전제 조건: 배열과 마찬가지로 Linked List는 선형 데이터 구조입니다. 배열과 달리 연결리스트의 요소는 인접한 위치에 저장되지 않으며, 아래 그림과 같이 포인터를 사용하여 요소를 연결합니다.
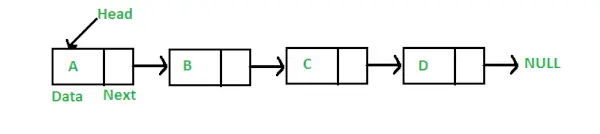
Java에서 LinkedList는 클래스로 표현되고 노드는 별도의 클래스로 표현될 수 있습니다. LinkedList 클래스에는 Node 클래스 유형의 참조가 포함되어 있습니다.
자바
class> LinkedList {> >Node head;>// head of list> >/* Linked list Node*/> >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node next;> >// Constructor to create a new node> >// Next is by default initialized> >// as null> >Node(>int> d) { data = d; }> >}> }> |
>
>
생성 및 삽입:
이 기사에서는 목록 삽입이 마지막에 수행됩니다. 즉, 주어진 연결 목록의 마지막 노드 뒤에 새 노드가 추가됩니다. 예를 들어 주어진 Linked List가 5->10->15->20->25이고 30을 삽입한다면 Linked List는 5->10->15->20->25->30이 됩니다. .
Linked List는 일반적으로 헤드 포인터로 표시되므로 마지막 노드까지 목록을 순회한 다음 마지막 노드 바로 옆을 새 노드로 변경해야 합니다.

구현:
자바
import> java.io.*;> > // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> > >Node head;>// head of list> > >// Linked list Node.> >// This inner class is made static> >// so that main() can access it> >static> class> Node {> > >int> data;> >Node next;> > >// Constructor> >Node(>int> d)> >{> >data = d;> >next =>null>;> >}> >}> > >// Method to insert a new node> >public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,>int> data)> >{> >// Create a new node with given data> >Node new_node =>new> Node(data);> > > >// If the Linked List is empty,> >// then make the new node as head> >if> (list.head ==>null>) {> >list.head = new_node;> >}> >else> {> >// Else traverse till the last node> >// and insert the new_node there> >Node last = list.head;> >while> (last.next !=>null>) {> >last = last.next;> >}> > >// Insert the new_node at last node> >last.next = new_node;> >}> > >// Return the list by head> >return> list;> >}> > >// Method to print the LinkedList.> >public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> >{> >Node currNode = list.head;> > >System.out.print(>'LinkedList: '>);> > >// Traverse through the LinkedList> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Print the data at current node> >System.out.print(currNode.data +>' '>);> > >// Go to next node> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >}> > >// Driver code> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >/* Start with the empty list. */> >LinkedList list =>new> LinkedList();> > >//> >// ******INSERTION******> >//> > >// Insert the values> >list = insert(list,>1>);> >list = insert(list,>2>);> >list = insert(list,>3>);> >list = insert(list,>4>);> >list = insert(list,>5>);> >list = insert(list,>6>);> >list = insert(list,>7>);> >list = insert(list,>8>);> > >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8>
순회: 순회를 위해 아래에는 헤드 노드에서 마지막 노드까지 목록을 순회하여 주어진 목록을 인쇄하는 범용 함수 printList()가 있습니다.
구현:
자바
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> >Node head;>// head of list> >// Linked list Node.> >// Node is a static nested class> >// so main() can access it> >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node next;> >// Constructor> >Node(>int> d)> >{> >data = d;> >next =>null>;> >}> >}> >// Method to insert a new node> >public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> >int> data)> >{> >// Create a new node with given data> >Node new_node =>new> Node(data);> >new_node.next =>null>;> >// If the Linked List is empty,> >// then make the new node as head> >if> (list.head ==>null>) {> >list.head = new_node;> >}> >else> {> >// Else traverse till the last node> >// and insert the new_node there> >Node last = list.head;> >while> (last.next !=>null>) {> >last = last.next;> >}> >// Insert the new_node at last node> >last.next = new_node;> >}> >// Return the list by head> >return> list;> >}> >// Method to print the LinkedList.> >public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> >{> >Node currNode = list.head;> >System.out.print(>'LinkedList: '>);> >// Traverse through the LinkedList> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Print the data at current node> >System.out.print(currNode.data +>' '>);> >// Go to next node> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >}> >// **************MAIN METHOD**************> >// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >/* Start with the empty list. */> >LinkedList list =>new> LinkedList();> >//> >// ******INSERTION******> >//> >// Insert the values> >list = insert(list,>1>);> >list = insert(list,>2>);> >list = insert(list,>3>);> >list = insert(list,>4>);> >list = insert(list,>5>);> >list = insert(list,>6>);> >list = insert(list,>7>);> >list = insert(list,>8>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8>
KEY로 삭제:
삭제 프로세스는 다음과 같이 이해될 수 있습니다.
수행 할:
'key'가 주어지면 연결된 목록에서 이 키가 처음 나타나는 것을 삭제합니다. .
방법:
연결된 목록에서 노드를 삭제하려면 다음 단계를 수행하십시오.
- 목록에서 처음 나타나는 키를 검색하세요.
- 이제 다음 세 가지 조건 중 하나가 있을 수 있습니다.
- 사례 1: 열쇠는 다음 위치에서 발견됩니다. 머리
- 이 경우 노드의 헤드를 현재 헤드의 다음 노드로 변경합니다.
- 교체된 헤드 노드의 메모리를 해제합니다.
- 사례 2: 키는 중간이나 마지막에서 발견됩니다. 머리
- 이 경우 삭제할 노드의 이전 노드를 찾으세요.
- 다음 이전 노드를 현재 노드의 다음 노드로 변경합니다.
- 교체된 노드의 메모리를 해제합니다.
- 사례 3: 목록에서 키를 찾을 수 없습니다.
- 이 경우 아무런 작업도 수행할 필요가 없습니다.

구현:
자바
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> >Node head;>// head of list> >// Linked list Node.> >// Node is a static nested class> >// so main() can access it> >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node next;> >// Constructor> >Node(>int> d)> >{> >data = d;> >next =>null>;> >}> >}> >// Method to insert a new node> >public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> >int> data)> >{> >// Create a new node with given data> >Node new_node =>new> Node(data);> >new_node.next =>null>;> >// If the Linked List is empty,> >// then make the new node as head> >if> (list.head ==>null>) {> >list.head = new_node;> >}> >else> {> >// Else traverse till the last node> >// and insert the new_node there> >Node last = list.head;> >while> (last.next !=>null>) {> >last = last.next;> >}> >// Insert the new_node at last node> >last.next = new_node;> >}> >// Return the list by head> >return> list;> >}> >// Method to print the LinkedList.> >public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> >{> >Node currNode = list.head;> >System.out.print(>'LinkedList: '>);> >// Traverse through the LinkedList> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Print the data at current node> >System.out.print(currNode.data +>' '>);> >// Go to next node> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >System.out.println();> >}> >// **************DELETION BY KEY**************> >// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY> >public> static> LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,> >int> key)> >{> >// Store head node> >Node currNode = list.head, prev =>null>;> >//> >// CASE 1:> >// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted> >if> (currNode !=>null> && currNode.data == key) {> >list.head = currNode.next;>// Changed head> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' found and deleted'>);> >// Return the updated List> >return> list;> >}> >//> >// CASE 2:> >// If the key is somewhere other than at head> >//> >// Search for the key to be deleted,> >// keep track of the previous node> >// as it is needed to change currNode.next> >while> (currNode !=>null> && currNode.data != key) {> >// If currNode does not hold key> >// continue to next node> >prev = currNode;> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >// If the key was present, it should be at currNode> >// Therefore the currNode shall not be null> >if> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Since the key is at currNode> >// Unlink currNode from linked list> >prev.next = currNode.next;> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' found and deleted'>);> >}> >//> >// CASE 3: The key is not present> >//> >// If key was not present in linked list> >// currNode should be null> >if> (currNode ==>null>) {> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' not found'>);> >}> >// return the List> >return> list;> >}> >// **************MAIN METHOD**************> >// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >/* Start with the empty list. */> >LinkedList list =>new> LinkedList();> >//> >// ******INSERTION******> >//> >// Insert the values> >list = insert(list,>1>);> >list = insert(list,>2>);> >list = insert(list,>3>);> >list = insert(list,>4>);> >list = insert(list,>5>);> >list = insert(list,>6>);> >list = insert(list,>7>);> >list = insert(list,>8>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >//> >// ******DELETION BY KEY******> >//> >// Delete node with value 1> >// In this case the key is ***at head***> >deleteByKey(list,>1>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node with value 4> >// In this case the key is present ***in the> >// middle***> >deleteByKey(list,>4>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node with value 10> >// In this case the key is ***not present***> >deleteByKey(list,>10>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8>
위치에서 삭제:
이 삭제 프로세스는 다음과 같이 이해될 수 있습니다.
수행 할:
주어진 '위치' , 연결리스트에서 이 위치의 노드를 삭제합니다. .
방법:
이를 수행하는 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
- 노드의 인덱스를 세어 목록을 탐색합니다.
- 각 인덱스에 대해 인덱스를 위치와 동일하게 일치시킵니다.
- 이제 다음 세 가지 조건 중 하나가 있을 수 있습니다.
- 사례 1: 위치가 0입니다. 즉, 머리가 삭제됩니다.
- 이 경우 노드의 헤드를 현재 헤드의 다음 노드로 변경합니다.
- 교체된 헤드 노드의 메모리를 해제합니다.
- 사례 2: 위치가 0보다 크지만 목록 크기보다 작습니다. 즉, 머리 부분을 제외하고 중간이나 마지막에 있습니다.
- 이 경우 삭제할 노드의 이전 노드를 찾습니다.
- 이전 노드의 다음 노드를 현재 노드의 다음 노드로 변경합니다.
- 교체된 노드의 메모리를 해제합니다.
- 사례 3: 위치가 목록 크기보다 큽니다. 즉, 목록에서 위치를 찾을 수 없습니다.
- 이 경우 아무런 작업도 수행할 필요가 없습니다.

구현:
자바
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> >Node head;>// head of list> >// Linked list Node.> >// Node is a static nested class> >// so main() can access it> >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node next;> >// Constructor> >Node(>int> d)> >{> >data = d;> >next =>null>;> >}> >}> >// Method to insert a new node> >public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> >int> data)> >{> >// Create a new node with given data> >Node new_node =>new> Node(data);> >new_node.next =>null>;> >// If the Linked List is empty,> >// then make the new node as head> >if> (list.head ==>null>) {> >list.head = new_node;> >}> >else> {> >// Else traverse till the last node> >// and insert the new_node there> >Node last = list.head;> >while> (last.next !=>null>) {> >last = last.next;> >}> >// Insert the new_node at last node> >last.next = new_node;> >}> >// Return the list by head> >return> list;> >}> >// Method to print the LinkedList.> >public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> >{> >Node currNode = list.head;> >System.out.print(>'LinkedList: '>);> >// Traverse through the LinkedList> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Print the data at current node> >System.out.print(currNode.data +>' '>);> >// Go to next node> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >System.out.println();> >}> >// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION> >public> static> LinkedList> >deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list,>int> index)> >{> >// Store head node> >Node currNode = list.head, prev =>null>;> >//> >// CASE 1:> >// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be> >// deleted> >if> (index ==>0> && currNode !=>null>) {> >list.head = currNode.next;>// Changed head> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element deleted'>);> >// Return the updated List> >return> list;> >}> >//> >// CASE 2:> >// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the> >// size of LinkedList> >//> >// The counter> >int> counter =>0>;> >// Count for the index to be deleted,> >// keep track of the previous node> >// as it is needed to change currNode.next> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >if> (counter == index) {> >// Since the currNode is the required> >// position Unlink currNode from linked list> >prev.next = currNode.next;> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element deleted'>);> >break>;> >}> >else> {> >// If current position is not the index> >// continue to next node> >prev = currNode;> >currNode = currNode.next;> >counter++;> >}> >}> >// If the position element was found, it should be> >// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be> >// null> >//> >// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the> >// LinkedList> >//> >// In this case, the currNode should be null> >if> (currNode ==>null>) {> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element not found'>);> >}> >// return the List> >return> list;> >}> >// **************MAIN METHOD**************> >// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >/* Start with the empty list. */> >LinkedList list =>new> LinkedList();> >//> >// ******INSERTION******> >//> >// Insert the values> >list = insert(list,>1>);> >list = insert(list,>2>);> >list = insert(list,>3>);> >list = insert(list,>4>);> >list = insert(list,>5>);> >list = insert(list,>6>);> >list = insert(list,>7>);> >list = insert(list,>8>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >//> >// ******DELETION AT POSITION******> >//> >// Delete node at position 0> >// In this case the key is ***at head***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>0>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node at position 2> >// In this case the key is present ***in the> >// middle***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>2>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node at position 10> >// In this case the key is ***not present***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>10>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 0 position element deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 position element deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 position element not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8>
모든 작업:
다음은 각 작업을 함께 적용하는 전체 프로그램입니다.
자바
import> java.io.*;> // Java program to implement> // a Singly Linked List> public> class> LinkedList {> >Node head;>// head of list> >// Linked list Node.> >// Node is a static nested class> >// so main() can access it> >static> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node next;> >// Constructor> >Node(>int> d)> >{> >data = d;> >next =>null>;> >}> >}> >// **************INSERTION**************> >// Method to insert a new node> >public> static> LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,> >int> data)> >{> >// Create a new node with given data> >Node new_node =>new> Node(data);> >new_node.next =>null>;> >// If the Linked List is empty,> >// then make the new node as head> >if> (list.head ==>null>) {> >list.head = new_node;> >}> >else> {> >// Else traverse till the last node> >// and insert the new_node there> >Node last = list.head;> >while> (last.next !=>null>) {> >last = last.next;> >}> >// Insert the new_node at last node> >last.next = new_node;> >}> >// Return the list by head> >return> list;> >}> >// **************TRAVERSAL**************> >// Method to print the LinkedList.> >public> static> void> printList(LinkedList list)> >{> >Node currNode = list.head;> >System.out.print(>'
LinkedList: '>);> >// Traverse through the LinkedList> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Print the data at current node> >System.out.print(currNode.data +>' '>);> >// Go to next node> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >System.out.println(>'
'>);> >}> >// **************DELETION BY KEY**************> >// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY> >public> static> LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,> >int> key)> >{> >// Store head node> >Node currNode = list.head, prev =>null>;> >//> >// CASE 1:> >// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted> >if> (currNode !=>null> && currNode.data == key) {> >list.head = currNode.next;>// Changed head> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' found and deleted'>);> >// Return the updated List> >return> list;> >}> >//> >// CASE 2:> >// If the key is somewhere other than at head> >//> >// Search for the key to be deleted,> >// keep track of the previous node> >// as it is needed to change currNode.next> >while> (currNode !=>null> && currNode.data != key) {> >// If currNode does not hold key> >// continue to next node> >prev = currNode;> >currNode = currNode.next;> >}> >// If the key was present, it should be at currNode> >// Therefore the currNode shall not be null> >if> (currNode !=>null>) {> >// Since the key is at currNode> >// Unlink currNode from linked list> >prev.next = currNode.next;> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' found and deleted'>);> >}> >//> >// CASE 3: The key is not present> >//> >// If key was not present in linked list> >// currNode should be null> >if> (currNode ==>null>) {> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(key +>' not found'>);> >}> >// return the List> >return> list;> >}> >// **************DELETION AT A POSITION**************> >// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION> >public> static> LinkedList> >deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list,>int> index)> >{> >// Store head node> >Node currNode = list.head, prev =>null>;> >//> >// CASE 1:> >// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be> >// deleted> >if> (index ==>0> && currNode !=>null>) {> >list.head = currNode.next;>// Changed head> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element deleted'>);> >// Return the updated List> >return> list;> >}> >//> >// CASE 2:> >// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the> >// size of LinkedList> >//> >// The counter> >int> counter =>0>;> >// Count for the index to be deleted,> >// keep track of the previous node> >// as it is needed to change currNode.next> >while> (currNode !=>null>) {> >if> (counter == index) {> >// Since the currNode is the required> >// position Unlink currNode from linked list> >prev.next = currNode.next;> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element deleted'>);> >break>;> >}> >else> {> >// If current position is not the index> >// continue to next node> >prev = currNode;> >currNode = currNode.next;> >counter++;> >}> >}> >// If the position element was found, it should be> >// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be> >// null> >//> >// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the> >// LinkedList> >//> >// In this case, the currNode should be null> >if> (currNode ==>null>) {> >// Display the message> >System.out.println(> >index +>' position element not found'>);> >}> >// return the List> >return> list;> >}> >// **************MAIN METHOD**************> >// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >/* Start with the empty list. */> >LinkedList list =>new> LinkedList();> >//> >// ******INSERTION******> >//> >// Insert the values> >list = insert(list,>1>);> >list = insert(list,>2>);> >list = insert(list,>3>);> >list = insert(list,>4>);> >list = insert(list,>5>);> >list = insert(list,>6>);> >list = insert(list,>7>);> >list = insert(list,>8>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >//> >// ******DELETION BY KEY******> >//> >// Delete node with value 1> >// In this case the key is ***at head***> >deleteByKey(list,>1>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node with value 4> >// In this case the key is present ***in the> >// middle***> >deleteByKey(list,>4>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node with value 10> >// In this case the key is ***not present***> >deleteByKey(list,>10>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >//> >// ******DELETION AT POSITION******> >//> >// Delete node at position 0> >// In this case the key is ***at head***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>0>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node at position 2> >// In this case the key is present ***in the> >// middle***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>2>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >// Delete node at position 10> >// In this case the key is ***not present***> >deleteAtPosition(list,>10>);> >// Print the LinkedList> >printList(list);> >}> }> |
>
우분투 빌드 필수사항
>산출
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 found and deleted LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 not found LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8 0 position element deleted LinkedList: 3 5 6 7 8 2 position element deleted LinkedList: 3 5 7 8 10 position element not found LinkedList: 3 5 7 8>
