이 기사에서는 Java 프로그래밍 언어를 사용하여 파일에 쓰는 다양한 방법을 살펴보겠습니다. Java의 Java FileWriter 클래스는 문자 지향 데이터를 파일에 쓰는 데 사용됩니다. 이 클래스는 Java에서 파일 처리에 사용되는 문자 지향 클래스이기 때문입니다.
많이있다 Java로 파일에 쓰는 방법 다음과 같이 목표를 달성할 수 있는 많은 클래스와 메서드가 있기 때문입니다.
- 사용 쓰기문자열() 방법
- FileWriter 클래스 사용
- BufferedWriter 클래스 사용
- FileOutputStream 클래스 사용
방법 1: writeString() 메소드 사용
이 메소드는 Java 버전 11에서 지원됩니다. 이 메소드는 4개의 매개변수를 사용할 수 있습니다. 파일 경로, 문자 순서, 문자 세트, 옵션이 있습니다. 이 메소드가 파일에 쓰려면 처음 두 매개변수가 필수입니다. 문자를 파일의 내용으로 씁니다. 파일 경로를 반환하고 네 가지 유형의 예외를 발생시킬 수 있습니다. 파일의 내용이 짧을 때 사용하면 더 좋습니다.
예: 의 사용법을 보여줍니다. 쓰기문자열() Files 클래스 아래에 있는 메서드를 사용하여 파일에 데이터를 씁니다. 또 다른 클래스인 Path는 내용이 기록될 경로와 함께 파일 이름을 할당하는 데 사용됩니다. Files 클래스에는 다음과 같은 또 다른 메소드가 있습니다. 읽기문자열() 코드에 사용된 기존 파일의 내용을 읽고 내용이 파일에 올바르게 기록되었는지 확인합니다.
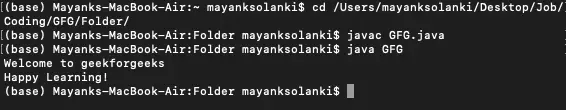
자바
포티네니 램
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >throws> IOException> >{> >// Assigning the content of the file> >String text> >=>'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'>;> >// Defining the file name of the file> >Path fileName = Path.of(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into the file> >Files.writeString(fileName, text);> >// Reading the content of the file> >String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> >// Printing the content inside the file> >System.out.println(file_content);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!>
방법 2: FileWriter 클래스 사용
파일 내용이 짧은 경우 FileWriter 클래스를 사용하여 파일에 쓰는 것이 더 나은 옵션입니다. 또한 writeString() 메소드와 같이 파일의 내용으로 문자 스트림을 작성합니다. 이 클래스의 생성자는 기본 문자 인코딩과 기본 버퍼 크기(바이트)를 정의합니다.
아래 예제에서는 FileWriter 클래스를 사용하여 콘텐츠를 파일에 쓰는 방법을 보여줍니다. 파일에 쓰려면 파일 이름을 사용하여 FileWriter 클래스의 개체를 만들어야 합니다. 다음으로 write() 메서드를 사용하여 파일에 텍스트 변수의 값을 씁니다. 파일을 쓰는 동안 오류가 발생하면 IOException이 발생하고 오류 메시지는 catch 블록에서 인쇄됩니다.
예:
자바
C++ 세트
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Content to be assigned to a file> >// Custom input just for illustration purposes> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Create a FileWriter object> >// to write in the file> >FileWriter fWriter =>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into file> >// Note: The content taken above inside the> >// string> >fWriter.write(text);> >// Printing the contents of a file> >System.out.println(text);> >// Closing the file writing connection> >fWriter.close();> >// Display message for successful execution of> >// program on the console> >System.out.println(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exception occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
배쉬 엘리프
>
>산출
File is created successfully with the content.>

방법 3: BufferedWriter 클래스 사용
문자 출력 스트림에 텍스트를 쓰는 데 사용됩니다. 기본 버퍼 크기를 가지고 있지만 큰 버퍼 크기를 할당할 수 있습니다. 문자, 문자열 및 배열을 작성하는 데 유용합니다. 프롬프트 출력이 필요하지 않은 경우 파일에 데이터를 쓰기 위해 이 클래스를 작성기 클래스로 래핑하는 것이 좋습니다.
예:
자바
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assigning the file content> >// Note: Custom contents taken as input to> >// illustrate> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> >BufferedWriter f_writer> >=>new> BufferedWriter(>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>));> >// Step 2: Write text(content) to file> >f_writer.write(text);> >// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> >// on the terminal/CMD> >System.out.print(text);> >// Step 4: Display message showcasing> >// successful execution of the program> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> >f_writer.close();> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception on console> >// using getMessage() method> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
문자열을 int로
>
>산출
File is created successfully with the content.>

다음 예제에서는 BufferedWriter 클래스를 사용하여 파일에 쓰는 방법을 보여줍니다. 또한 파일에 콘텐츠를 쓰려면 FileWriter와 같은 BufferedWriter 클래스의 개체를 생성해야 합니다. 하지만 이 클래스는 큰 버퍼 크기를 사용하여 파일에 쓸 수 있는 큰 콘텐츠를 지원합니다.
방법 4: FileOutputStream 클래스 사용
원시 스트림 데이터를 파일에 쓰는 데 사용됩니다. FileWriter 및 BufferedWriter 클래스는 파일에 텍스트만 쓰는 데 사용되지만 바이너리 데이터는 FileOutputStream 클래스를 사용하여 쓸 수 있습니다.
FileOutputStream 클래스를 사용하여 파일에 데이터를 쓰는 방법은 다음 예제에 나와 있습니다. 또한 파일에 데이터를 쓰려면 파일 이름을 가진 클래스의 객체를 생성해야 합니다. 여기서 문자열 내용은 다음을 사용하여 파일에 기록되는 바이트 배열로 변환됩니다. 쓰다() 방법.
예:
자바
파이썬 또는
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assign the file content> >String fileContent =>'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'>;> >FileOutputStream outputStream =>null>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> >outputStream =>new> FileOutputStream(>'file.txt'>);> >// Step 2: Store byte content from string> >byte>[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> >// Step 3: Write into the file> >outputStream.write(strToBytes);> >// Print the success message (Optional)> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle the exception> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display the exception/s> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >// finally keyword is used with in try catch block> >// and this code will always execute whether> >// exception occurred or not> >finally> {> >// Step 4: Close the object> >if> (outputStream !=>null>) {> >// Note: Second try catch block ensures that> >// the file is closed even if an error> >// occurs> >try> {> >// Closing the file connections> >// if no exception has occurred> >outputStream.close();> >}> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display exceptions if occurred> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> >}> >}> }> |
>
>산출
File is created successfully with the content.>
