그만큼 플로이드-워샬 알고리즘 , 제작자의 이름을 따서 명명됨 로버트 플로이드와 스티븐 워샬 는 컴퓨터 과학 및 그래프 이론의 기본 알고리즘입니다. 가중치 그래프에서 모든 노드 쌍 사이의 최단 경로를 찾는 데 사용됩니다. 이 알고리즘은 매우 효율적이며 두 가지 모두를 사용하여 그래프를 처리할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 그리고 n 음의 간선 가중치 , 광범위한 네트워크 및 연결 문제를 해결하기 위한 다목적 도구입니다.
내용의 테이블
- 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘
- Floyd Warshall 알고리즘의 기본 아이디어
- 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘 알고리즘
- 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘의 의사 코드
- 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘의 예시
- Floyd Warshall 알고리즘의 복잡성 분석
- Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘이 희소 그래프가 아닌 조밀 그래프에 더 나은 이유는 무엇입니까?
- Floyd-Warshall과 관련된 중요한 인터뷰 질문
- Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘의 실제 응용
플로이드 워샬 알고리즘:
그만큼 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘 은 모든 쌍 최단 경로 알고리즘과 달리 데이크스트라 그리고 벨먼 포드 이는 단일 소스 최단 경로 알고리즘입니다. 이 알고리즘은 두 가지 모두에 대해 작동합니다. 감독 그리고 무방향 가중 그래프. 그러나 음수 주기(주기의 간선 합이 음수)가 있는 그래프에서는 작동하지 않습니다. 다음과 같다 동적 프로그래밍 모든 노드 쌍 사이의 최단 거리를 계산하기 위해 가능한 모든 노드를 통과하는 모든 가능한 경로를 확인하는 접근 방식입니다.
튜플 파이썬 정렬
Floyd Warshall 알고리즘의 기본 아이디어:
그래프가 있다고 가정하자 G[][] ~와 함께 안에 정점 1 에게 N . 이제 우리는 평가를 해야 합니다. 최단 경로 행렬[][] 어디야? hortestPathMatrix[i][j] 정점 사이의 최단 경로를 나타냅니다. 나 그리고 제이 .
분명히 사이의 최단 경로는 나 에게 제이 좀 있을 거야 케이 중간 노드 수. 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘의 기본 아이디어는 각 정점을 처리하는 것입니다. 1 에게 N 하나씩 중간 노드로 사용됩니다.
다음 그림은 floyd warshall 알고리즘에서 위의 최적 하위 구조 속성을 보여줍니다.
플로이드 워샬 알고리즘 알고리즘:
- 첫 번째 단계로 입력 그래프 행렬과 동일하게 해 행렬을 초기화합니다.
- 그런 다음 모든 정점을 중간 정점으로 간주하여 솔루션 행렬을 업데이트합니다.
- 아이디어는 모든 정점을 하나씩 선택하고 최단 경로의 중간 정점으로 선택한 정점을 포함하는 모든 최단 경로를 업데이트하는 것입니다.
- 정점 번호를 선택할 때 케이 중간 정점으로서 우리는 이미 정점을 고려했습니다. {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} 중간 정점으로.
- 모든 쌍에 대해 (나, 제이) 원본 정점과 대상 정점에는 각각 두 가지 가능한 경우가 있습니다.
- 케이 는 최단 경로의 중간 정점이 아닙니다. 나 에게 제이 . 우리는 가치를 유지합니다 거리[i][j] 그대로.
- 케이 는 에서 최단 경로에 있는 중간 꼭지점입니다. 나 에게 제이 . 우리는 거리[i][j] ~처럼 거리[i][k] + 거리[k][j], 만약에 dist[i][j]> dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]
플로이드 워샬 알고리즘의 의사 코드:>
k = 0 ~ n – 1의 경우
i = 0 ~ n - 1인 경우
j = 0 ~ n - 1인 경우
거리[i, j] = min(거리[i, j], 거리[i, k] + 거리[k, j])여기서 i = 소스 노드, j = 대상 노드, k = 중간 노드
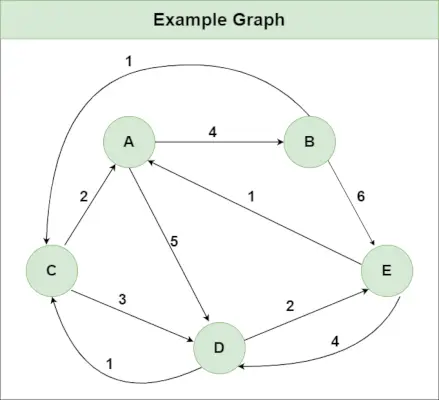
플로이드 워샬 알고리즘의 예시:
추천 연습 시도해 보세요!이미지에 표시된 것과 같은 그래프가 있다고 가정합니다.
1 단계 : Distance[i][j]= 가장자리의 가중치가 되도록 입력 그래프를 사용하여 Distance[][] 행렬을 초기화합니다. 나 에게 제이 , 또한 Distance[i][j] = Infinity(가장자리가 없는 경우) 나 에게 제이.
2 단계 : 노드 처리 ㅏ 중간 노드로 사용하고 다음 공식을 사용하여 모든 {i,j} 노드 쌍에 대해 Distance[][]를 계산합니다.
데이터베이스에 연결 자바= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], (i에서 까지의 거리) ㅏ ) + (로부터의 거리 ㅏ j )))
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], 거리[i][ ㅏ ] + 거리[ ㅏ ][제이])3단계 : 노드 처리 비 중간 노드로 사용하고 다음 공식을 사용하여 모든 {i,j} 노드 쌍에 대해 Distance[][]를 계산합니다.
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], (i에서 까지의 거리) 비 ) + (로부터의 거리 비 j )))
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], 거리[i][ 비 ] + 거리[ 비 ][제이])4단계 : 노드 처리 씨 중간 노드로 사용하고 다음 공식을 사용하여 모든 {i,j} 노드 쌍에 대해 Distance[][]를 계산합니다.
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], (i에서 까지의 거리) 씨 ) + (로부터의 거리 씨 j )))
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], 거리[i][ 씨 ] + 거리[ 씨 ][제이])5단계 : 노드 처리 디 중간 노드로 사용하고 다음 공식을 사용하여 모든 {i,j} 노드 쌍에 대해 Distance[][]를 계산합니다.
mysql 워크벤치를 사용하는 방법= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], (i에서 까지의 거리) 디 ) + (로부터의 거리 디 j )))
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], 거리[i][ 디 ] + 거리[ 디 ][제이])6단계 : 노드 처리 그리고 중간 노드로 사용하고 다음 공식을 사용하여 모든 {i,j} 노드 쌍에 대해 Distance[][]를 계산합니다.
C의 2차원 배열 프로그램= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], (i에서 까지의 거리) 그리고 ) + (로부터의 거리 그리고 j )))
= 거리[i][j] = 최소 (거리[i][j], 거리[i][ 그리고 ] + 거리[ 그리고 ][제이])7단계 : 모든 노드가 중간 노드로 처리되었으므로 이제 업데이트된 Distance[][] 행렬을 응답 행렬로 반환할 수 있습니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // C++ Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm #include using namespace std; // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 4 /* Define Infinite as a large enough value.This value will be used for vertices not connected to each other */ #define INF 99999 // A function to print the solution matrix void printSolution(int dist[][V]); // Solves the all-pairs shortest path // problem using Floyd Warshall algorithm void floydWarshall(int dist[][V]) { int i, j, k; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ----> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination for the // above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path from // i to j, then update the value of // dist[i][j] if (dist[i][j]>(dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]) && (dist[k][j] != INF && dist[i][k] != INF)) dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } // 최단 거리 행렬을 인쇄합니다. printSolution(dist); } /* 솔루션을 인쇄하는 유틸리티 함수 */ void printSolution(int dist[][V]) { cout<< 'The following matrix shows the shortest ' 'distances' ' between every pair of vertices
'; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) cout << 'INF' << ' '; else cout << dist[i][j] << ' '; } cout << endl; } } // Driver's code int main() { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ int 그래프[V][V] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; // 함수 호출 floydWarshall(graph); 0을 반환합니다. } // 이 코드는 Mythri J L이 제공한 것입니다.> 씨 // C Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm #include // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 4 /* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This value will be used for vertices not connected to each other */ #define INF 99999 // A function to print the solution matrix void printSolution(int dist[][V]); // Solves the all-pairs shortest path // problem using Floyd Warshall algorithm void floydWarshall(int dist[][V]) { int i, j, k; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ----> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination for the // above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path from // i to j, then update the value of // dist[i][j] if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution(dist); } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int dist[][V]) { printf( 'The following matrix shows the shortest distances' ' between every pair of vertices
'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) printf('%7s', 'INF'); else printf('%7d', dist[i][j]); } printf('
'); } } // driver's code int main() { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ int 그래프[V][V] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; // 함수 호출 floydWarshall(graph); 0을 반환합니다. }> 자바 // Java program for Floyd Warshall All Pairs Shortest // Path algorithm. import java.io.*; import java.lang.*; import java.util.*; class AllPairShortestPath { final static int INF = 99999, V = 4; void floydWarshall(int dist[][]) { int i, j, k; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ----> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination for the // above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path // from i to j, then update the value of // dist[i][j] if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution(dist); } void printSolution(int dist[][]) { System.out.println( 'The following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices'); for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) System.out.print('INF '); else System.out.print(dist[i][j] + ' '); } System.out.println(); } } // Driver's code public static void main(String[] args) { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ int 그래프[][] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; AllPairShortestPath a = new AllPairShortestPath(); // 함수 호출 a.floydWarshall(graph); } } // 제공: Aakash Hasija> 파이썬3 # Python3 Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm # Number of vertices in the graph V = 4 # Define infinity as the large # enough value. This value will be # used for vertices not connected to each other INF = 99999 # Solves all pair shortest path # via Floyd Warshall Algorithm def floydWarshall(graph): ''' dist[][] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest distances between every pair of vertices ''' ''' initializing the solution matrix same as input graph matrix OR we can say that the initial values of shortest distances are based on shortest paths considering no intermediate vertices ''' dist = list(map(lambda i: list(map(lambda j: j, i)), graph)) ''' Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주합니다. ----> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k} ''' for k in range(V): # 모든 정점을 하나씩 소스로 선택 for i in range(V): # 위에서 선택한 소스에 대한 대상으로 모든 정점을 선택합니다 for j in range(V): # 정점 k가 i에서 j까지 # 최단 경로에 있으면 dist[i][의 값을 업데이트합니다. j] dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] ) printSolution(dist) # 솔루션을 인쇄하는 유틸리티 함수 def printSolution (dist): print('다음 행렬은 모든 정점 쌍 사이의 최단 거리를 보여줍니다') for i in range(V): for j in range(V): if(dist[i][j] == INF): print('%7s' % ('INF'), end=' ') else: print('%7d ' % (dist[i][j]), end=' ') if j == V-1: print() # 드라이버 코드 if __name__ == '__main__': ''' 10 (0)------ ->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 ''' 그래프 = [[0, 5, INF, 10], [INF, 0, 3, INF], [INF, INF, 0 , 1], [INF, INF, INF, 0] ] # 함수 호출 floydWarshall(graph) # 이 코드는 Mythri J L에 의해 제공되었습니다.> 씨# // C# program for Floyd Warshall All // Pairs Shortest Path algorithm. using System; public class AllPairShortestPath { readonly static int INF = 99999, V = 4; void floydWarshall(int[, ] graph) { int[, ] dist = new int[V, V]; int i, j, k; // Initialize the solution matrix // same as input graph matrix // Or we can say the initial // values of shortest distances // are based on shortest paths // considering no intermediate // vertex for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { dist[i, j] = graph[i, j]; } } /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ---> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source // one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest // path from i to j, then update // the value of dist[i][j] if (dist[i, k] + dist[k, j] < dist[i, j]) { dist[i, j] = dist[i, k] + dist[k, j]; } } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution(dist); } void printSolution(int[, ] dist) { Console.WriteLine( 'Following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices'); for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j) { if (dist[i, j] == INF) { Console.Write('INF '); } else { Console.Write(dist[i, j] + ' '); } } Console.WriteLine(); } } // Driver's Code public static void Main(string[] args) { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ int[, ] 그래프 = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0 , 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; AllPairShortestPath a = new AllPairShortestPath(); // 함수 호출 a.floydWarshall(graph); } } // 이 기사는 // Abdul Mateen Mohammed가 기고했습니다.> 자바스크립트 // A JavaScript program for Floyd Warshall All // Pairs Shortest Path algorithm. var INF = 99999; class AllPairShortestPath { constructor() { this.V = 4; } floydWarshall(graph) { var dist = Array.from(Array(this.V), () =>new Array(this.V).fill(0)); var i, j, k; // 해 행렬을 초기화합니다 // 입력 그래프 행렬과 동일합니다 // 또는 // 최단 거리의 초기 값은 // 최단 경로를 기반으로 한다고 말할 수 있습니다. // 중간 요소를 고려하지 않습니다. // (i = 0; i에 대한 정점)< this.V; i++) { for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) { dist[i][j] = graph[i][j]; } } /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ---> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for (k = 0; k< this.V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source // one by one for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest // path from i to j, then update // the value of dist[i][j] if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) { dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix this.printSolution(dist); } printSolution(dist) { document.write( 'Following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices ' ); for (var i = 0; i < this.V; ++i) { for (var j = 0; j < this.V; ++j) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) { document.write(' INF '); } else { document.write(' ' + dist[i][j] + ' '); } } document.write(' '); } } } // Driver Code /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ var 그래프 = [ [0, 5, INF, 10], [INF, 0, 3, INF], [INF, INF, 0, 1] , [INF, INF, INF, 0], ]; var a = new AllPairShortestPath(); // 솔루션 인쇄 a.floydWarshall(graph); // 이 코드는 rdtaank에 의해 제공되었습니다.> PHP // PHP Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm // Solves the all-pairs shortest path problem // using Floyd Warshall algorithm function floydWarshall ($graph, $V, $INF) { /* dist[][] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest distances between every pair of vertices */ $dist = array(array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0)); /* Initialize the solution matrix same as input graph matrix. Or we can say the initial values of shortest distances are based on shortest paths considering no intermediate vertex. */ for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) $dist[$i][$j] = $graph[$i][$j]; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->반복을 시작하기 전에 모든 정점 쌍 사이에 최단 거리가 있으므로 최단 거리는 집합 {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}의 정점만 중간 정점으로 간주됩니다. ----> 반복 종료 후 정점 번호. k는 중간 정점 집합에 추가되고 집합은 {0, 1, 2, .. k}가 됩니다. */ for ($k = 0; $k< $V; $k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path from // i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j] if ($dist[$i][$k] + $dist[$k][$j] < $dist[$i][$j]) $dist[$i][$j] = $dist[$i][$k] + $dist[$k][$j]; } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution($dist, $V, $INF); } /* A utility function to print solution */ function printSolution($dist, $V, $INF) { echo 'The following matrix shows the ' . 'shortest distances between ' . 'every pair of vertices
'; for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) { if ($dist[$i][$j] == $INF) echo 'INF ' ; else echo $dist[$i][$j], ' '; } echo '
'; } } // Drivers' Code // Number of vertices in the graph $V = 4 ; /* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This value will be used for vertices not connected to each other */ $INF = 99999 ; /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------->(2) 3 */ $graph = array(array(0, 5, $INF, 10), array($INF, 0, 3, $INF), array($ INF, $INF, 0, 1), 배열($INF, $INF, $INF, 0)); // 함수 호출 floydWarshall($graph, $V, $INF); // 이 코드는 Ryuga가 제공한 것입니다. ?>> 산출
The following matrix shows the shortest distances between every pair of vertices 0 5 8 9 INF 0 3 4 INF INF 0 1 INF INF INF 0>
Floyd Warshall 알고리즘의 복잡성 분석:
- 시간 복잡도: 오(V삼), 여기서 V는 그래프의 정점 수이고 각각 크기가 V인 세 개의 중첩 루프를 실행합니다.
- 보조 공간: 오(V2), 각 노드 쌍의 최단 거리를 저장하기 위해 2차원 행렬을 생성합니다.
메모 : 위 프로그램은 최단 거리만 인쇄합니다. 별도의 2D 매트릭스에 선행 정보를 저장하여 최단 경로를 인쇄하도록 솔루션을 수정할 수도 있습니다.
Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘이 희소 그래프가 아닌 조밀 그래프에 더 나은 이유는 무엇입니까?
조밀한 그래프 : 꼭짓점의 수에 비해 변의 수가 현저히 많은 그래프.
희소 그래프 : 간선의 개수가 매우 적은 그래프입니다.그래프에 얼마나 많은 간선이 있더라도 플로이드 워샬 알고리즘 O(V삼) 번 따라서 가장 적합합니다. 조밀한 그래프 . 희소 그래프의 경우, 존슨의 알고리즘 더 적합합니다.
Floyd-Warshall과 관련된 중요한 인터뷰 질문:
- Floyd Warshall 알고리즘을 사용하여 그래프에서 음의 순환을 감지하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- Floyd-warshall 알고리즘은 Dijkstra 알고리즘과 어떻게 다른가요?
- Floyd-warshall 알고리즘은 Bellman-Ford 알고리즘과 어떻게 다릅니까?
Floyd-Warshall 알고리즘의 실제 적용:
- 컴퓨터 네트워킹에서 이 알고리즘은 네트워크의 모든 노드 쌍 사이의 최단 경로를 찾는 데 사용될 수 있습니다. 이는 다음과 같이 불린다. 네트워크 라우팅 .
- 비행 연결성 항공 산업에서는 공항 간 최단 경로를 찾습니다.
- GIS ( 지리정보시스템 ) 애플리케이션에는 도로 네트워크와 같은 공간 데이터를 분석하여 위치 간 최단 경로를 찾는 경우가 많습니다.
- Kleene의 알고리즘 Floyd Warshall을 일반화한 것으로, 정규 언어에 대한 정규 표현을 찾는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.







