배열은 인접한 메모리 위치를 갖는 유사한 유형의 요소로 구성된 동종 모음입니다.
배열은 사용자 정의 데이터 유형입니다.
배열은 유사한 데이터 유형의 요소를 저장하는 데이터 구조 유형입니다. 배열에는 고정된 요소 집합만 저장할 수 있습니다. 객체로 사용할 수도 있습니다.
배열은 인덱스 기반 저장소로, 첫 번째 요소는 인덱스 0에 저장됩니다. 아래 구조는 배열의 구조를 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
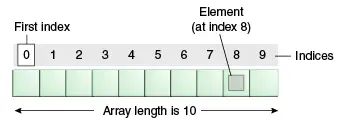
배열의 특성
- 배열은 동일한 데이터 유형을 갖는 요소를 저장합니다.
- 연속된 메모리 위치에 저장된 배열 요소입니다.
- 2차원 배열 요소의 저장은 연속적인 메모리 위치에 행 단위로 저장됩니다.
- 배열 이름은 시작 요소의 주소를 나타냅니다.
- 배열의 크기는 선언 시 초기화되어야 합니다.
- 배열 크기는 변수가 아닌 상수 표현식이어야 합니다.
- 요소의 해당 인덱스 값을 지정하여 배열 요소를 검색할 수 있습니다.
이점
코드 최적화: 배열은 코드를 최적화하는 데 도움이 되어 프로그램의 속도와 성능을 향상시킵니다. 이를 통해 배열 데이터를 보다 효율적으로 검색하거나 정렬할 수 있습니다.
무작위 액세스: 이는 배열의 모든 데이터에 일정한 시간(위치 및 크기에 관계없이)에 액세스할 수 있는 기능을 제공합니다. 따라서 우리는 임의의 인덱스 위치에 있는 배열의 모든 데이터를 직접 얻을 수 있습니다.
불리
크기 제한: 배열을 사용하면 고정된 개수의 요소만 저장할 수 있습니다. 배열이 선언되면 크기를 변경할 수 없습니다. 따라서 선언된 것보다 더 많은 요소를 삽입하려는 경우에는 불가능합니다.
배열 선언
JavaScript와 마찬가지로 TypeScript도 배열을 지원합니다. 배열을 선언하는 방법에는 두 가지가 있습니다.
1. 대괄호를 사용합니다.
let array_name[:datatype] = [val1,val2,valn..]
예:
let fruits: string[] = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
2. 일반 배열 유형을 사용합니다.
자바스크립트 문자열 다듬기
let array_name: Array = [val1,val2,valn..]
예:
let fruits: Array = ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Banana'];
TypeScript의 배열 유형
배열에는 두 가지 유형이 있습니다.
- 1차원 배열
- 다차원 배열

1차원 배열
1차원 배열은 데이터를 저장하기 위해 하나의 행만 포함하는 선형 배열 유형입니다. 단일 대괄호('[]') 세트가 있습니다. 행 또는 열 인덱스를 사용하여 해당 요소에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
통사론
let array_name[:datatype];
초기화
array_name = [val1,val2,valn..]
예
let arr:number[]; arr = [1, 2, 3, 4] console.log('Array[0]: ' +arr[0]); console.log('Array[1]: ' +arr[1]);
산출:
Array[0]: 1 Array[1]: 2
다차원 배열
다차원 배열은 하나 이상의 배열을 포함하는 배열입니다. 다차원 배열에서 데이터는 행 및 열 기반 인덱스(행렬 형식이라고도 함)에 저장됩니다. 2차원 배열(2-D 배열)은 다차원 배열의 가장 간단한 형태입니다.

통사론
let arr_name:datatype[][] = [ [a1,a2,a3], [b1,b2,b3] ];
초기화
let arr_name:datatype[initial_array_index][referenced_array_index] = [ [val1,val2,val 3], [v1,v2,v3]];
예
var mArray:number[][] = [[1,2,3],[5,6,7]] ; console.log(mArray[0][0]); console.log(mArray[0][1]); console.log(mArray[0][2]); console.log(); console.log(mArray[1][0]); console.log(mArray[1][1]); console.log(mArray[1][2]);
산출:
1 2 3 5 6 7
배열 객체
배열 객체를 사용하면 단일 변수에 여러 값을 저장할 수 있습니다. Array 객체를 사용하여 배열을 만들 수 있습니다. Array 생성자는 배열 생성을 위해 다음 인수를 전달하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 배열의 크기를 나타내는 숫자 값 또는
- 쉼표로 구분된 값 목록입니다.
통사론
let arr_name:datatype[] = new Array(values);
예
//array by using the Array object. let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint','2200','Java','Abhishek'); for(var i = 0;i <arr.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2200 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Array Traversal by using a for...in loop</h3> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <h3>Passing Arrays to Functions</h3> <p>We can pass arrays to functions by specifying the array name without an index.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)></pre></arr.length;i++)> for...in 루프를 사용한 배열 탐색
예
let i:any; let arr:string[] = ['JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek']; for(i in arr) { console.log(arr[i]) } 산출:
JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek
배열을 함수에 전달하기
인덱스 없이 배열 이름을 지정하여 배열을 함수에 전달할 수 있습니다.
예
C 프로그래밍 포함
let arr:string[] = new Array('JavaTpoint', '2300', 'Java', 'Abhishek'); //Passing arrays in function function display(arr_values:string[]) { for(let i = 0;i <arr_values.length;i++) { console.log(arr[i]); } calling arrays in function display(arr); < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> JavaTpoint 2300 Java Abhishek </pre> <hr> <h2>TypeScript Spread operator</h2> <p>The spread operator is used to initialize arrays and objects from another array or object. We can also use it for object de-structuring. It is a part of the ES 6 version.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <pre> let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray); </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6 </pre> <hr> <h2>Array Methods</h2> <p>The list of array methods with their description is given below.</p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>SN</th> <th>Method</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> <tr> <td>1.</td> <td>concat()</td> <td>It is used to joins two arrays and returns the combined result.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.</td> <td>copyWithin()</td> <td>It copies a sequence of an element within the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.</td> <td>every()</td> <td>It returns true if every element in the array satisfies the provided testing function.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.</td> <td>fill()</td> <td>It fills an array with a static value from the specified start to end index.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.</td> <td>indexOf()</td> <td>It returns the index of the matching element in the array, otherwise -1.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.</td> <td>includes()</td> <td>It is used to check whether the array contains a certain element or not.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>7.</td> <td>Join()</td> <td>It is used to joins all elements of an array into a string.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>8.</td> <td>lastIndexOf()</td> <td>It returns the last index of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>9.</td> <td>Pop()</td> <td>It is used to removes the last elements of the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>10.</td> <td>Push()</td> <td>It is used to add new elements to the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11.</td> <td>reverse()</td> <td>It is used to reverse the order of an element in the array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12.</td> <td>Shift()</td> <td>It is used to removes and returns the first element of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>13.</td> <td>slice()</td> <td>It returns the section fo an array in the new array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>14.</td> <td>sort()</td> <td>It is used to sort the elements of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>15.</td> <td>splice()</td> <td>It is used to add or remove the elements from an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>16.</td> <td>toString()</td> <td>It returns the string representation of an array.</td> </tr> <tr> <td>17.</td> <td>unshift()</td> <td>It is used to add one or more elements to the beginning of an array.</td> </tr> </table></arr_values.length;i++)> TypeScript 스프레드 연산자
스프레드 연산자는 다른 배열이나 객체의 배열과 객체를 초기화하는 데 사용됩니다. 객체 구조 분해에도 사용할 수 있습니다. ES 6 버전의 일부입니다.
예
let arr1 = [ 1, 2, 3]; let arr2 = [ 4, 5, 6]; //Create new array from existing array let copyArray = [...arr1]; console.log('CopiedArray: ' +copyArray); //Create new array from existing array with more elements let newArray = [...arr1, 7, 8]; console.log('NewArray: ' +newArray); //Create array by merging two arrays let mergedArray = [...arr1, ...arr2]; console.log('MergedArray: ' +mergedArray);
산출:
CopiedArray: 1,2,3 NewArray: 1,2,3,7,8 MergedArray: 1,2,3,4,5,6
배열 방법
설명과 함께 배열 메소드 목록이 아래에 제공됩니다.
| SN | 방법 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 연결() | 두 개의 배열을 결합하고 결합된 결과를 반환하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 2. | 복사 내부() | 배열 내의 요소 시퀀스를 복사합니다. |
| 삼. | 모든() | 배열의 모든 요소가 제공된 테스트 함수를 충족하면 true를 반환합니다. |
| 4. | 채우다() | 지정된 시작부터 끝 인덱스까지 정적 값으로 배열을 채웁니다. |
| 5. | 인덱스() | 배열에서 일치하는 요소의 인덱스를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 -1을 반환합니다. |
| 6. | 포함() | 배열에 특정 요소가 포함되어 있는지 여부를 확인하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 7. | 가입하다() | 배열의 모든 요소를 문자열로 결합하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 8. | 마지막 인덱스Of() | 배열에 있는 요소의 마지막 인덱스를 반환합니다. |
| 9. | 팝() | 배열의 마지막 요소를 제거하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 10. | 푸시() | 배열에 새 요소를 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 열하나. | 뒤집다() | 배열의 요소 순서를 바꾸는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 12. | 옮기다() | 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 제거하고 반환하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 13. | 일부분() | 새 배열의 배열에 대한 섹션을 반환합니다. |
| 14. | 종류() | 배열의 요소를 정렬하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 열 다섯. | 접착() | 배열에서 요소를 추가하거나 제거하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 16. | toString() | 배열의 문자열 표현을 반환합니다. |
| 17. | 쉬프트 해제() | 배열의 시작 부분에 하나 이상의 요소를 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. |
