너비 우선 검색(BFS) 그리고 깊이 우선 검색(DFS) 그래프와 트리를 탐색하거나 검색하는 데 사용되는 두 가지 기본 알고리즘입니다. 이 기사에서는 너비 우선 검색과 깊이 우선 검색의 기본적인 차이점을 다룹니다.
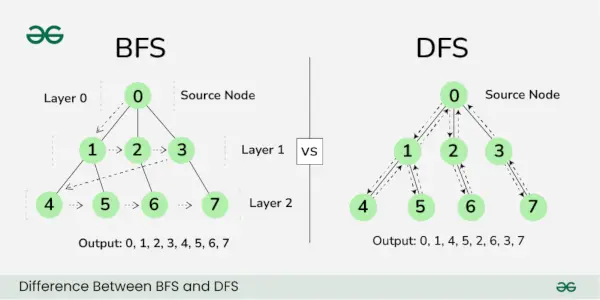
BFS와 DFS의 차이점
너비 우선 검색(BFS) :
BFS, 너비 우선 검색, 그래프에서 최단 경로를 찾는 정점 기반 기술입니다. 그것은 산출:
A, B, C, D, E, F>
암호:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; // This class represents a directed graph using adjacency // list representation class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists list * 조정; 공개: 그래프(int V); // 생성자 // 그래프에 간선을 추가하는 함수 void addEdge(int v, int w); // 주어진 소스로부터 BFS 순회를 인쇄합니다. s void BFS(int s); }; Graph::Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = 새 목록 [V]; } void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); // v의 목록에 w를 추가합니다. } void Graph::BFS(int s) { // 모든 정점을 방문하지 않은 것으로 표시 bool* Visited = new bool[V]; for (int i = 0; i< V; i++) visited[i] = false; // Create a queue for BFS list 대기줄; // 현재 노드를 방문한 것으로 표시하고 대기열에 넣습니다.[s] = true; queue.push_back(s); // 'i'는 정점 목록의 모든 인접한 정점을 가져오는 데 사용됩니다. ::반복자 i; // 정수에서 문자로의 매핑 생성 char map[6] = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F ' }; while (!queue.empty()) { // 큐에서 정점을 꺼내서 인쇄합니다. s = queue.front(); 시합<< map[s] << ' '; // Use the mapping to print // the original label queue.pop_front(); // Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex // s If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark // it visited and enqueue it for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) { if (!visited[*i]) { queue.push_back(*i); visited[*i] = true; } } } } int main() { // Create a graph given in the diagram /* A / B C / / D E F */ Graph g(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(0, 2); g.addEdge(1, 3); g.addEdge(2, 4); g.addEdge(2, 5); cout << 'Breadth First Traversal is: '; g.BFS(0); // Start BFS from A (0) return 0; }> 파이썬 from collections import deque # This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self, V): self.V = V # No. of vertices self.adj = [[] for _ in range(V)] # Adjacency lists # Function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self, v, w): self.adj[v].append(w) # Add w to v’s list # Prints BFS traversal from a given source s def BFS(self, s): # Mark all the vertices as not visited visited = [False] * self.V # Create a queue for BFS queue = deque() # Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it visited[s] = True queue.append(s) # Create a mapping from integers to characters mapping = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'] while queue: # Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it s = queue.popleft() # Use the mapping to print the original label print(mapping[s], end=' ') # Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s # If an adjacent has not been visited, then mark it visited # and enqueue it for i in self.adj[s]: if not visited[i]: queue.append(i) visited[i] = True if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a graph given in the diagram # A # / # B C # / / # D E F g = Graph(6) g.addEdge(0, 1) g.addEdge(0, 2) g.addEdge(1, 3) g.addEdge(2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 5) print('Breadth First Traversal is: ', end='') g.BFS(0) # Start BFS from A (0)> 자바스크립트 // This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation class Graph { constructor(V) { this.V = V; // No. of vertices this.adj = new Array(V).fill(null).map(() =>[]); // 인접 목록 배열 } // 그래프에 간선을 추가하는 함수 addEdge(v, w) { this.adj[v].push(w); // v의 목록에 w를 추가합니다. } // 주어진 소스에서 BFS 순회를 수행하는 함수 s BFS(s) { // 모든 정점을 방문하지 않은 것으로 표시 let Visited = new Array(this.V).fill(false); // BFS용 큐 생성 let queue = []; // 현재 노드를 방문한 것으로 표시하고 대기열에 넣습니다.[s] = true; 대기열.푸시(들); // 정수에서 문자로 매핑 let map = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']; while (queue.length> 0) { // 큐에서 정점을 꺼내서 인쇄합니다. s = queue.shift(); console.log(map[s] + ' '); // 매핑을 사용하여 원래 레이블을 인쇄합니다. // 대기열에서 제거된 정점의 모든 인접 정점을 가져옵니다. // 인접 정점을 방문하지 않은 경우 방문한 것으로 표시하고 // 대기열에 넣습니다(let i of this.adj[s) ]) { if (!visited[i]) { queue.push(i); 방문[i] = true; } } } } } // 주요 함수 function main() { // 다이어그램에 주어진 그래프를 생성합니다 /* A / B C / / D E F */ let g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(0, 2); g.addEdge(1, 3); g.addEdge(2, 4); g.addEdge(2, 5); console.log('너비 우선 순회: '); g.BFS(0); // A(0)에서 BFS 시작 } // 메인 함수 실행 main();> 산출
Breadth First Traversal is: A B C D E F>
깊이 우선 검색(DFS) :
DFS, 깊이 우선 검색 는 에지 기반 기술입니다. 그것은 산출:
A, B, C, D, E, F>
BFS와 DFS의 차이점:
| 매개변수 | BFS | DFS |
|---|---|---|
| 다음을 의미합니다. | BFS는 너비 우선 검색을 나타냅니다. | DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색을 의미합니다. |
| 데이터 구조 | BFS(Breadth First Search)는 최단 경로를 찾기 위해 Queue 데이터 구조를 사용합니다. | DFS(Depth First Search)는 Stack 데이터 구조를 사용합니다. |
| 정의 | BFS는 다음 레벨로 이동하기 전에 먼저 동일한 레벨의 모든 노드를 살펴보는 순회 접근 방식입니다. | DFS는 순회가 루트 노드에서 시작하여 근처에 방문하지 않은 노드가 없는 노드에 도달할 때까지 가능한 한 노드를 통해 진행하는 순회 접근 방식이기도 합니다. |
| 개념적 차이 | BFS는 레벨별로 트리를 구축합니다. | DFS는 하위 트리별로 트리 하위 트리를 구축합니다. |
| 사용된 접근법 | FIFO(First In First Out) 개념에 따라 작동합니다. | LIFO(Last In First Out) 개념에 따라 작동합니다. |
| 적합 | BFS는 주어진 소스에 더 가까운 정점을 검색하는 데 더 적합합니다. | DFS는 소스와 떨어진 곳에 솔루션이 있을 때 더 적합합니다. |
| 응용 | BFS는 이분 그래프, 최단 경로 등 다양한 응용 분야에 사용됩니다. | DFS는 비순환 그래프 및 강하게 연결된 구성 요소 찾기 등과 같은 다양한 응용 프로그램에 사용됩니다. |
또한 참조하시기 바랍니다 이진 트리의 BFS와 DFS 이진 트리 탐색의 차이점에 대해 설명합니다.
