Java에는 데이터 크기와 사용 사례에 따라 텍스트 파일을 읽는 여러 가지 방법이 있습니다. 그만큼 java.io 그리고 java.nio.file 패키지 파일 읽기를 효율적으로 처리하기 위해 여러 클래스를 제공합니다. 일반적인 접근 방식을 하나씩 논의해 보겠습니다.
1. BufferedReader 클래스 사용
버퍼링된 리더 클래스는 문자 스트림에서 텍스트를 읽고 효율적인 읽기를 위해 문자를 버퍼링합니다. 에 감싸인 경우가 많습니다. 파일리더 또는 입력스트림리더 성능을 향상시키기 위해.
통사론
JavaBufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(정수 크기의 리더);
import java.io.*; public class UsingBufferReader { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // Creating BufferedReader for Input BufferedReader bfri = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = bfri.readLine(); BufferedReader bfro = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path)); String st; while ((st = bfro.readLine()) != null) System.out.println(st); } }
산출
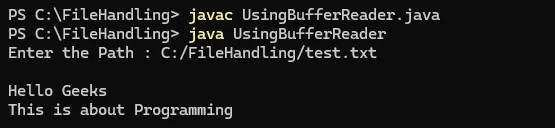 산출
산출2. 텍스트 파일을 읽기 위한 FileReader 클래스
그만큼 FileReader 클래스 Java에서 텍스트 파일을 읽는 데 사용됩니다. 파일에서 문자를 읽으며 일반 텍스트를 읽는 데 적합합니다. 이 클래스의 생성자는 기본 문자 인코딩과 기본 바이트 버퍼 크기가 적절하다고 가정합니다.
이 클래스에 정의된 생성자는 다음과 같습니다.
- FileReader(파일 파일): 읽을 파일이 주어지면 새 FileReader를 생성합니다.
- FileReader(파일 설명자 fd): 읽을 FileDescriptor가 지정된 새 FileReader를 만듭니다.
- FileReader(문자열 파일 이름): 읽을 파일 이름이 지정된 새 FileReader를 만듭니다.
import java.io.*; public class UsingFileReader { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = br.readLine(); FileReader fr = new FileReader(path); int i; // Holds true till there is nothing to read while ((i = fr.read()) != -1) // Print all the content of a file System.out.print((char)i); } }
산출
 산출
산출3. 텍스트 파일을 읽기 위한 스캐너 클래스
스캐너 클래스 다음을 사용하여 텍스트 파일을 읽고 기본 유형이나 문자열을 구문 분석하는 간단한 방법을 제공합니다. 정규 표현식 . 구분 기호(기본적으로 공백)를 사용하여 입력을 토큰으로 분할합니다.
예시 1: 루프를 사용하여
Javaimport java.io.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class UsingScannerClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = br.readLine(); // pass the path to the file as a parameter File file = new File(path); Scanner sc = new Scanner(file); while (sc.hasNextLine()) System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); } }
산출
es5 대 es6
 산출
산출예 2: 루프를 사용하지 않고
Javaimport java.io.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class ReadingEntireFileWithoutLoop { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = br.readLine(); File file = new File(path); Scanner sc = new Scanner(file); // we just need to use \Z as delimiter sc.useDelimiter('\Z'); System.out.println(sc.next()); } }
산출
 산출
산출4. 목록에서 전체 파일 읽기
우리는 다음을 사용하여 전체 텍스트 파일을 목록으로 읽을 수 있습니다. Files.readAllLines() 의 방법 java.nio.file 패키지 . 파일의 각 줄은 목록의 한 요소가 됩니다.
통사론
공개 정적 목록 readAllLines(Path pathCharset cs)가 IOException을 발생시킵니다.
이 방법은 다음을 줄 종결자로 인식합니다.
- u000Du000A -> 캐리지 리턴 + 라인 피드
- u000A -> 줄 바꿈
- u000D -> 캐리지 리턴
import java.io.*; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.nio.file.*; import java.util.*; public class ReadFileIntoList { public static List<String> readFileInList(String fileName) { // Created List of String List<String> lines = Collections.emptyList(); try { lines = Files.readAllLines( Paths.get(fileName) StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return lines; } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = br.readLine(); List l = readFileInList(path); // Iterator iterating over List Iterator<String> itr = l.iterator(); while (itr.hasNext()) System.out.println(itr.next()); } }
산출
 산출
산출5. 텍스트 파일을 문자열로 읽기
Java에서는 전체 텍스트 파일을 단일 문자열로 읽을 수 있습니다. 이는 파일 내용을 한 줄씩 처리하기보다는 전체적으로 처리하려는 경우에 유용합니다.
통사론:
C# 코드 예제
문자열 데이터 = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(fileName)));
예:
Javapackage io; import java.nio.file.*; public class ReadTextAsString { public static String readFileAsString(String fileName) throws Exception { String data = ''; data = new String( Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(fileName))); return data; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.print('Enter the Path : '); // Reading File name String path = br.readLine(); String data = readFileAsString(path); System.out.println(data); } }
산출
 산출 퀴즈 만들기
산출 퀴즈 만들기 