이진 트리 트리 형태의 비선형 데이터 구조로 데이터를 계층적 형태로 저장하기 때문에 주로 정렬, 검색에 사용됩니다. 이 섹션에서는 다음 내용을 학습합니다. Java에서 이진 트리 데이터 구조 구현 . 또한 이진 트리 데이터 구조에 대한 간단한 설명을 제공합니다.
이진 트리
각 노드(부모)가 최대 두 개의 자식 노드(왼쪽 및 오른쪽)를 갖는 트리를 이진 트리라고 합니다. 최상위 노드를 루트 노드라고 합니다. 이진 트리에서 노드에는 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 자식 노드의 데이터와 포인터(주소)가 포함됩니다.
그만큼 키 이진 트리의 트리 루트 사이의 가장자리 수 그리고 가장 먼(가장 깊은) 잎. 나무라면 비어 있는 , 높이는 0 . 노드의 높이는 다음과 같이 표시됩니다. 시간 .
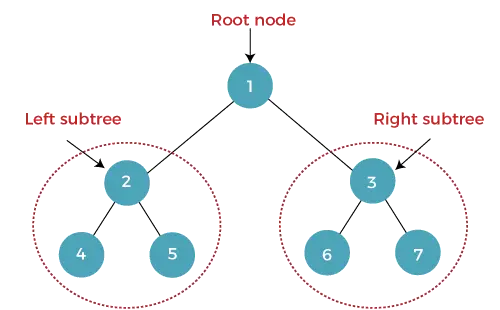
위 이진 트리의 높이는 2입니다.
다음 공식을 사용하여 잎과 노드의 수를 계산할 수 있습니다.
저녁과 저녁의 차이
- 최대 리프 노드 수는 이진 트리입니다. 2시간
- 최대 노드 수는 이진 트리입니다. 2h+1-1
여기서, h는 이진 트리의 높이입니다.
이진 트리의 예

이진 트리의 유형
데이터 구조에는 다음과 같은 유형의 이진 트리가 있습니다.
- 완전/엄격 이진 트리
- 완전한 이진 트리
- 완벽한 이진 트리
- 균형 이진 트리
- 루트 이진 트리
- 퇴화된/병리학적 이진 트리
- 확장 이진 트리
- 기울어진 이진 트리
- 왼쪽으로 치우친 이진 트리
- 오른쪽으로 치우친 이진 트리
- 스레드 이진 트리
- 단일 스레드 이진 트리
- 이중 스레드 이진 트리
Java의 이진 트리 구현
이진 트리를 구현하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다. 이 섹션에서는 LinkedList 데이터 구조를 사용하여 이진 트리를 구현합니다. 이와 함께 노드를 검색하고 이진 트리에 노드를 삽입하는 순회 순서도 구현합니다.
bash 읽기 파일
LinkedList를 사용한 이진 트리 구현
연산
세 가지 속성, 즉 왼쪽 데이터와 오른쪽 데이터를 포함하는 노드 클래스를 정의합니다. 여기서 left는 노드의 왼쪽 자식을 나타내고 right는 노드의 오른쪽 자식을 나타냅니다.
- 노드가 생성되면 데이터가 노드의 데이터 속성으로 전달되고 왼쪽과 오른쪽이 모두 null로 설정됩니다.
- 속성 루트가 있는 다른 클래스를 정의하십시오.
- 루트는 트리의 루트 노드를 나타내며 이를 null로 초기화합니다.
- 루트가 null인지, 즉 트리가 비어 있는지 확인합니다. 새 노드를 루트로 추가합니다.
- 그렇지 않으면 대기열에 루트가 추가됩니다.
- 변수 노드는 현재 노드를 나타냅니다.
- 먼저 노드에 왼쪽 자식과 오른쪽 자식이 있는지 확인합니다. 그렇다면 두 노드를 모두 대기열에 추가합니다.
- 왼쪽 자식이 없으면 새 노드를 왼쪽 자식으로 추가합니다.
- 왼쪽이 있으면 새 노드를 오른쪽 자식으로 추가합니다.
- 전체 트리를 순회한 다음 왼쪽 자식, 루트, 오른쪽 자식을 차례로 인쇄합니다.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } 산출:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
이진 트리 작업
이진 트리에서는 다음 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 삽입
- 삭제
- 찾다
- 순회
이진 트리에 노드를 삽입하는 Java 프로그램
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } 산출:
다이애나 메리 블랙커
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Java에서 노드를 삭제하는 Java 프로그램
연산
- 루트부터 시작하여 이진 트리에서 가장 깊고 오른쪽에 있는 노드와 삭제하려는 노드를 찾습니다.
- 가장 오른쪽에 있는 노드의 데이터를 삭제하려는 노드로 교체합니다.
- 그런 다음 가장 오른쪽에 있는 노드를 삭제합니다.
다음 그림을 고려하십시오.

삭제Node.java
여러 줄 주석 파워쉘
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } 산출:
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
이진 트리에서 노드를 검색하는 Java 프로그램
연산
- 왼쪽 데이터와 오른쪽 데이터라는 세 가지 속성을 갖는 노드 클래스를 정의합니다. 여기서 left는 노드의 왼쪽 자식을 나타내고 right는 노드의 오른쪽 자식을 나타냅니다.
- 노드가 생성되면 데이터가 노드의 데이터 속성으로 전달되고 왼쪽과 오른쪽이 모두 null로 설정됩니다.
- 두 개의 속성 루트와 플래그를 갖는 다른 클래스를 정의하십시오.
- Root는 트리의 루트 노드를 나타내며 이를 null로 초기화합니다.
- 플래그는 주어진 노드가 트리에 존재하는지 여부를 확인하는 데 사용됩니다. 처음에는 false로 설정됩니다.
- 루트가 null인지, 즉 트리가 비어 있는지 확인합니다.
- 트리가 비어 있지 않으면 임시 데이터를 값과 비교합니다. 동일하면 플래그를 true로 설정하고 반환합니다.
- searchNode()를 재귀적으로 호출하여 왼쪽 하위 트리를 탐색하고 값이 왼쪽 하위 트리에 있는지 확인합니다.
- searchNode()를 재귀적으로 호출하여 오른쪽 하위 트리를 탐색하고 값이 오른쪽 하위 트리에 있는지 확인합니다.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } 산출:
Element is present in the binary tree.
이진 트리 탐색
| 순회 순서 | 첫 방문 | 두 번째 방문 | 세 번째 방문 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 중순 | 왼쪽 하위 트리를 순서대로 방문 | 루트 노드 방문 | 오른쪽 하위 트리를 순서대로 방문 |
| 선주문 | 루트 노드 방문 | 선주문의 왼쪽 하위 트리 방문 | 선주문의 오른쪽 하위 트리 방문 |
| 우편 주문 | 후위 순서로 왼쪽 하위 트리 방문 | 후위의 오른쪽 하위 트리 방문 | 루트 노드 방문 |
참고: 위의 세 가지 순회 외에 경계 순회라는 또 다른 순회 순서가 있습니다.
Inorder, Preorder 및 Postorder Traversal을 탐색하는 Java 프로그램
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } 산출:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
위의 연산 외에도 큰 노드, 가장 작은 노드, 모든 노드의 합과 같은 연산을 수행할 수도 있습니다.
이진 트리에서 가장 큰 노드를 찾는 Java 프로그램
가장 큰Node.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } 산출:
안드로이드에서 애플리케이션 숨기기를 해제하는 방법
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
이진 트리에서 가장 작은 노드를 찾는 Java 프로그램
연산
- 데이터, 왼쪽 및 오른쪽의 세 가지 속성을 갖는 노드 클래스를 정의합니다. 여기서 left는 노드의 왼쪽 자식을 나타내고 right는 노드의 오른쪽 자식을 나타냅니다.
- 노드가 생성되면 데이터가 노드의 데이터 속성으로 전달되고 왼쪽과 오른쪽 모두 null로 설정됩니다.
- 속성 루트가 있는 다른 클래스를 정의하십시오.
뿌리 트리의 루트 노드를 나타내고 이를 null로 초기화합니다.
- 여부를 확인합니다. 루트가 null입니다. , 이는 트리가 비어 있음을 의미합니다.
- tree가 비어 있지 않으면 임시 데이터를 저장할 변수 min을 정의합니다.
- MinimalElement()를 재귀적으로 호출하여 왼쪽 하위 트리의 최소 노드를 찾습니다. 해당 값을 leftMin에 저장합니다. min 값을 leftMin과 비교하고 최소값 2를 min에 저장합니다.
- MinimalElement()를 재귀적으로 호출하여 오른쪽 하위 트리의 최소 노드를 찾습니다. 해당 값을 rightMin에 저장합니다. min 값을 rightMin과 비교하여 최대값 2를 min에 저장합니다.
- 결국 min은 이진 트리에서 가장 작은 노드를 보유하게 됩니다.
가장 작은Node.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } 산출:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
이진 트리의 최대 너비를 찾는 Java 프로그램
연산
- 왼쪽 데이터와 오른쪽 데이터라는 세 가지 속성을 갖는 노드 클래스를 정의합니다. 여기서 left는 노드의 왼쪽 자식을 나타내고 right는 노드의 오른쪽 자식을 나타냅니다.
- 노드가 생성되면 데이터가 노드의 데이터 속성으로 전달되고 왼쪽과 오른쪽이 모두 null로 설정됩니다.
- 속성 루트가 있는 다른 클래스를 정의하십시오.
뿌리 트리의 루트 노드를 나타내고 이를 null로 초기화합니다.
- maxWidth 변수는 모든 레벨에 존재하는 최대 노드 수를 저장합니다.
- 큐는 이진 트리를 수준별로 탐색하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 루트가 null인지, 즉 트리가 비어 있는지 확인합니다.
- 그렇지 않은 경우 루트 노드를 대기열에 추가합니다. 변수 nodeInLevel은 각 수준의 노드 수를 추적합니다.
- nodeInLevel > 0이면 대기열 앞쪽에서 노드를 제거하고 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 자식을 대기열에 추가합니다. 첫 번째 반복에서는 노드 1이 제거되고 해당 하위 노드 2와 3이 대기열에 추가됩니다. 두 번째 반복에서는 노드 2가 제거되고 해당 자식 4와 5가 대기열에 추가되는 식입니다.
- MaxWidth는 max(maxWidth, nodeInLevel)를 저장합니다. 따라서 특정 시점에서 최대 노드 수를 나타냅니다.
- 이는 트리의 모든 수준을 통과할 때까지 계속됩니다.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } 산출:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
