순환 연결 리스트란 무엇입니까?
그만큼 순환 연결 리스트 모든 노드가 연결되어 원을 이루는 연결리스트입니다. 순환 연결 리스트에서는 첫 번째 노드와 마지막 노드가 서로 연결되어 원을 형성합니다. 끝에 NULL이 없습니다.
순환 연결 리스트
일반적으로 순환 연결 목록에는 두 가지 유형이 있습니다.
- 순환형 단일 연결 리스트: 순환 단일 연결 목록에서 목록의 마지막 노드에는 목록의 첫 번째 노드에 대한 포인터가 포함됩니다. 우리가 시작한 동일한 노드에 도달할 때까지 순환 단일 연결 리스트를 탐색합니다. 순환형 단일 연결 리스트에는 시작이나 끝이 없습니다. 노드의 다음 부분에는 null 값이 없습니다.
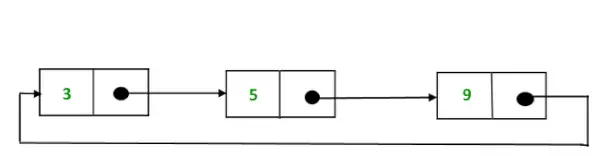
원형 단일 연결 리스트 표현
땅콩 대 땅콩
- 순환 이중 연결 리스트: 순환 이중 연결 리스트(Circular Double Linked List)는 이중 연결 리스트(Double Linked List)와 순환 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List)의 속성을 모두 가지고 있는데, 두 개의 연속된 요소가 이전 포인터와 다음 포인터로 연결되거나 연결되고 마지막 노드가 다음 포인터로 첫 번째 노드를 가리키고 첫 번째 노드도 다음 포인터를 가리킵니다. 이전 포인터에 의한 마지막 노드.
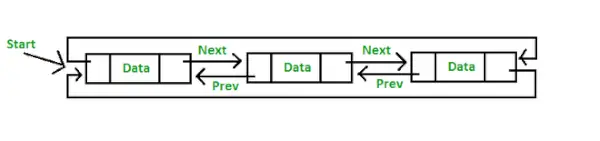
순환 이중 연결 리스트의 표현
메모: 우리는 순환 연결 리스트의 작동을 나타내기 위해 단일 순환 연결 리스트를 사용할 것입니다.
순환 연결 리스트의 표현:
순환 연결 목록은 마지막 노드를 첫 번째 노드에 연결한다는 점을 제외하면 단일 연결 목록과 유사합니다.
순환 연결 목록의 노드 표현:
자바의 스택C++
// Class Node, similar to the linked list class Node{ int value; // Points to the next node. Node next; }> 씨 struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; };> 자바 public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> 씨# public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> 자바스크립트 class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> PHP class Node { public $data; public $next; function __construct($data) { $this->데이터 = $데이터; $this->다음 = null; } }> 파이썬3 # Class Node, similar to the linked list class Node: def __init__(self,data): self.data = data self.next = None>
원형 단일 연결 리스트의 예:

순환 연결 리스트의 예
위의 순환 단일 연결 리스트는 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있습니다.
C++ // Initialize the Nodes. Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
씨 Node* one = createNode(3); Node* two = createNode(5); Node* three = createNode(9); // Connect nodes one->다음 = 2; 2->다음 = 3; 3->다음 = 1;>
자바 // Define the Node class class Node { int value; Node next; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } // Initialize the Nodes. Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;> 씨# Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
자바스크립트 let one = new Node(3); let two = new Node(5); let three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
PHP $one = new Node(3); $two = new Node(5); $three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes $one->다음 = ; ->다음 = ; ->다음 = ;>
파이썬3 # Initialize the Nodes. one = Node(3) two = Node(5) three = Node(9) # Connect nodes one.next = two two.next = three three.next = one>
설명: 위 프로그램에서 1, 2, 3은 각각 값 3, 5, 9를 갖는 노드이며 다음과 같이 순환 방식으로 연결됩니다.
- 노드 1의 경우: Next 포인터는 노드 2의 주소를 저장합니다.
- 노드 2의 경우: Next는 노드 3의 주소를 저장합니다.
- 노드 3의 경우: 그만큼 다음은 노드 1을 가리킵니다.
순환 연결 리스트의 작업:
단일 연결 목록과 유사한 순환 연결 목록에서 다음과 같은 몇 가지 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 삽입
- 삭제
1. 순환 연결 리스트에 삽입:
노드는 세 가지 방법으로 추가할 수 있습니다.
- 목록의 시작 부분에 삽입
- 목록 끝에 삽입
- 노드 사이에 삽입
1) 목록 시작 부분에 삽입: 목록 시작 부분에 노드를 삽입하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- T라고 하는 노드를 만듭니다.
- T -> 다음 = 마지막 -> 다음으로 만듭니다.
- 마지막 -> 다음 = T.
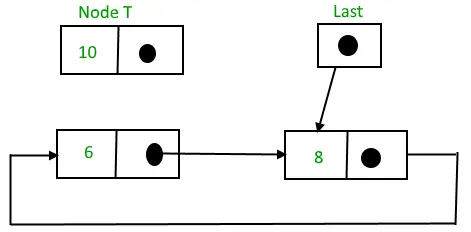
삽입 전 순환 연결 리스트
그런 다음,
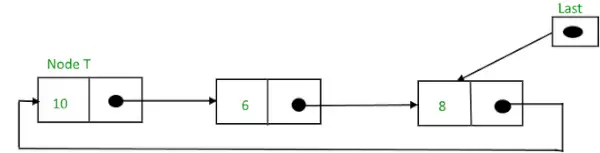
삽입 후 순환 연결 리스트
2) 목록 끝에 삽입: 목록 끝에 노드를 삽입하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- T라고 하는 노드를 만듭니다.
- T -> 다음 = 마지막 -> 다음으로 만듭니다.
- 마지막 -> 다음 = T.
- 마지막 = T.
삽입 전,
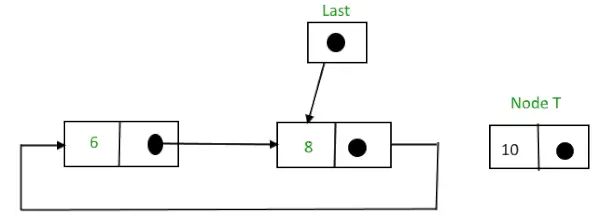
끝에 노드를 삽입하기 전의 순환 연결 목록
b 플러스 트리
삽입 후,
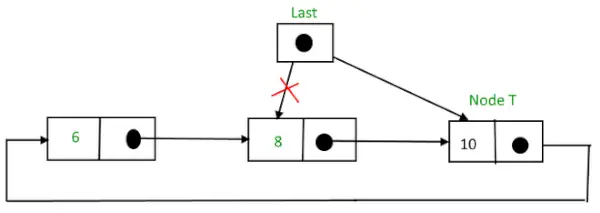
끝에 노드 삽입 후 순환 연결 리스트
삼) 노드 사이에 삽입: 두 노드 사이에 노드를 삽입하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- T라고 하는 노드를 만듭니다.
- T를 삽입해야 하는 노드를 검색합니다. 즉, 노드가 P라고 가정합니다.
- T -> 다음 = P -> 다음으로 만듭니다.
- P -> 다음 = T.
노드의 값이 10이 된 후에 12를 삽입해야 한다고 가정하면,
문자열 자바 추가
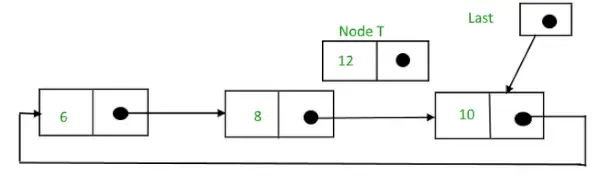
삽입 전 순환 연결 리스트
검색 후 삽입 후,
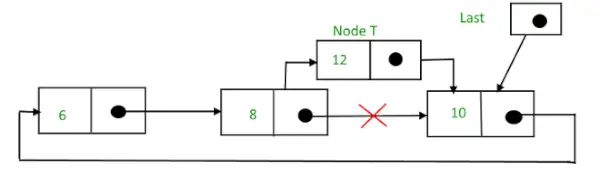
삽입 후 순환 연결 리스트
2. 순환 연결 리스트에서 삭제:
1) 순환 연결 리스트의 유일한 노드인 경우에만 노드를 삭제합니다.
- 노드의 메모리를 해제합니다.
- 마지막 값은 NULL이어야 합니다. 노드는 항상 다른 노드를 가리키므로 NULL 할당이 필요하지 않습니다.
모든 노드를 시작점으로 설정할 수 있습니다.
노드는 처음부터 마지막까지 빠르게 이동됩니다.
2) 마지막 노드 삭제:
프로그램과 스크립트의 차이점
- 마지막 노드 이전에 노드를 찾습니다(임시로 둡니다).
- temp의 마지막 노드 옆에 있는 노드의 주소를 유지합니다.
- 마지막 기억을 삭제해
- 마지막에 temp를 넣어주세요
3) 순환 연결 리스트에서 노드를 삭제합니다. 노드가 주어지고 우리의 임무는 순환 연결 리스트에서 해당 노드를 삭제하는 것입니다.
연산:
사례 1 : 목록이 비어 있습니다.
- 목록이 비어 있으면 간단히 반환됩니다.
사례 2 :목록이 비어 있지 않습니다.
- 목록이 비어 있지 않으면 두 개의 포인터를 정의합니다. 현재 그리고 이전 포인터를 초기화하고 현재 와 더불어 머리 마디.
- 다음을 사용하여 목록을 탐색합니다. 현재 삭제할 노드를 찾고 curr로 다음 노드로 이동하기 전에 매번 prev = curr로 설정합니다.
- 노드가 발견되면 목록에서 유일한 노드인지 확인합니다. 그렇다면 head = NULL 및 free(curr)를 설정하십시오.
- 목록에 노드가 두 개 이상 있으면 해당 노드가 목록의 첫 번째 노드인지 확인하세요. 이를 확인하기 위한 조건( curr == head). 그렇다면 마지막 노드에 도달할 때까지 prev를 이동합니다. prev가 마지막 노드에 도달한 후 head = head -> next 및 prev -> next = head로 설정합니다. 현재 삭제
- curr가 첫 번째 노드가 아닌 경우 목록의 마지막 노드인지 확인합니다. 이를 확인하는 조건은 (curr -> next == head) 입니다.
- curr가 마지막 노드인 경우. prev -> next = head로 설정하고 free(curr)로 노드 curr를 삭제합니다.
- 삭제할 노드가 첫 번째 노드도 마지막 노드도 아닌 경우 prev -> next = curr -> next로 설정하고 curr를 삭제합니다.
- 노드가 목록에 없으면 헤드를 반환하고 아무 작업도 수행하지 않습니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // C++ program to delete a given key from // linked list. #include using namespace std; // Structure for a node class Node { public: int data; Node* next; }; // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list void push(Node** head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. Node* ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1->데이터 = 데이터; ptr1->다음 = *head_ref; // 연결 리스트가 NULL이 아니면 // 마지막 노드의 다음을 설정합니다. if (*head_ref != NULL) { // head 앞의 노드를 찾아 // 그 다음을 업데이트합니다. 노드* 임시 = *head_ref; while (temp->next != *head_ref) temp = temp->next; 임시->다음 = ptr1; } else // 첫 번째 노드의 경우 ptr1->next = ptr1; *head_ref = ptr1; } // 주어진 // 순환 연결 리스트의 노드를 인쇄하는 함수 void printList(Node* head) { Node* temp = head; if (head != NULL) { do { cout<< temp->데이터<< ' '; temp = temp->다음; } while (temp != 헤드); } cout<< endl; } // Function to delete a given node // from the list void deleteNode(Node** head, int key) { // If linked list is empty if (*head == NULL) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if ((*head)->data == key && (*head)->next == *head) { free(*head); *머리 = NULL; 반품; } 노드 *last = *head, *d; // 헤드를 삭제할 경우 if ((*head)->data == key) { // 목록의 마지막 노드를 찾습니다 while (last->next != *head) last = last->next; // 마지막 노드를 // head의 다음 노드, 즉 // 목록의 두 번째 노드를 가리킵니다. last->next = (*head)->next; 무료(*머리); *머리 = 마지막->다음; 반품; } // 삭제할 노드를 찾을 수 없거나 // 목록의 끝에 도달하지 않았습니다. while (last->next != *head && last->next->data != key) { last = last ->다음; } // 삭제할 노드가 발견된 경우 if (last->next->data == key) { d = last->next; 마지막->다음 = d->다음; 무료(d); } 그렇지 않으면<< 'Given node is not found in the list!!!
'; } // Driver code int main() { // Initialize lists as empty Node* head = NULL; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 푸시(&헤드, 2); push(&헤드, 5); push(&헤드, 7); push(&헤드, 8); push(&헤드, 10); 시합<< 'List Before Deletion: '; printList(head); deleteNode(&head, 7); cout << 'List After Deletion: '; printList(head); return 0; }> 씨 #include #include // Structure for a node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list void push(struct Node** head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. struct Node* ptr1 = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); ptr1->데이터 = 데이터; ptr1->다음 = *head_ref; // 연결된 목록이 NULL이 아니면 // 마지막 노드의 다음을 설정합니다. if (*head_ref != NULL) { // head 앞의 노드를 찾아 // 그 다음을 업데이트합니다. 구조체 노드* 임시 = *head_ref; while (temp->next != *head_ref) temp = temp->next; 임시->다음 = ptr1; } else // 첫 번째 노드의 경우 ptr1->next = ptr1; *head_ref = ptr1; } // 주어진 // 원형 연결 리스트의 노드를 인쇄하는 함수 void printList(struct Node* head) { struct Node* temp = head; if (head != NULL) { do { printf('%d ', temp->data); 온도 = 온도->다음; } while (temp != 헤드); } printf('
'); } // 리스트에서 // 주어진 노드를 삭제하는 함수 void deleteNode(struct Node** head, int key) { // 연결 리스트가 비어 있는 경우 if (*head == NULL) return; // 목록에 // 단일 노드만 포함된 경우 if ((*head)->data == key && (*head)->next == *head) { free(*head); *머리 = NULL; 반품; } 구조체 노드 *last = *head, *d; // 헤드를 삭제할 경우 if ((*head)->data == key) { // 목록의 마지막 노드를 찾습니다 while (last->next != *head) last = last->next; // 마지막 노드를 head의 다음 // 즉 // 목록의 두 번째 노드를 가리킵니다. last->next = (*head)->next; 무료(*머리); *머리 = 마지막->다음; 반품; } // 삭제할 노드를 찾을 수 없거나 // 목록의 끝에 도달하지 않았습니다. while (last->next != *head && last->next->data != key) { last = last ->다음; } // 삭제할 노드가 발견된 경우 if (last->next->data == key) { d = last->next; 마지막->다음 = d->다음; 무료(d); } else printf('주어진 노드는 목록에서 찾을 수 없습니다!!!
'); } // 드라이버 코드 int main() { // 목록을 빈 구조체로 초기화합니다. Node* head = NULL; // 생성된 연결리스트는 // 2->5->7->8->10이 됩니다. push(&head, 2); push(&헤드, 5); push(&헤드, 7); push(&헤드, 8); push(&헤드, 10); printf('삭제 전 목록: '); printList(헤드); deleteNode(&head, 7); printf('삭제 후 목록: '); printList(헤드); 0을 반환합니다. }> 자바 // Java program to delete a given key from // linked list. import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class GFG { /* structure for a node */ static class Node { int data; Node next; }; /* Function to insert a node at the beginning of a Circular linked list */ static Node push(Node head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head as next // of it. Node ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head_ref; /* If linked list is not null then set the next of last node */ if (head_ref != null) { // Find the node before head and update // next of it. Node temp = head_ref; while (temp.next != head_ref) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } else ptr1.next = ptr1; /*For the first node */ head_ref = ptr1; return head_ref; } /* Function to print nodes in a given circular linked list */ static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; if (head != null) { do { System.out.printf('%d ', temp.data); temp = temp.next; } while (temp != head); } System.out.printf('
'); } /* Function to delete a given node from the list */ static Node deleteNode(Node head, int key) { if (head == null) return null; int flag = 0; // Find the required node Node curr = head, prev = new Node(); while (curr.data != key) { if (curr.next == head) { System.out.printf( 'Given node is not found in the list!!!
'); flag = 1; break; } prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } // Check if the element is not present in the list if (flag == 1) return head; // Check if node is only node if (curr == head && curr.next == head) { head = null; return head; } // If more than one node, check if // it is first node if (curr == head) { prev = head; while (prev.next != head) prev = prev.next; head = curr.next; prev.next = head; } // check if node is last node else if (curr.next == head) { prev.next = head; } else { prev.next = curr.next; } return head; } /* Driver code */ public static void main(String args[]) { /* Initialize lists as empty */ Node head = null; /* Created linked list will be 2.5.7.8.10 */ head = push(head, 2); head = push(head, 5); head = push(head, 7); head = push(head, 8); head = push(head, 10); System.out.printf('List Before Deletion: '); printList(head); head = deleteNode(head, 7); System.out.printf('List After Deletion: '); printList(head); } } // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> 씨# using System; // Structure for a node public class Node { public int data; public Node next; } // Class for Circular Linked List public class CircularLinkedList { // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list public static void Push(ref Node head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. Node ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head_ref; // If linked list is not NULL then // set the next of last node if (head_ref != null) { // Find the node before head and // update next of it. Node temp = head_ref; while (temp.next != head_ref) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } else // For the first node ptr1.next = ptr1; head_ref = ptr1; } // Function to print nodes in a given // circular linked list public static void PrintList(Node head) { Node temp = head; if (head != null) { do { Console.Write(temp.data + ' '); temp = temp.next; } while (temp != head); } Console.WriteLine(); } // Function to delete a given node // from the list public static void DeleteNode(ref Node head, int key) { // If linked list is empty if (head == null) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if (head.data == key && head.next == head) { head = null; return; } Node last = head, d; // If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key) { // Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head) last = last.next; // Point last node to the next of // head i.e. the second node // of the list last.next = head.next; head = last.next; return; } // Either the node to be deleted is // not found or the end of list // is not reached while (last.next != head && last.next.data != key) { last = last.next; } // If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key) { d = last.next; last.next = d.next; } else Console.WriteLine( 'Given node is not found in the list!!!'); } // Driver code public static void Main() { // Initialize lists as empty Node head = null; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 푸시(기준 헤드, 2); Push(참조 헤드, 5); 푸시(참조 헤드, 7); 푸시(참조 헤드, 8); Push(참조 헤드, 10); Console.Write('삭제 전 목록: '); PrintList(헤드); DeleteNode(참조 헤드, 7); Console.Write('삭제 후 목록: '); PrintList(헤드); } }> 자바스크립트 // Javascript program to delete a given key from linked list. // Structure for a node class Node { constructor() { this.data; this.next; } } // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list function push(head, data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. var ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head; // If linked list is not NULL then // set the next of last node if (head != null) { // Find the node before head and // update next of it. let temp = head; while (temp.next != head) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } // For the first node else ptr1.next = ptr1; head = ptr1; return head; } // Function to print nodes in a given // circular linked list function printList(head) { let tempp = head; if (head != null) { do { console.log(tempp.data); tempp = tempp.next; } while (tempp != head); } } // Function to delete a given node // from the list function deleteNode(head, key) { // If linked list is empty if (head == null) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if (head.data == key && head.next == head) { head = null; return; } let last = head; // If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key) { // Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head) last = last.next; // Point last node to the next of // head i.e. the second node // of the list last.next = head.next; head = last.next; return; } // Either the node to be deleted is // not found or the end of list // is not reached while (last.next != head && last.next.data != key) { last = last.next; } // If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key) { d = last.next; last.next = d.next; d = null; } else console.log('Given node is not found in the list!!!'); } // Driver code // Initialize lists as empty head = null; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 머리 = push(머리, 2); 머리 = 푸시(머리, 5); 머리 = 푸시(머리, 7); 머리 = 푸시(머리, 8); 머리 = 푸시(머리, 10); console.log('삭제 전 목록: '); printList(헤드); deleteNode(헤드, 7); console.log('삭제 후 목록: '); printList(헤드);> 파이썬3 # Python program to delete a given key from linked list class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to insert a node at the # beginning of a Circular linked list def push(head, data): # Create a new node and make head as next of it. newP = Node(data) newP.next = head # If linked list is not NULL then # set the next of last node if head != None: # Find the node before head and # update next of it. temp = head while (temp.next != head): temp = temp.next temp.next = newP else: newP.next = newP head = newP return head # Function to print nodes in a given circular linked list def printList(head): if head == None: print('List is Empty') return temp = head.next print(head.data, end=' ') if (head != None): while (temp != head): print(temp.data, end=' ') temp = temp.next print() # Function to delete a given node # from the list def deleteNode(head, key): # If linked list is empty if (head == None): return # If the list contains only a # single node if (head.data == key and head.next == head): head = None return last = head # If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key): # Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head): last = last.next # Point last node to the next of # head i.e. the second node # of the list last.next = head.next head = last.next return # Either the node to be deleted is # not found or the end of list # is not reached while (last.next != head and last.next.data != key): last = last.next # If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key): d = last.next last.next = d.next d = None else: print('Given node is not found in the list!!!') # Driver code # Initialize lists as empty head = None # Created linked list will be # 2->5->7->8->10 머리 = 밀기(머리, 2) 머리 = 밀기(머리, 5) 머리 = 밀기(머리, 7) 머리 = 밀기(머리, 8) 머리 = 밀기(머리, 10) print('삭제 전 목록: ') printList(head) deleteNode(head, 7) print('삭제 후 목록: ') printList(head)> 산출
List Before Deletion: 10 8 7 5 2 List After Deletion: 10 8 5 2>
시간 복잡도: O(N), 삭제할 요소가 마지막 요소이고 전체 목록을 이동해야 하는 경우 최악의 경우가 발생합니다.
보조 공간: O(1), 일정한 추가 공간이 사용됩니다.
순환 연결 목록의 장점:
- 모든 노드가 시작점이 될 수 있습니다. 어느 지점에서든 시작하여 전체 목록을 탐색할 수 있습니다. 처음 방문한 노드를 다시 방문할 때 중지하면 됩니다.
- 대기열 구현에 유용합니다. 같지 않은 이것 구현 시 순환 연결 리스트를 사용하면 전면과 후면에 대해 두 개의 포인터를 유지할 필요가 없습니다. 마지막으로 삽입된 노드에 대한 포인터를 유지할 수 있으며 앞부분은 항상 마지막 노드 다음으로 얻을 수 있습니다.
- 순환 목록은 목록을 반복적으로 탐색하는 애플리케이션에 유용합니다. 예를 들어, 여러 응용 프로그램이 PC에서 실행 중인 경우 운영 체제는 실행 중인 응용 프로그램을 목록에 넣은 다음 순환하여 각 응용 프로그램에 실행할 시간을 제공한 다음 잠시 기다리게 하는 것이 일반적입니다. CPU는 다른 응용 프로그램에 제공됩니다. 운영 체제에서는 목록의 끝에 도달하면 목록의 맨 앞으로 순환할 수 있도록 순환 목록을 사용하는 것이 편리합니다.
- 순환 이중 연결 목록은 다음과 같은 고급 데이터 구조를 구현하는 데 사용됩니다. 피보나치 힙 .
- 순환 연결 목록을 구현하는 것은 트리나 그래프와 같은 다른 복잡한 데이터 구조에 비해 상대적으로 쉬울 수 있습니다.
순환 연결 리스트의 단점:
- 단일 연결 목록에 비해 순환 목록은 더 복잡합니다.
- 순환 목록을 뒤집는 것은 순환 목록을 단일 또는 이중으로 뒤집는 것보다 더 복잡합니다.
- 코드를 주의 깊게 처리하지 않으면 무한 루프에 빠질 수 있습니다.
- 목록의 끝을 찾고 루프를 제어하는 것이 더 어렵습니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 특정 응용 프로그램에서 효율적일 수 있지만 목록을 정렬하거나 검색해야 하는 경우와 같은 특정 경우에는 다른 데이터 구조보다 성능이 느려질 수 있습니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 개별 노드에 대한 직접 액세스를 제공하지 않습니다.
순환 연결 목록의 응용:
- 멀티플레이어 게임에서는 이를 사용하여 각 플레이어에게 플레이할 기회를 제공합니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 운영 체제에서 실행 중인 여러 응용 프로그램을 구성하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 애플리케이션은 OS에 의해 반복됩니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 자원 할당 문제에 사용될 수 있습니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 일반적으로 순환 버퍼를 구현하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 순환 연결 목록은 시뮬레이션과 게임에 사용될 수 있습니다.
왜 순환 연결 리스트인가?
- 노드는 항상 다른 노드를 가리키므로 NULL 할당이 필요하지 않습니다.
- 모든 노드를 시작점으로 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 노드는 처음부터 마지막까지 빠르게 이동됩니다.
다음 게시물: 순환 연결 목록 | 세트 2(순회) 순환 단일 연결 목록 | 삽입 위의 코드/알고리즘에서 버그를 발견하거나 동일한 문제를 해결할 수 있는 다른 방법을 찾으면 의견을 작성해 주세요.
