삽입 정렬과 선택 정렬은 널리 사용되는 두 가지 정렬 알고리즘이며, 주요 차이점은 정렬된 순서에서 요소를 선택하고 배치하는 방법에 있습니다.
선택 정렬:
- 선택 정렬에서는 입력 배열을 정렬된 부분과 정렬되지 않은 부분의 두 부분으로 나눕니다.
- 알고리즘은 정렬되지 않은 부분에서 최소 요소를 반복적으로 찾아 이를 정렬되지 않은 부분의 가장 왼쪽 요소와 교환하여 정렬된 부분을 한 요소만큼 확장합니다.
- 선택 정렬은 모든 경우에 O(n^2)의 시간 복잡도를 갖습니다.
삽입 정렬:
- 삽입 정렬에서는 입력 배열도 정렬된 부분과 정렬되지 않은 부분의 두 부분으로 나뉩니다.
알고리즘은 정렬되지 않은 부분에서 요소를 선택하여 정렬된 부분의 올바른 위치에 배치하고 더 큰 요소를 오른쪽으로 한 위치 이동합니다.
삽입 정렬은 최악의 경우 O(n^2)의 시간 복잡도를 가지지만 부분적으로 정렬된 배열에서는 더 나은 성능을 발휘할 수 있으며 최상의 경우의 시간 복잡도는 O(n)입니다.
주요 차이점: - 선택 정렬은 정렬되지 않은 부분을 스캔하여 최소 요소를 찾고, 삽입 정렬은 정렬된 부분을 스캔하여 요소를 배치할 올바른 위치를 찾습니다.
선택 정렬은 삽입 정렬보다 교체 횟수가 적지만 비교 횟수는 더 많습니다.
삽입 정렬은 입력 배열이 부분적으로 정렬되거나 거의 정렬된 경우 선택 정렬보다 효율적이고, 선택 정렬은 배열이 매우 정렬되지 않은 경우 더 효율적입니다.
요약하면 두 알고리즘 모두 시간 복잡도는 비슷하지만 선택 및 배치 방법이 다릅니다. 둘 사이의 선택은 입력 데이터의 특성과 당면한 문제의 특정 요구 사항에 따라 달라집니다.
삽입 정렬의 장점:
- 간단하고 이해하기 쉽고 구현하기 쉽습니다.
- 작은 데이터 세트 또는 거의 정렬된 데이터에 효율적입니다.
- 내부 정렬 알고리즘은 추가 메모리가 필요하지 않음을 의미합니다.
- 안정적인 정렬 알고리즘. 즉, 입력 배열에서 동일한 요소의 상대적 순서를 유지합니다.
삽입 정렬의 단점:
- 대규모 데이터 세트 또는 역순 데이터에는 비효율적이며 최악의 경우 시간 복잡도는 O(n^2)입니다.
- 삽입 정렬에는 스왑이 많아 최신 컴퓨터에서는 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.
선택 정렬의 장점:
- 간단하고 이해하기 쉽고 구현하기 쉽습니다.
- 작은 데이터 세트 또는 거의 정렬된 데이터에 효율적입니다.
- 내부 정렬 알고리즘은 추가 메모리가 필요하지 않음을 의미합니다.
선택 정렬의 단점:
- 최악의 경우 시간 복잡도가 O(n^2)이므로 대규모 데이터 세트에는 비효율적입니다.
- 선택 정렬에는 비교가 많기 때문에 최신 컴퓨터에서는 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.
- 불안정한 정렬 알고리즘. 즉, 입력 배열에서 동일한 요소의 상대적 순서를 유지하지 못할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
이번 포스팅에서는 삽입정렬과 선택정렬의 차이점에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
삽입 정렬 는 손에 들고 있는 카드를 정렬하는 방식과 유사하게 작동하는 간단한 정렬 알고리즘입니다. 배열은 사실상 정렬된 부분과 정렬되지 않은 부분으로 분할됩니다. 정렬되지 않은 부분의 값이 선택되어 정렬된 부분의 올바른 위치에 배치됩니다.
연산:
크기가 n인 배열을 오름차순으로 정렬하려면 다음을 수행하세요.
- 배열에 대해 arr[1]부터 arr[n]까지 반복합니다.
- 현재 요소(키)를 이전 요소와 비교합니다.
- 핵심 요소가 이전 요소보다 작은 경우 이전 요소와 비교합니다. 더 큰 요소를 한 위치 위로 이동하여 교체된 요소를 위한 공간을 만듭니다.
아래는 삽입 정렬을 설명하는 이미지입니다.
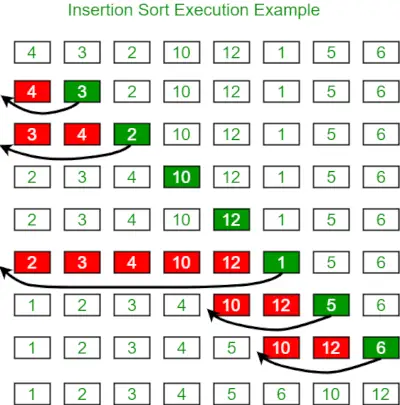
다음은 동일한 프로그램입니다.
C++
// C++ program for the insertion sort> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Function to sort an array using> // insertion sort> void> insertionSort(>int> arr[],>int> n)> {> >int> i, key, j;> >for> (i = 1; i key = arr[i]; j = i - 1; // Move elements of arr[0..i-1], // that are greater than key to // one position ahead of their // current position while (j>= 0 && arr[j]> 키) { arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; j = j - 1; } arr[j + 1] = 키; } } // N 크기의 배열을 인쇄하는 함수 void printArray(int arr[], int n) { int i; // (i = 0; i cout)에 대한 배열을 인쇄합니다.<< arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 }; int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // Function Call insertionSort(arr, N); printArray(arr, N); return 0; }> |
>
>
자바
// Java program for the above approach> import> java.util.*;> class> GFG> {> > // Function to sort an array using> // insertion sort> static> void> insertionSort(>int> arr[],>int> n)> {> >int> i, key, j;> >for> (i =>1>; i { key = arr[i]; j = i - 1; // Move elements of arr[0..i-1], // that are greater than key to // one position ahead of their // current position while (j>= 0 && arr[j]> 키) { arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; j = j - 1; } arr[j + 1] = 키; } } // N 크기의 배열을 인쇄하는 함수 static void printArray(int arr[], int n) { int i; // 배열을 인쇄합니다(i = 0; i System.out.print(arr[i] + ' '); } System.out.println(); } // 드라이버 코드 public static void main(String[ ] args) { int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 }; int N = arr.length; // 삽입 정렬(arr, N) } } // 이 코드는 code_hunt에서 제공한 것입니다.> |
>
>
파이썬3
# Python 3 program for the insertion sort> # Function to sort an array using> # insertion sort> def> insertionSort(arr, n):> >i>=> 0> >key>=> 0> >j>=> 0> >for> i>in> range>(>1>,n,>1>):> >key>=> arr[i]> >j>=> i>-> 1> ># Move elements of arr[0..i-1],> ># that are greater than key to> ># one position ahead of their> ># current position> >while> (j>>=> 0> and> arr[j]>키):> >arr[j>+> 1>]>=> arr[j]> >j>=> j>-> 1> >arr[j>+> 1>]>=> key> # Function to print an array of size N> def> printArray(arr, n):> >i>=> 0> ># Print the array> >for> i>in> range>(n):> >print>(arr[i],end>=> ' '>)> >print>(>'
'>,end>=> '')> # Driver Code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >arr>=> [>12>,>11>,>13>,>5>,>6>]> >N>=> len>(arr)> ># Function Call> >insertionSort(arr, N)> >printArray(arr, N)> > ># This code is contributed by bgangwar59.> |
>
>
씨#
// C# program for the above approach> using> System;> class> GFG> {> >// Function to sort an array using> >// insertion sort> >static> void> insertionSort(>int>[] arr,>int> n)> >{> >int> i, key, j;> >for> (i = 1; i { key = arr[i]; j = i - 1; // Move elements of arr[0..i-1], // that are greater than key to // one position ahead of their // current position while (j>= 0 && arr[j]> 키) { arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; j = j - 1; } arr[j + 1] = 키; } } // N 크기의 배열을 인쇄하는 함수 static void printArray(int[] arr, int n) { int i; // 배열 인쇄 for (i = 0; i { Console.Write(arr[i] + ' '); } Console.WriteLine(); } // 드라이버 코드 static public void Main() { int[] arr = new int[] { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 }; int N = arr.Length; // 삽입 정렬(arr, N); printArray(arr, N) } // Dharanendra LV 님이 기고> |
>
>
자바스크립트
> // JavaScript program for the above approach> // Function to sort an array using> // insertion sort> function> insertionSort(arr,n)> {> >let i, key, j;> >for> (i = 1; i { key = arr[i]; j = i - 1; // Move elements of arr[0..i-1], // that are greater than key to // one position ahead of their // current position while (j>= 0 && arr[j]> 키) { arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; j = j - 1; } arr[j + 1] = 키; } } // N 크기의 배열을 인쇄하는 함수 function printArray(arr,n) { let i; // 배열을 인쇄합니다(i = 0; i document.write(arr[i] + ' '); } document.write(' '); } // 드라이버 코드 let arr=[12, 11 , 13, 5, 6]; let N = arr.length; // 함수 호출 insertSort(arr, N); printArray(arr, N); // 이 코드는 avanitrachhadiya2155에서 제공됩니다. |
>5 6 11 12 13>
그만큼 선택 정렬 알고리즘은 정렬되지 않은 부분에서 최소 요소(오름차순 고려)를 반복적으로 찾아 처음에 배치하여 배열을 정렬합니다. 알고리즘은 주어진 배열에서 두 개의 하위 배열을 유지합니다.
- 하위 배열이 이미 정렬되어 있습니다.
- 나머지 하위 배열은 정렬되지 않습니다.
선택 정렬을 반복할 때마다 정렬되지 않은 하위 배열에서 최소 요소(오름차순 고려)가 선택되어 정렬된 하위 배열로 이동됩니다.
다음은 위의 단계를 설명하는 예입니다.
arr[] = 64 25 12 22 11 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...4] // and place it at beginning 11 25 12 22 64 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...4] // and place it at beginning of arr[1...4] 11 12 25 22 64 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...4] // and place it at beginning of arr[2...4] 11 12 22 25 64 // Find the minimum element in arr[3...4] // and place it at beginning of arr[3...4] 11 12 22 25 64>
다음은 동일한 프로그램입니다.
C++
// C++ program for implementation of> // selection sort> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Function to swap two number> void> swap(>int>* xp,>int>* yp)> {> >int> temp = *xp;> >*xp = *yp;> >*yp = temp;> }> // Function to implement the selection> // sort> void> selectionSort(>int> arr[],>int> n)> {> >int> i, j, min_idx;> >// One by one move boundary of> >// unsorted subarray> >for> (i = 0; i // Find the minimum element // in unsorted array min_idx = i; for (j = i + 1; j if (arr[j] min_idx = j; // Swap the found minimum element // with the first element swap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]); } } // Function to print an array void printArray(int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i cout << arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); // Function Call selectionSort(arr, n); cout << 'Sorted array:
'; // Print the array printArray(arr, n); return 0; }> |
>
>
자바
// Java program for implementation of> // selection sort> import> java.util.*;> class> GFG> {> // Function to implement the selection> // sort> static> void> selectionSort(>int> arr[],>int> n)> {> >int> i, j, min_idx;> >// One by one move boundary of> >// unsorted subarray> >for> (i =>0>; i 1; i++) { // Find the minimum element // in unsorted array min_idx = i; for (j = i + 1; j if (arr[j] min_idx = j; // Swap the found minimum element // with the first element int temp = arr[min_idx]; arr[min_idx]= arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } } // Function to print an array static void printArray(int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i System.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); } System.out.println(); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 }; int n = arr.length; // Function Call selectionSort(arr, n); System.out.print('Sorted array:
'); // Print the array printArray(arr, n); } } // This code is contributed by aashish1995> |
>
>
파이썬3
# Python3 program for implementation of> # selection sort> # Function to implement the selection> # sort> def> selectionSort(arr, n):> ># One by one move boundary of> ># unsorted subarray> >for> i>in> range>(n>-> 1>):> ># Find the minimum element> ># in unsorted array> >min_idx>=> i> >for> j>in> range>(i>+> 1>, n):> >if> (arr[j] min_idx = j # Swap the found minimum element # with the first element arr[min_idx], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[min_idx] # Function to print an array def printArray(arr, size): for i in range(size): print(arr[i], end = ' ') print() # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11] n = len(arr) # Function Call selectionSort(arr, n) print('Sorted array: ') # Print the array printArray(arr, n) # This code is contributed by ukasp> |
>
>
씨#
모니터 화면 크기 확인하는 방법
// C# program for implementation of> // selection sort> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> // Function to implement the selection> // sort> static> void> selectionSort(>int> []arr,>int> n)> {> >int> i, j, min_idx;> >// One by one move boundary of> >// unsorted subarray> >for> (i = 0; i { // Find the minimum element // in unsorted array min_idx = i; for (j = i + 1; j if (arr[j] min_idx = j; // Swap the found minimum element // with the first element int temp = arr[min_idx]; arr[min_idx]= arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } } // Function to print an array static void printArray(int []arr, int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i Console.Write(arr[i]+ ' '); } Console.WriteLine(); } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { int []arr = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 }; int n = arr.Length; // Function Call selectionSort(arr, n); Console.Write('Sorted array:
'); // Print the array printArray(arr, n); } } // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1> |
>
>
자바스크립트
> // Javascript program for implementation of> // selection sort> // Function to implement the selection> // sort> function> selectionSort(arr, n)> {> >let i, j, min_idx;> > >// One by one move boundary of> >// unsorted subarray> >for>(i = 0; i { // Find the minimum element // in unsorted array min_idx = i; for(j = i + 1; j if (arr[j] min_idx = j; // Swap the found minimum element // with the first element let temp = arr[min_idx]; arr[min_idx]= arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } } // Function to print an array function printArray(arr, size) { let i; for(i = 0; i { document.write(arr[i] + ' '); } document.write(' '); } // Driver Code let arr = [ 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 ]; let n = arr.length; // Function Call selectionSort(arr, n); document.write('Sorted array: '); // Print the array printArray(arr, n); // This code is contributed by rag2127> |
>
>산출:
Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 64>
삽입 정렬과 선택 정렬의 표 차이:
| 삽입 정렬 | 선택 정렬 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 배열의 값 집합을 정렬하려면 미리 정렬된 배열에 값을 삽입합니다. | 목록에서 최소/최대 숫자를 찾아 오름차순/내림차순으로 정렬합니다. |
| 2. | 안정적인 정렬 알고리즘입니다. | 불안정한 정렬 알고리즘입니다. |
| 삼. | 배열이 이미 오름차순으로 되어 있는 경우 최상의 시간 복잡도는 Ω(N)입니다. Θ(N2) 최악의 경우와 평균적인 경우입니다. | 최선의 경우 최악의 경우와 평균 선택 정렬의 복잡성은 Θ(N2). |
| 4. | 이 정렬 알고리즘에서 수행되는 비교 작업 수는 수행된 스와핑 수보다 적습니다. | 이 정렬 알고리즘에서 수행되는 비교 작업의 수는 수행된 스와핑보다 많습니다. |
| 5. | 선택 정렬보다 효율적입니다. | 삽입정렬에 비해 효율성이 떨어집니다. |
| 6. | 여기에서는 요소가 미리 알려져 있으므로 요소를 배치할 올바른 위치를 검색합니다. | 요소를 넣을 위치는 이전에 알려져 있으며 해당 위치에 삽입할 요소를 검색합니다. |
| 7. | 삽입 정렬은 다음과 같은 경우에 사용됩니다.
| 선택 정렬은 다음과 같은 경우에 사용됩니다.
|
| 8. | 삽입 정렬은 적응형입니다. 즉, 이미 상당히 정렬된 데이터 세트에 효율적입니다. 시간 복잡도는 오(kn) 입력의 각 요소가 다음보다 크지 않은 경우 케이 정렬된 위치에서 멀리 떨어진 곳에 위치 | 선택 정렬은 내부 비교 정렬 알고리즘입니다. |
