 for (int i : topOrder) System.out.print(i + ' '); } } // 드라이버 코드 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 위 다이어그램에 주어진 그래프를 생성합니다. Graph g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(5, 2); g.addEdge(5, 0); g.addEdge(4, 0); g.addEdge(4, 1); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 1); System.out.println( '다음은 주어진 그래프의 위상 정렬입니다'); g.topologicalSort(); } }> 파이썬3 from collections import defaultdict class Graph: def __init__(self, vertices): # Number of vertices self.V = vertices # Dictionary to store adjacency lists self.adj = defaultdict(list) def addEdge(self, u, v): # Function to add an edge to the graph self.adj[u].append(v) def topologicalSort(self): # Function to perform Topological Sort # Create a list to store in-degree of all vertices in_degree = [0] * self.V # Traverse adjacency lists to fill in_degree of vertices for i in range(self.V): for j in self.adj[i]: in_degree[j] += 1 # Create a queue and enqueue all vertices with in-degree 0 q = [] for i in range(self.V): if in_degree[i] == 0: q.append(i) # Initialize count of visited vertices count = 0 # Create a list to store topological order top_order = [] # One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue # adjacent vertices if in-degree of adjacent becomes 0 while q: # Extract front of queue (or perform dequeue) # and add it to topological order u = q.pop(0) top_order.append(u) # Iterate through all its neighbouring nodes # of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree # by 1 for node in self.adj[u]: # If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue in_degree[node] -= 1 if in_degree[node] == 0: q.append(node) count += 1 # Check if there was a cycle if count != self.V: print('Graph contains cycle') return # Print topological order print('Topological Sort:', top_order) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a graph given in the above diagram g = Graph(6) g.addEdge(5, 2) g.addEdge(5, 0) g.addEdge(4, 0) g.addEdge(4, 1) g.addEdge(2, 3) g.addEdge(3, 1) print('Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph') g.topologicalSort()> 자바스크립트 // Class to represent a graph class Graph { constructor(V) { this.V = V; // No. of vertices this.adj = new Array(V); // Array containing adjacency lists for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // Function to add an edge to the graph addEdge(v, w) { this.adj[v].push(w); // Add w to v’s list. } // Function to perform Topological Sort topologicalSort() { // Create a array to store in-degree of all vertices let inDegree = new Array(this.V).fill(0); // Traverse adjacency lists to fill inDegree of vertices for (let v = 0; v < this.V; v++) { for (let w of this.adj[v]) { inDegree[w]++; } } // Create a queue and enqueue all vertices with in-degree 0 let queue = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { if (inDegree[i] === 0) { queue.push(i); } } // Initialize count of visited vertices let count = 0; // Create an array to store topological order let topOrder = []; // One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue // adjacent vertices if in-degree of adjacent becomes 0 while (queue.length !== 0) { // Extract front of queue and add it to topological order let u = queue.shift(); topOrder.push(u); // Iterate through all its neighboring nodes // of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree by 1 for (let w of this.adj[u]) { // If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue if (--inDegree[w] === 0) { queue.push(w); } } count++; } // Check if there was a cycle if (count !== this.V) { console.log('Graph contains cycle'); return; } // Print topological order console.log('Topological Sort of the given graph:'); console.log(topOrder.join(' ')); } } // Driver code // Create a graph given in the above diagram let g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(5, 2); g.addEdge(5, 0); g.addEdge(4, 0); g.addEdge(4, 1); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 1); console.log('Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph:'); g.topologicalSort(); //This code is contributed by Utkarsh> 산출
Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph 4 5 2 0 3 1>
시간 복잡도:
그래프를 구성하는 데 필요한 시간 복잡도는 O(V + E)입니다. 여기서 V는 꼭지점 수이고 E는 간선 수입니다.
BFS를 사용하여 위상 정렬을 수행하는 데 필요한 시간 복잡도는 O(V + E)입니다. 여기서 V는 정점 수이고 E는 가장자리 수입니다. 이는 BFS 순회 중에 각 정점과 각 가장자리를 한 번씩 방문하기 때문입니다.
공간 복잡도:
인접 목록을 사용하여 그래프를 저장하기 위한 공간 복잡도는 O(V + E)입니다. 여기서 V는 정점 수이고 E는 간선 수입니다.
O(V) 공간이 필요한 정점의 차수를 저장하는 데 추가 공간이 사용됩니다.
대기열은 BFS 순회에 사용되며 최대 V 꼭지점을 포함할 수 있습니다. 따라서 큐의 공간복잡도는 O(V)이다.
전반적으로 알고리즘의 공간 복잡도는 그래프 저장, 차수 배열 및 대기열로 인해 O(V + E)입니다.
요약하면, 제공된 구현의 시간 복잡도는 O(V + E)이고, 공간 복잡도도 O(V + E)입니다.
메모: 여기서는 스택 대신 배열을 사용할 수도 있습니다. 배열이 사용되는 경우 요소를 역순으로 인쇄하여 토폴로지 정렬을 얻습니다.
토폴로지 정렬의 장점:
- 종속성에 따라 작업이나 이벤트를 예약하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 방향성 그래프에서 주기를 감지합니다.
- 선행 제약 조건이 있는 문제를 해결하는 데 효율적입니다.
위상 정렬의 단점:
- 방향성 비순환 그래프(DAG)에만 적용 가능하며 순환 그래프에는 적합하지 않습니다.
- 고유하지 않을 수 있으며 여러 개의 유효한 토폴로지 순서가 존재할 수 있습니다.
- 노드와 간선이 많은 대형 그래프에는 비효율적입니다.
위상 정렬의 응용:
- 작업 일정 및 프로젝트 관리.
- 패키지 관리 시스템의 종속성 해결.
- 소프트웨어 빌드 시스템에서 컴파일 순서를 결정합니다.
- 운영 체제의 교착 상태 감지.
- 대학의 코스 일정.
관련 기사:
- 위상 정렬을 위한 Kahn의 알고리즘
- 방향성 비순환 그래프의 모든 토폴로지 정렬