AVL 트리:
AVL 트리는 자체 균형 이진 검색 트리( BST ) 왼쪽과 오른쪽 하위 트리의 높이 차이는 다음보다 클 수 없습니다. 하나 모든 노드에 대해.
삽입 정렬
AVL 트리의 예:
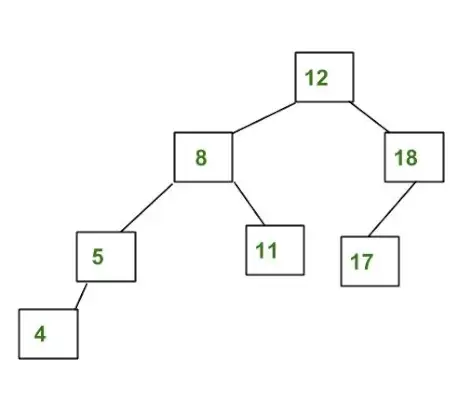
위 트리는 모든 노드의 왼쪽 하위 트리와 오른쪽 하위 트리의 높이 차이가 1보다 작거나 같기 때문에 AVL입니다.
AVL 트리가 아닌 트리의 예:

위 트리는 8과 12에 대한 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 하위 트리의 높이 차이가 1보다 크기 때문에 AVL이 아닙니다.
왜 AVL 트리인가?
대부분의 BST 작업(예: 검색, 최대값, 최소값, 삽입, 삭제 등)에는 오) 시간은 어디에 시간 BST의 높이입니다. 이러한 작업의 비용은 다음과 같습니다. 에) 한 동안 왜곡된 이진 트리 . 나무의 높이가 그대로 유지되는지 확인하면 O(로그(n)) 모든 삽입 및 삭제 후에는 다음의 상한을 보장할 수 있습니다. O(로그(n)) 이 모든 작업에 대해. AVL 트리의 높이는 항상 O(로그(n)) 어디 N 트리의 노드 수입니다.
삽입 AVL 트리에서:
삽입할 때마다 주어진 트리가 AVL로 유지되도록 하려면 표준 BST 삽입 작업을 강화하여 일부 재조정을 수행해야 합니다.
다음은 BST 속성을 위반하지 않고 BST 균형을 맞추기 위해 수행할 수 있는 두 가지 기본 작업입니다(키(왼쪽)
- 왼쪽 회전
- 오른쪽 회전
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 및 / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>권장 연습 AVL 트리 삽입 시도해 보세요!
삽입을 위해 따라야 할 단계:
새로 삽입된 노드를 ~ 안에
- 표준 수행 BST 삽입하다 ~ 안에 .
- 에서 시작 ~ 안에 , 위로 올라가서 첫 번째를 찾으세요 불균형 노드 . 허락하다 와 함께 첫 번째 불균형 노드가 되고, 그리고 될 어린이 ~의 와 함께 그 길로 오는 길은 ~ 안에 에게 와 함께 그리고 엑스 될 손자 ~의 와 함께 그 길로 오는 길은 ~ 안에 에게 와 함께 .
- 루트가 있는 하위 트리에 적절한 회전을 수행하여 트리의 균형을 재조정합니다. 와 함께. 다음과 같이 처리해야 하는 4가지 경우가 있을 수 있습니다. x,y 그리고 와 함께 4가지로 정리할 수 있다.
- 가능한 4가지 배열은 다음과 같습니다.
- y는 z의 왼쪽 자식이고 x는 y의 왼쪽 자식입니다(왼쪽 왼쪽 케이스).
- y는 z의 왼쪽 자식이고 x는 y의 오른쪽 자식입니다(왼쪽 오른쪽 케이스).
- y는 z의 오른쪽 자식이고 x는 y의 오른쪽 자식입니다(오른쪽 오른쪽 사례).
- y는 z의 오른쪽 자식이고 x는 y의 왼쪽 자식입니다(오른쪽 왼쪽 케이스).
위에서 언급한 4가지 경우에 수행할 작업은 다음과 같습니다. 모든 경우에 우리는 단지 재균형 루트가 있는 하위 트리 와 함께 그리고 전체 트리는 뿌리를 둔 하위 트리의 높이(적절한 회전 후)에 따라 균형을 이룹니다. 와 함께 삽입 전과 동일해집니다.
1. 왼쪽 왼쪽 케이스
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. 왼쪽 오른쪽 케이스
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. 오른쪽 오른쪽 사례
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. 오른쪽 왼쪽 케이스
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
AVL 트리에 삽입하는 그림





접근하다:
아이디어는 재귀 BST 삽입을 사용하는 것입니다. 삽입 후 상향식 방식으로 모든 조상에 대한 포인터를 하나씩 얻습니다. 따라서 위로 이동하기 위해 부모 포인터가 필요하지 않습니다. 재귀 코드 자체는 위로 이동하여 새로 삽입된 노드의 모든 조상을 방문합니다.
아이디어를 구현하려면 아래에 언급된 단계를 따르세요.
- 정상적인 수행 BST 삽입.
- 현재 노드는 새로 삽입된 노드의 조상 중 하나여야 합니다. 업데이트 키 현재 노드의.
- 균형 요소를 얻으십시오 (왼쪽 하위 트리 높이 – 오른쪽 하위 트리 높이) 현재 노드의.
- 균형 요소가 다음보다 큰 경우 1, 그러면 현재 노드는 불균형 상태이고 우리는 왼쪽 왼쪽 케이스 또는 왼쪽 오른쪽 케이스 . 있는지 확인하려면 왼쪽 왼쪽 케이스 여부에 관계없이 새로 삽입된 키를 왼쪽 하위 트리 루트 .
- 균형 요소가 다음보다 작은 경우 -1 , 현재 노드는 불균형이며 오른쪽 오른쪽 케이스 또는 오른쪽-왼쪽 케이스에 있습니다. Right Right 케이스인지 확인하려면 새로 삽입된 키를 오른쪽 하위 트리 루트에 있는 키와 비교하세요.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->키;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>비)? a : b;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->열쇠 = 열쇠;> >node->왼쪽 = NULL;> >node->오른쪽 = NULL;> >node->높이 = 1;>// new node is initially> >// added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->왼쪽;> >Node *T2 = x->오른쪽;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->오른쪽 = y;> >y->왼쪽 = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y->높이 = 최대(높이(y->왼쪽),> >height(y->오른쪽)) + 1;> >x->높이 = 최대(높이(x->왼쪽),> >height(x->오른쪽)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->오른쪽;> >Node *T2 = y->왼쪽;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->왼쪽 = x;> >x->오른쪽 = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x->높이 = 최대(높이(x->왼쪽),> >height(x->오른쪽)) + 1;> >y->높이 = 최대(높이(y->왼쪽),> >height(y->오른쪽)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->왼쪽) - 높이(N->오른쪽);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(노드->왼쪽, 키);> >else> if> (key>노드->키)> >node->right = insert(노드->오른쪽, 키);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->높이 = 1 + 최대(높이(노드->왼쪽),> >height(node->오른쪽));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && 키 왼쪽->키)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->오른쪽->키)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && 키> 노드->왼쪽->키)> >{> >node->left = leftRotate(노드->왼쪽);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->키)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(노드->오른쪽);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->왼쪽); preOrder(루트->오른쪽); } } // 드라이버 코드 int main() { Node *root = NULL; /* 위 그림에 주어진 트리 구성 */ root = insert(root, 10); 루트 = 삽입(루트, 20); 루트 = 삽입(루트, 30); 루트 = 삽입(루트, 40); 루트 = 삽입(루트, 50); 루트 = 삽입(루트, 25); /* 구성된 AVL 트리는 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
씨
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->키;> }> > // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>비)? a : b;> }> > /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->열쇠 = 열쇠;> >node->왼쪽 = NULL;> >node->오른쪽 = NULL;> >node->높이 = 1;>// new node is initially added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->왼쪽;> >struct> Node *T2 = x->오른쪽;> > >// Perform rotation> >x->오른쪽 = y;> >y->왼쪽 = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y->높이 = 최대(높이(y->왼쪽),> >height(y->오른쪽)) + 1;> >x->높이 = 최대(높이(x->왼쪽),> >height(x->오른쪽)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->오른쪽;> >struct> Node *T2 = y->왼쪽;> > >// Perform rotation> >y->왼쪽 = x;> >x->오른쪽 = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x->높이 = 최대(높이(x->왼쪽),> >height(x->오른쪽)) + 1;> >y->높이 = 최대(높이(y->왼쪽),> >height(y->오른쪽)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->왼쪽) - 높이(N->오른쪽);> }> > // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->left = insert(노드->왼쪽, 키);> >else> if> (key>노드->키)> >node->right = insert(노드->오른쪽, 키);> >else> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->높이 = 1 + 최대(높이(노드->왼쪽),> >height(node->오른쪽));> > >/* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && 키 왼쪽->키)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->오른쪽->키)> >return> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && 키> 노드->왼쪽->키)> >{> >node->left = leftRotate(노드->왼쪽);> >return> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->키)> >{> >node->right = rightRotate(노드->오른쪽);> >return> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->열쇠);> >preOrder(root->왼쪽);> >preOrder(root->오른쪽);> >}> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
자바
자바에서 문자를 문자열로 변환
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>비) ? a : b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, 키); else // 중복 키는 허용되지 않습니다. return node; /* 2. 이 조상 노드의 높이 업데이트 */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. 이 조상 노드의 균형 요소를 가져와 이 노드가 불균형이 되었는지 확인합니다. */ int Balance = getBalance(node); // 이 노드의 균형이 맞지 않으면 // 4가지 경우가 있습니다. Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance<-1 && key>node.right.key) return leftRotate(node); // 왼쪽 오른쪽 Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(노드); } // 오른쪽 왼쪽 케이스 if (균형<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
파이썬3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 및 키 반환 self.rightRotate(root) # 사례 2 - 오른쪽 균형이 맞으면 오른쪽<-1 and key>root.right.val: return self.leftRotate(root) # 사례 3 - 왼쪽 오른쪽 if 균형> 1이고 키> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root ) # 사례 4 - 균형이 맞으면 오른쪽 왼쪽<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
씨#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>비) ? a : b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = insert(node.right, 키); else // 중복 키는 허용되지 않습니다. return node; /* 2. 이 조상 노드의 높이 업데이트 */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. 이 조상 노드의 균형 요소를 가져와 이 노드가 불균형이 되었는지 확인합니다. */ int Balance = getBalance(node); // 이 노드가 불균형이 되면 // 4가지 경우가 있습니다. Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return leftRotate(node) ; // 왼쪽 오른쪽 케이스 if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left) return rightRotate(node) } // 오른쪽 왼쪽 케이스 if (balance<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
자바스크립트
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>비? a : b;> >}> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>node.key) node.right = this.insert(node.right, key); // 중복 키는 허용되지 않습니다. 그렇지 않으면 노드를 반환합니다. /* 2. 이 조상 노드의 높이 업데이트 */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(node.left), this.height(node.right)); /* 3. 이 조상 노드의 균형 요소를 가져와 이 노드가 불균형이 되었는지 확인합니다. */ var Balance = this.getBalance(node); // 이 노드가 불균형이 되면 // 4가지 경우가 있습니다. Left Left Case if (balance> 1 && key return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) return this. leftRotate(node); // 왼쪽 오른쪽 Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left) return this.rightRotate(node); 왼쪽 케이스 if(잔고<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root);> |
>
>산출
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
복잡성 분석
시간 복잡도: O(log(n)), 삽입용
보조 공간: 오(1)
회전 작업(왼쪽 및 오른쪽 회전)에는 몇 개의 포인터만 변경되므로 일정한 시간이 걸립니다. 높이를 업데이트하고 균형 요소를 얻는 데에도 일정한 시간이 걸립니다. 따라서 AVL 삽입의 시간 복잡도는 O(h)인 BST 삽입과 동일하게 유지됩니다. 여기서 h는 트리의 높이입니다. AVL 트리는 균형을 이루므로 높이는 O(Logn)입니다. 따라서 AVL 삽입의 시간 복잡도는 O(Logn)입니다.
레드 블랙 트리와의 비교:
AVL 트리 및 Red Black과 같은 기타 자체 균형 검색 트리는 모든 기본 작업을 O(log n) 시간 내에 완료하는 데 유용합니다. AVL 트리는 Red-Black 트리에 비해 균형이 더 잘 잡혀 있지만 삽입 및 삭제 중에 더 많은 회전이 발생할 수 있습니다. 따라서 애플리케이션에 삽입과 삭제가 자주 발생하는 경우 Red Black 트리가 선호됩니다. 그리고 삽입과 삭제가 덜 빈번하고 검색이 더 자주 수행된다면 AVL 트리가 Red Black Tree보다 선호되어야 합니다.
다음은 AVL Tree 삭제 대상 게시물입니다.
AVL 트리 | 세트 2(삭제)
