Java 클래스와 객체는 객체지향 프로그래밍(OOP)의 기초를 형성합니다. 실제 엔터티를 모델링하고 구조화된 방식으로 코드를 구성하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 클래스는 공통 속성과 동작을 공유하는 객체를 만드는 데 사용되는 청사진입니다.
- 객체는 클래스의 인스턴스입니다. 이는 클래스 템플릿에서 생성된 특정 엔터티를 나타냅니다.
예를 들어 Dog는 클래스입니다. Tommy는 해당 클래스의 객체입니다.
안드로이드 버전 기록
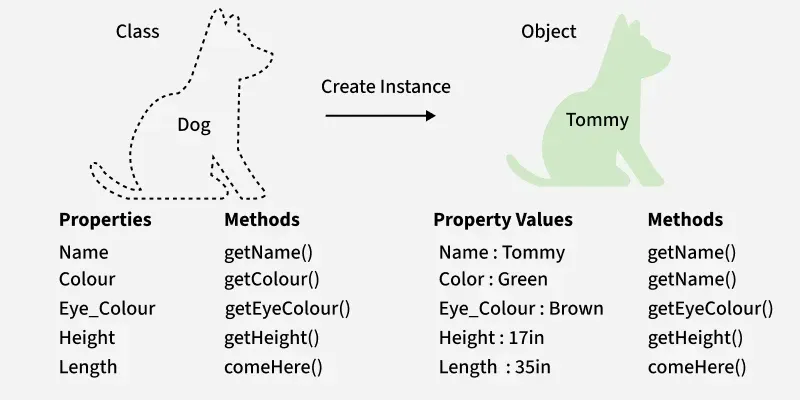 클래스와 객체(여기서 Dog는 클래스이고 Bobby는 객체입니다)
클래스와 객체(여기서 Dog는 클래스이고 Bobby는 객체입니다)자바 클래스
클래스는 객체의 데이터와 동작을 정의하는 청사진입니다. 관련 필드와 메소드를 하나의 단위로 그룹화합니다. 해당 멤버에 대한 메모리는 객체가 생성될 때만 할당됩니다.
- 공유 구조로 객체를 생성하기 위한 템플릿 역할을 합니다.
- 인스턴스화될 때까지 필드에 대한 메모리를 차지하지 않습니다.
- 필드 메소드 생성자 중첩 클래스 및 인터페이스를 포함할 수 있습니다.
class Student { int id; String n; public Student(int id String n) { this.id = id; this.n = n; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student(10 'Alice'); System.out.println(s1.id); System.out.println(s1.n); } }
산출
10 Alice
자바 객체
객체는 해당 데이터와 작업에 액세스하기 위해 생성된 클래스의 인스턴스입니다. 각 객체는 고유한 상태를 보유합니다.
- 상태 : 필드에 저장된 값입니다.
- 행동 : 메소드를 통해 정의된 작업입니다.
- 신원 : 한 개체를 다른 개체와 구별합니다.
객체는 고객 제품이나 서클과 같은 실제 항목을 반영합니다. 기본이 아닌 개체는 참조가 스택에 남아 있는 동안 힙에 저장됩니다.
 Java 객체(개의 예)
Java 객체(개의 예)객체 인스턴스화
객체 생성을 인스턴스화라고 합니다. 클래스의 모든 인스턴스는 서로 다른 상태 값을 저장하면서 구조와 동작을 공유합니다.
 Java 객체 선언
Java 객체 선언선언:
개 터피;
이는 단지 참조를 선언하는 것뿐입니다. 객체가 생성되지 않고 참조가 null을 유지합니다.
초기화:
tuffy = new Dog('터피' '빠삐용' 5 '흰색');
 초기화
초기화new 연산자는 메모리를 할당하고 생성자를 호출합니다.
예: 클래스 정의 및 사용
Javapublic class Dog { String name; String breed; int age; String color; public Dog(String name String breed int age String color) { this.name = name; this.breed = breed; this.age = age; this.color = color; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getBreed() { return breed; } public int getAge() { return age; } public String getColor() { return color; } @Override public String toString() { return 'Name is: ' + name + 'nBreed age and color are: ' + breed + ' ' + age + ' ' + color; } public static void main(String[] args) { Dog tuffy = new Dog('tuffy' 'papillon' 5 'white'); System.out.println(tuffy); } }
산출
Name is: tuffy Breed age and color are: papillon 5 white
메모: 모든 클래스에는 적어도 하나의 생성자가 있습니다. 아무것도 정의되지 않은 경우 Java는 상위 생성자를 호출하는 인수 없는 기본 생성자를 제공합니다.
메소드/함수를 사용하여 객체 초기화
Javapublic class Geeks { static String name; static float price; static void set(String n float p) { name = n; price = p; } static void get() { System.out.println('Software name is: ' + name); System.out.println('Software price is: ' + price); } public static void main(String[] args) { Geeks.set('Visual Studio' 0.0f); Geeks.get(); } }
산출
Software name is: Visual Studio Software price is: 0.0
Java에서 객체를 생성하는 방법
Java는 네 가지 표준 접근 방식을 지원합니다.
자바 차트
1. 새로운 키워드 사용
객체를 생성하는 가장 직접적인 방법입니다.
Java// creating object of class Test Test t = new Test();
2. 리플렉션 사용
Spring과 같은 프레임워크에서 볼 수 있듯이 동적 클래스 로딩에 사용됩니다.
Javaclass Student { public Student() {} } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class c = Class.forName('Student'); Student s = (Student) c.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); System.out.println(s); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
산출
Student@1dbd16a6
3. clone() 메소드 사용
clone()은 기존 객체의 복사본을 만듭니다. 클래스는 Cloneable을 구현해야 합니다.
Javaclass Geeks implements Cloneable { String name = 'GeeksForGeeks'; @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { Geeks g1 = new Geeks(); Geeks g2 = (Geeks) g1.clone(); System.out.println(g2.name); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
산출
GeeksForGeeks
4. 역직렬화 사용
역직렬화는 파일에 저장된 상태에서 객체를 읽는 기술입니다. 객체는 저장된 바이트 스트림에서 다시 생성됩니다.
참조 Java의 직렬화/역직렬화 .
Javaimport java.io.*; class Student implements Serializable { private String name; public Student(String name) { this.name = name; } public String toString() { return 'Student: ' + name; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream('student.ser'))) { out.writeObject(new Student('Alice')); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try (ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream('student.ser'))) { Student s = (Student) in.readObject(); System.out.println(s); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
산출
Student: Alice
단일 참조는 서로 다른 시간에 서로 다른 객체를 가리킬 수 있습니다.
JavaTest test = new Test(); test = new Test();
상속에서는 자식 개체에 대한 부모 참조를 사용하는 것이 일반적입니다.
JavaAnimal obj = new Dog(); obj = new Cat();
참조되지 않은 객체는 가비지 수집 대상이 됩니다.
익명 객체
익명 객체는 참조 없이 생성되며 일회성 작업에 즉시 사용됩니다.
np.clip
- 참조 변수 없음: 개체를 재사용할 수 없습니다.
- 생성 및 사용하면 단기 작업을 위해 메모리가 즉시 절약됩니다.
- 이벤트 처리(예: 버튼 클릭)에서 일반적입니다.
new Dog('Max' 'Labrador' 3 'Black').getName();
UI 이벤트 처리에서 일반적입니다.
퀴즈 만들기