- RSS 형식 자체는 자동화된 프로세스와 사람 모두가 비교적 쉽게 읽을 수 있습니다.
- 이 튜토리얼에서 처리되는 RSS는 인기 뉴스 웹사이트의 주요 뉴스 기사에 대한 RSS 피드입니다. 확인하실 수 있습니다 여기 . 우리의 목표는 이 RSS 피드(또는 XML 파일)를 처리하고 나중에 사용할 수 있도록 다른 형식으로 저장하는 것입니다.
#Python code to illustrate parsing of XML files # importing the required modules import csv import requests import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET def loadRSS(): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests.get(url) # saving the xml file with open('topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb') as f: f.write(resp.content) def parseXML(xmlfile): # create element tree object tree = ET.parse(xmlfile) # get root element root = tree.getroot() # create empty list for news items newsitems = [] # iterate news items for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item: # special checking for namespace object content:media if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] else: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems.append(news) # return news items list return newsitems def savetoCSV(newsitems filename): # specifying the fields for csv file fields = ['guid' 'title' 'pubDate' 'description' 'link' 'media'] # writing to csv file with open(filename 'w') as csvfile: # creating a csv dict writer object writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile fieldnames = fields) # writing headers (field names) writer.writeheader() # writing data rows writer.writerows(newsitems) def main(): # load rss from web to update existing xml file loadRSS() # parse xml file newsitems = parseXML('topnewsfeed.xml') # store news items in a csv file savetoCSV(newsitems 'topnews.csv') if __name__ == '__main__': # calling main function main()
- 지정된 URL에서 RSS 피드를 로드하고 XML 파일로 저장합니다.
- XML 파일을 구문 분석하여 뉴스를 각 사전이 단일 뉴스 항목인 사전 목록으로 저장합니다.
- 뉴스 항목을 CSV 파일에 저장합니다.
- 위의 예에서 사용된 뉴스 웹사이트의 더 많은 RSS 피드를 살펴볼 수 있습니다. 다른 RSS 피드도 구문 분석하여 위 예제의 확장 버전을 만들 수 있습니다.
- 크리켓 팬이신가요? 그 다음에 이것 RSS 피드에 관심이 있으실 겁니다! 이 XML 파일을 구문 분석하여 라이브 크리켓 경기에 대한 정보를 스크랩하고 데스크톱 알림을 만드는 데 사용할 수 있습니다!
def loadRSS(): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests.get(url) # saving the xml file with open('topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb') as f: f.write(resp.content) Here we first created a HTTP response object by sending an HTTP request to the URL of the RSS feed. The content of response now contains the XML file data which we save as topnewsfeed.xml 우리 로컬 디렉토리에 있습니다. 요청 모듈의 작동 방식에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음 문서를 참조하세요. Python을 사용한 GET 및 POST 요청 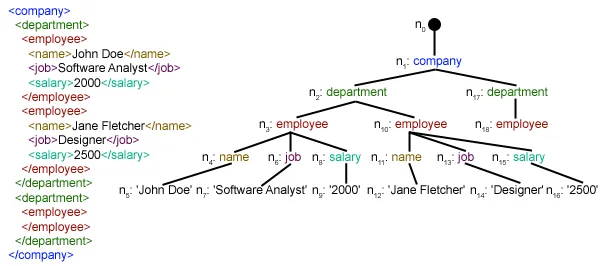 여기서 우리는 사용하고 있습니다 xml.etree.ElementTree (줄여서 ET라고 부름) 모듈입니다. Element Tree에는 이 목적을 위해 두 가지 클래스가 있습니다. 요소트리 전체 XML 문서를 트리로 표현하고 요소 이 트리의 단일 노드를 나타냅니다. 전체 문서와의 상호 작용(파일 읽기 및 쓰기)은 일반적으로 요소트리 수준. 단일 XML 요소 및 해당 하위 요소와의 상호 작용은 요소 수준. 알았어 그럼 살펴보자 구문 분석XML() function now:
여기서 우리는 사용하고 있습니다 xml.etree.ElementTree (줄여서 ET라고 부름) 모듈입니다. Element Tree에는 이 목적을 위해 두 가지 클래스가 있습니다. 요소트리 전체 XML 문서를 트리로 표현하고 요소 이 트리의 단일 노드를 나타냅니다. 전체 문서와의 상호 작용(파일 읽기 및 쓰기)은 일반적으로 요소트리 수준. 단일 XML 요소 및 해당 하위 요소와의 상호 작용은 요소 수준. 알았어 그럼 살펴보자 구문 분석XML() function now: tree = ET.parse(xmlfile)Here we create an 요소트리 전달된 내용을 구문 분석하여 개체 xml 파일.
root = tree.getroot()뿌리 뽑기() 함수는 루트를 반환 나무 로서 요소 object.
for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): Now once you have taken a look at the structure of your XML file you will notice that we are interested only in 목 요소. ./채널/항목 실제로는 XPath 구문(XPath는 XML 문서의 일부를 지정하기 위한 언어입니다). 여기서 우리는 모든 것을 찾고 싶습니다 목 손자 채널 의 아이들 뿌리 ('.'으로 표시) 요소입니다. 지원되는 XPath 구문에 대해 자세히 알아볼 수 있습니다. 여기 . for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item: # special checking for namespace object content:media if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] else: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems.append(news) Now we know that we are iterating through 목 각각의 요소 목 요소에는 하나의 뉴스가 포함됩니다. 그래서 우리는 빈 공간을 만듭니다 소식 dictionary in which we will store all data available about news item. To iterate though each child element of an element we simply iterate through it like this: for child in item:Now notice a sample item element here:
 We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this:
We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this: if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] 자식.속성 요소와 관련된 모든 속성의 사전입니다. 여기에 우리가 관심이 있는 것은 URL ~의 속성 미디어:컨텐츠 namespace tag. Now for all other children we simply do: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') 아이.태그 하위 요소의 이름을 포함합니다. 자식.텍스트 stores all the text inside that child element. So finally a sample item element is converted to a dictionary and looks like this: {'description': 'Ignis has a tough competition already from Hyun.... 'guid': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'link': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'media': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rf/image_size_630x354/HT/... 'pubDate': 'Thu 12 Jan 2017 12:33:04 GMT ' 'title': 'Maruti Ignis launches on Jan 13: Five cars that threa..... } Then we simply append this dict element to the list 뉴스 기사 . 마지막으로 이 목록이 반환됩니다.  보시다시피 계층적 XML 파일 데이터가 간단한 CSV 파일로 변환되어 모든 뉴스 기사가 테이블 형식으로 저장됩니다. 이렇게 하면 데이터베이스 확장도 더 쉬워집니다. 또한 JSON과 유사한 데이터를 애플리케이션에서 직접 사용할 수도 있습니다! 이는 공개 API를 제공하지 않지만 일부 RSS 피드를 제공하는 웹사이트에서 데이터를 추출하는 가장 좋은 대안입니다. 위 기사에 사용된 모든 코드와 파일을 찾을 수 있습니다. 여기 . 다음은 무엇입니까?
보시다시피 계층적 XML 파일 데이터가 간단한 CSV 파일로 변환되어 모든 뉴스 기사가 테이블 형식으로 저장됩니다. 이렇게 하면 데이터베이스 확장도 더 쉬워집니다. 또한 JSON과 유사한 데이터를 애플리케이션에서 직접 사용할 수도 있습니다! 이는 공개 API를 제공하지 않지만 일부 RSS 피드를 제공하는 웹사이트에서 데이터를 추출하는 가장 좋은 대안입니다. 위 기사에 사용된 모든 코드와 파일을 찾을 수 있습니다. 여기 . 다음은 무엇입니까? 