입력 n에 대한 오일러의 Totient 함수 Φ(n)은 {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}에서 n에 상대적으로 소수인 숫자의 개수입니다. 즉, n이 GCD(최대 공약수)인 숫자입니다. 1입니다.
예:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1)은 1입니다.
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2)는 1이지만 gcd(2, 2)는 2입니다.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3)은 1이고 gcd(2, 3)은 1입니다.
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4)는 1이고 gcd(3, 4)는 1입니다.
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5)는 1, gcd(2, 5)는 1,
gcd(3, 5)는 1이고 gcd(4, 5)는 1입니다.
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6)은 1이고 gcd(5, 6)은 1입니다.
권장 연습 오일러 Totient 함수 사용해 보세요!
입력 n에 대해 Φ(n)을 계산하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
ㅏ 간단한 해결책 1부터 n-1까지의 모든 숫자를 반복하고 gcd를 사용하여 n을 1로 사용하여 숫자를 계산합니다. 다음은 입력 정수 n에 대해 오일러의 Totient 함수를 계산하는 간단한 방법의 구현입니다.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>자바 // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>파이썬3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>씨# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>자바스크립트 >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< 산출
파이(1) = 1 파이(2) = 1 파이(3) = 2 파이(4) = 2 파이(5) = 4 파이(6) = 2 파이(7) = 6 파이(8) = 4 파이( 9) = 6파이(10) = 4
긴 문자열 자바
위 코드는 gcd 함수를 O(n)번 호출합니다. gcd 함수의 시간 복잡도는 O(h)입니다. 여기서 h는 주어진 두 숫자 중 더 작은 숫자의 자릿수입니다. 그러므로, 시간 복잡도 위의 해는 O(N^2 log N)입니다. [어떻게 Φ가 최대 Log가 될 수 있습니까?101부터 n까지 모든 숫자에서 n자리]
보조 공간: 오(로그 N)
아래는 더 나은 솔루션 . 이 아이디어는 전체 함수의 값이 n의 곱 전체 소인수 p보다 낮다는 오일러의 곱 공식을 기반으로 합니다.
공식은 기본적으로 Φ(n)의 값이 n의 모든 소인수 p에 대해 (1 – 1/p)의 n 곱셈 부산물과 같다고 말합니다. 예를 들어 Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2의 값입니다.
우리는 다음에서 사용된 아이디어를 사용하여 모든 소인수를 찾을 수 있습니다. 이것 우편.
1) 초기화 : 결과 = n
2) 'p' = 2에서 sqrt(n)까지 루프를 실행하고 모든 'p'에 대해 다음을 수행합니다.
a) p가 n을 나누면,
설정: 결과 = 결과 * (1.0 - (1.0 / (부동) p));
모든 p 항목을 n으로 나눕니다.
3) 결과 반환
아래는 오일러의 곱 공식을 구현한 것입니다.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 return (int)result; } // 드라이버 코드 int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <씨 // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 return (int)result; } // 위 테스트를 위한 드라이버 프로그램 function int main() { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>자바 // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 return (int)result; } // 위 테스트를 위한 드라이버 프로그램 function public static void main(String args[]) { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>파이썬3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : 결과 -= 결과 // n # {1,2,....,n-1} 집합에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. # n이 소수인 경우 return int(result) # 드라이버 range(1, 11)의 n에 대해 위 함수를 테스트하는 프로그램: print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # 이 코드는 # Nikita Tiwari가 기여했습니다.>씨# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 return (int)result; } // 드라이버 코드 public static void Main() { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>자바스크립트 // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 returnparseInt(result); } // 드라이버 코드(let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $결과 -= $결과 / $n; //집합 {1,2,...,n-1}에서 모든 숫자는 n과 상대적으로 소수입니다. //n이 소수인 경우 return intval($result); } // ($n = 1; $n에 대한 드라이버 코드<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> 산출
파이(1) = 1 파이(2) = 1 파이(3) = 2 파이(4) = 2 파이(5) = 4 파이(6) = 2 파이(7) = 6 파이(8) = 4 파이( 9) = 6파이(10) = 4
시간 복잡도: O(Φ n 로그 n)
보조 공간: 오(1)
위의 방법으로 부동 소수점 계산을 피할 수 있습니다. 아이디어는 모든 소인수와 그 배수를 계산하고 n에서 이 수를 빼서 totient 함수 값을 얻는 것입니다(소인수와 소인수의 배수는 gcd를 1로 갖지 않습니다).
1) 결과를 n으로 초기화
2) 모든 숫자 'p'를 고려하십시오(여기서 'p'는 2에서 Φ(n)까지 다양함).
p가 n을 나누면 다음을 수행하십시오.
a) 1에서 n까지 p의 모든 배수를 뺍니다. [p의 모든 배수
n과 함께 1보다 큰 gcd(적어도 p)를 갖게 됩니다.]
b) n을 p로 반복적으로 나누어 n을 업데이트합니다.
3) 감소된 n이 1보다 크면 모든 배수를 제거합니다.
결과에서 n개.
아래는 위의 알고리즘을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; 결과 반환; } // 드라이버 코드 int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>씨 // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; 결과 반환; } // 위 테스트를 위한 드라이버 프로그램 function int main() { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>자바 // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; 결과 반환; } // 드라이버 코드 public static void main (String[] args) { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>파이썬3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): 결과 -= int(결과 / n); 결과 반환; # 범위(1, 11)의 n에 대한 드라이버 코드: print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # 이 코드는 # mits>'>에 의해 기여되었습니다.씨# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= 결과 / n; 결과 반환; } // 드라이버 코드 static public void Main () { int n; (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>자바스크립트 // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 결과 -= parsInt(result / n); 결과 반환; } // 드라이버 코드(let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $결과 -= (int)$결과 / $n; $결과를 반환합니다. } // ($n = 1; $n에 대한 드라이버 코드<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>>
산출 파이(1) = 1 파이(2) = 1 파이(3) = 2 파이(4) = 2 파이(5) = 4 파이(6) = 2 파이(7) = 6 파이(8) = 4 파이( 9) = 6파이(10) = 4
시간 복잡도: O(Φ n 로그 n)
보조 공간: 오(1)
위의 알고리즘을 이해하기 위해 예를 들어 보겠습니다.
자바의 회문
n = 10.
초기화: 결과 = 10
2는 소인수이므로 n = n/i = 5, 결과 = 5
3은 주요 요소가 아닙니다.
4*4가 작거나 같지 않으므로 for 루프는 3 이후에 중지됩니다.
10으로.
for 루프 이후 결과 = 5, n = 5
n> 1이므로 결과 = 결과 - 결과/n = 4
vlc로 YouTube 비디오 다운로드
오일러의 Totient 함수의 몇 가지 흥미로운 속성
1) 에 대한 소수 p ,phi(p) = p – 1
증거 :
2) 을 위한 두 개의 소수 a와 b
증거 :
예:
삼) 을 위한 소수 p ,
스크롤 휠이 작동하지 않습니다
증거 :
예:
4) 을 위한 두 개의 숫자 a와 b
특별한 경우 : gcd(a, b) = 1
예:
특별한 경우 :
5) n의 모든 제수에 대한 전체 함수 값의 합은 n과 같습니다.
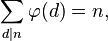
예:
n = 6
요인 = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
긴 문자열 자바
6) 가장 유명하고 중요한 특징은 다음과 같이 표현됩니다. 오일러의 정리 :
정리에 따르면 n과 a가 서로소인 경우
(또는 상대적으로 소수) 양의 정수, 그런 다음
ㅏΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
그만큼 RSA 암호화 시스템 다음 정리에 기초합니다.
m이 소수, 즉 p인 특별한 경우에 오일러의 정리는 소위 다음과 같이 변합니다. 페르마의 작은 정리 :
ㅏp-1Φ 1 (대 p)
7) 모듈로 n 추가에 따른 유한 순환 그룹의 생성기 수는 Φ(n)입니다. .
관련 기사:
n보다 작거나 같은 모든 숫자에 대한 오일러의 Totient 함수
다중 평가를 위해 최적화된 오일러 Totient 함수
참고자료:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
