텍스트가 주어짐 txt[0 . . . N-1] 그리고 패턴 침대[0 . . . M-1] , txt[]에서 pat[]의 모든 항목을 인쇄하는 검색(char pat[], char txt[]) 함수를 작성하세요. 당신은 N > 남 .
예:
권장되는 문제 해결 문제입력: txt[] = 이것은 테스트 텍스트입니다. pat[] = 테스트
산출: 인덱스 10에서 발견된 패턴
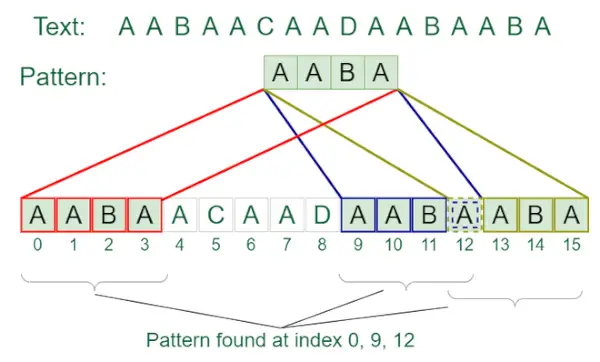
입력: txt[] = 당신의 아버지
팻[] = AABA
산출: 인덱스 0에서 발견된 패턴, 인덱스 9에서 발견된 패턴, 인덱스 12에서 발견된 패턴텍스트에 패턴이 도착함
우리는 Naive 패턴 검색 알고리즘에 대해 논의했습니다. 이전 게시물 . Naive 알고리즘의 최악의 복잡도는 O(m(n-m+1))입니다. KMP 알고리즘의 시간복잡도는 최악의 경우 O(n+m)이다.
KMP(Knuth Morris Pratt) 패턴 검색:
그만큼 순진한 패턴 검색 알고리즘 일치하는 문자가 많고 일치하지 않는 문자가 뒤따르는 경우에는 제대로 작동하지 않습니다.
예:
1) txt[] = AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAB, 팻[] = AAAAB
2) txt[] = ABABABCABABABCABABABC, pat[] = ABABAC(최악의 경우는 아니지만 Naive의 경우 나쁜 경우)
KMP 매칭 알고리즘은 패턴의 퇴화 특성(동일한 하위 패턴이 패턴에 두 번 이상 나타나는 패턴)을 사용하고 최악의 복잡도를 개선하여 O(n+m) .
KMP 알고리즘의 기본 아이디어는 불일치를 감지할 때마다(일부 일치 후) 다음 창의 텍스트에 있는 일부 문자를 이미 알고 있다는 것입니다. 우리는 이 정보를 활용하여 어쨌든 일치할 것으로 알고 있는 문자의 일치를 방지합니다.
매칭 개요
txt = AAAAABAAABA
팻 = AAAA
첫 번째 창을 비교합니다. txt ~와 함께 똑같다txt = AAAA 아버지
심지어 = AAAA [초기 위치]
우리는 일치하는 것을 찾습니다. 이것은 다음과 같다 순진한 문자열 매칭 .다음 단계에서는 다음 창을 비교합니다. txt ~와 함께 똑같다 .
txt = AAAAA 파괴하다
심지어 = AAAA [패턴이 한 위치 이동됨]KMP가 Naive보다 최적화를 수행하는 곳입니다. 이 두 번째 창에서는 패턴의 네 번째 A만 비교합니다.
현재 창이 일치하는지 여부를 결정하려면 현재 텍스트 창의 네 번째 문자를 사용하세요. 우리가 알고 있기 때문에
처음 세 문자는 어쨌든 일치하므로 처음 세 문자 일치는 건너뛰었습니다.전처리가 필요합니까?
위의 설명에서 건너뛸 문자 수를 어떻게 알 수 있는지에 대한 중요한 질문이 발생합니다. 이것을 알기 위해서는,
패턴을 사전 처리하고 건너뛸 문자 수를 알려주는 정수 배열 lps[]를 준비합니다.
전처리 개요:
- KMP 알고리즘은 pat[]를 전처리하고 보조를 구성합니다. lps[] 크기의 중 (패턴의 크기와 동일) 일치하는 동안 문자를 건너뛰는 데 사용됩니다.
- 이름 lps 접미사이기도 한 가장 긴 적절한 접두사를 나타냅니다. 적절한 접두사는 허용되지 않는 전체 문자열이 포함된 접두사입니다. 예를 들어 ABC의 접두사는 , A, AB 및 ABC입니다. 적절한 접두사는 , A 및 AB입니다. 문자열의 접미사는 , C, BC 및 ABC입니다.
- 하위 패턴에서 lps를 검색합니다. 보다 명확하게 우리는 접두사와 접미사가 모두 있는 패턴의 하위 문자열에 중점을 둡니다.
- i = 0 ~ m-1인 각 하위 패턴 pat[0..i]에 대해 lps[i]는 하위 패턴 pat[0..i의 접미사이기도 한 최대 일치 적절한 접두사의 길이를 저장합니다. ].
lps[i] = pat[0..i]의 접미사이기도 한 pat[0..i]의 가장 긴 고유 접두사입니다.
메모: lps[i]는 적절한 접미사이기도 한 가장 긴 접두사로 정의될 수도 있습니다. 전체 하위 문자열이 고려되지 않도록 한 곳에서 적절하게 사용해야 합니다.
lps[] 구성의 예:
AAAA 패턴의 경우 lps[]는 [0, 1, 2, 3]입니다.
ABCDE 패턴의 경우 lps[]는 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]입니다.
파일 리눅스 수정AABAACAABAA 패턴의 경우 lps[]는 [0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]입니다.
AAACAAAAAC 패턴의 경우 lps[]는 [0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4]입니다.
AAABAAA 패턴의 경우 lps[]는 [0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3]입니다.
전처리 알고리즘:
전처리 부분에서는
- 우리는 다음과 같이 값을 계산합니다. lps[] . 이를 위해 가장 긴 접두사 접미사 값의 길이를 추적합니다(우리는 오직 이 목적을 위한 변수) 이전 인덱스의 경우
- 초기화한다 lps[0] 그리고 오직 0으로.
- 만약에 팻[len] 그리고 침대 일치, 우리는 증가 오직 1씩 증가한 값을 lps[i]에 할당합니다.
- pat[i]와 pat[len]이 일치하지 않고 len이 0이 아니면 len을 lps[len-1]로 업데이트합니다.
- 보다 계산LPSArray() 자세한 내용은 아래 코드에서
전처리(또는 lps[] 구성) 예시:
팻[] = AAAAAAA
=> len = 0, i = 0:
- lps[0]은 항상 0이므로 i = 1로 이동합니다.
=> len = 0, i = 1:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행하세요.
- len = 1, lps[1] = 1, i = 2로 설정합니다.
=> len = 1, i = 2:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행하세요.
- len = 2, lps[2] = 2, i = 3으로 설정합니다.
=> len = 2, i = 3:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하지 않고 len> 0이므로,
- len = lps[len-1] = lps[1] = 1로 설정합니다.
=> len = 1, i = 3:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하지 않고 len> 0이므로,
- len = lps[len-1] = lps[0] = 0
=> len = 0, i = 3:
라지니칸트
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하지 않고 len = 0이므로,
- lps[3] = 0 및 i = 4로 설정
=> len = 0, i = 4:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행합니다.
- len = 1, lps[4] = 1, i = 5로 설정합니다.
=> len = 1, i = 5:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행합니다.
- len = 2, lps[5] = 2, i = 6으로 설정합니다.
=> len = 2, i = 6:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행합니다.
- len = 3, lps[6] = 3, i = 7
=> len = 3, i = 7:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하지 않고 len> 0이므로,
- len = lps[len-1] = lps[2] = 2로 설정
=> len = 2, i = 7:
- pat[len]과 pat[i]가 일치하므로 len++를 수행합니다.
- lps[i]에 저장하고 i++를 수행합니다.
- len = 3, lps[7] = 3, i = 8
전체 lps[]를 구성했으므로 여기에서 멈춥니다.
KMP 알고리즘 구현:
와 달리 순진한 알고리즘 , 패턴을 하나씩 슬라이드하고 각 교대조의 모든 문자를 비교하는 경우 lps[]의 값을 사용하여 일치시킬 다음 문자를 결정합니다. 아이디어는 어쨌든 일치할 것으로 알고 있는 문자를 일치하지 않는 것입니다.
다음 위치를 결정하기 위해(또는 건너뛸 문자 수를 알기 위해) lps[]를 사용하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
- j = 0인 pat[j]와 현재 텍스트 창의 문자 비교를 시작합니다.
- txt[i]와 pat[j] 문자를 계속 일치시키고 pat[j]와 txt[i]가 유지되는 동안 i와 j를 계속 증가시킵니다. 어울리는 .
- 우리가 볼 때 불일치
- 우리는 문자 pat[0..j-1]이 txt[i-j…i-1]과 일치한다는 것을 알고 있습니다(j는 0으로 시작하고 일치하는 경우에만 증가한다는 점에 유의하세요).
- 우리는 또한 (위의 정의로부터) lps[j-1]이 적절한 접두사와 접미사인 pat[0…j-1]의 문자 수라는 것을 알고 있습니다.
- 위의 두 가지 점에서 우리는 이러한 문자가 어쨌든 일치할 것임을 알고 있기 때문에 이러한 lps[j-1] 문자를 txt[i-j…i-1]과 일치시킬 필요가 없다는 결론을 내릴 수 있습니다. 이를 이해하기 위해 위의 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
아래는 위 알고리즘의 그림입니다.
txt[] =를 고려하십시오. 아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아아 , 팻[] = AAAA
위의 LPS 구축 프로세스를 따르면 lps[] = {0, 1, 2, 3}
-> i = 0, j = 0: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++, j++ 수행
-> i = 1, j = 1: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++, j++ 수행
-> i = 2, j = 2: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++, j++ 수행
-> i = 3, j = 3: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++, j++ 수행
-> i = 4, j = 4: j = M이므로 인쇄 패턴을 찾아 j를 재설정합니다. 제이 = lps[j-1] = lps[3] = 삼
여기서는 Naive 알고리즘과 달리 처음 3개를 일치시키지 않습니다.
이 창의 문자입니다. 위 단계의 lps[j-1] 값은 일치시킬 다음 문자의 인덱스를 제공했습니다.-> i = 4, j = 3: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++, j++ 수행
-> i = 5, j = 4: j == M이므로 인쇄 패턴을 찾아 j를 재설정합니다. 제이 = lps[j-1] = lps[3] = 삼
Naive 알고리즘과 달리 이 창의 처음 세 문자를 일치시키지 않습니다. 위 단계에서 lps[j-1] 값은 일치시킬 다음 문자의 인덱스를 제공했습니다.-> i = 5, j = 3: txt[i]와 pat[j]는 일치하지 않고 j> 0이면 j만 변경합니다. 제이 = lps[j-1] = lps[2] = 2
-> i = 5, j = 2: txt[i]와 pat[j]는 일치하지 않고 j> 0이면 j만 변경합니다. 제이 = lps[j-1] = lps[1] = 1
-> i = 5, j = 1: txt[i]와 pat[j]는 일치하지 않고 j> 0이면 j만 변경합니다. 제이 = lps[j-1] = lps[0] = 0
-> i = 5, j = 0: txt[i]와 pat[j]는 일치하지 않으며 j는 0이므로 i++를 수행합니다.
-> i = 6, j = 0: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++ 및 j++ 수행
-> i = 7, j = 1: txt[i] 및 pat[j] 일치, i++ 및 j++ 수행
패턴의 문자와 비교할 수 있는 충분한 문자가 텍스트에 있을 때까지 이 방법을 계속합니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++
자바의 정규식
// C++ program for implementation of KMP pattern searching> // algorithm> #include> void> computeLPSArray(>char>* pat,>int> M,>int>* lps);> // Prints occurrences of pat[] in txt[]> void> KMPSearch(>char>* pat,>char>* txt)> {> >int> M =>strlen>(pat);> >int> N =>strlen>(txt);> >// create lps[] that will hold the longest prefix suffix> >// values for pattern> >int> lps[M];> >// Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[] array)> >computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps);> >int> i = 0;>// index for txt[]> >int> j = 0;>// index for pat[]> >while> ((N - i)>= (M - j)) {> >if> (pat[j] == txt[i]) {> >j++;> >i++;> >}> >if> (j == M) {> >printf>(>'Found pattern at index %d '>, i - j);> >j = lps[j - 1];> >}> >// mismatch after j matches> >else> if> (i // Do not match lps[0..lps[j-1]] characters, // they will match anyway if (j != 0) j = lps[j - 1]; else i = i + 1; } } } // Fills lps[] for given pattern pat[0..M-1] void computeLPSArray(char* pat, int M, int* lps) { // length of the previous longest prefix suffix int len = 0; lps[0] = 0; // lps[0] is always 0 // the loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1 int i = 1; while (i if (pat[i] == pat[len]) { len++; lps[i] = len; i++; } else // (pat[i] != pat[len]) { // This is tricky. Consider the example. // AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar // to search step. if (len != 0) { len = lps[len - 1]; // Also, note that we do not increment // i here } else // if (len == 0) { lps[i] = 0; i++; } } } } // Driver code int main() { char txt[] = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB'; char pat[] = 'ABABCABAB'; KMPSearch(pat, txt); return 0; }> |
>
>
자바
// JAVA program for implementation of KMP pattern> // searching algorithm> class> KMP_String_Matching {> >void> KMPSearch(String pat, String txt)> >{> >int> M = pat.length();> >int> N = txt.length();> >// create lps[] that will hold the longest> >// prefix suffix values for pattern> >int> lps[] =>new> int>[M];> >int> j =>0>;>// index for pat[]> >// Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[]> >// array)> >computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps);> >int> i =>0>;>// index for txt[]> >while> ((N - i)>= (M - j)) {> >if> (pat.charAt(j) == txt.charAt(i)) {> >j++;> >i++;> >}> >if> (j == M) {> >System.out.println(>'Found pattern '> >+>'at index '> + (i - j));> >j = lps[j ->1>];> >}> >// mismatch after j matches> >else> if> (i && pat.charAt(j) != txt.charAt(i)) { // Do not match lps[0..lps[j-1]] characters, // they will match anyway if (j != 0) j = lps[j - 1]; else i = i + 1; } } } void computeLPSArray(String pat, int M, int lps[]) { // length of the previous longest prefix suffix int len = 0; int i = 1; lps[0] = 0; // lps[0] is always 0 // the loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1 while (i if (pat.charAt(i) == pat.charAt(len)) { len++; lps[i] = len; i++; } else // (pat[i] != pat[len]) { // This is tricky. Consider the example. // AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar // to search step. if (len != 0) { len = lps[len - 1]; // Also, note that we do not increment // i here } else // if (len == 0) { lps[i] = len; i++; } } } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { String txt = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB'; String pat = 'ABABCABAB'; new KMP_String_Matching().KMPSearch(pat, txt); } } // This code has been contributed by Amit Khandelwal.> |
>
>
파이썬3
카잘 아가르왈
# Python3 program for KMP Algorithm> def> KMPSearch(pat, txt):> >M>=> len>(pat)> >N>=> len>(txt)> ># create lps[] that will hold the longest prefix suffix> ># values for pattern> >lps>=> [>0>]>*>M> >j>=> 0> # index for pat[]> ># Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[] array)> >computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps)> >i>=> 0> # index for txt[]> >while> (N>-> i)>>=> (M>-> j):> >if> pat[j]>=>=> txt[i]:> >i>+>=> 1> >j>+>=> 1> >if> j>=>=> M:> >print>(>'Found pattern at index '> +> str>(i>->j))> >j>=> lps[j>->1>]> ># mismatch after j matches> >elif> i and pat[j] != txt[i]: # Do not match lps[0..lps[j-1]] characters, # they will match anyway if j != 0: j = lps[j-1] else: i += 1 # Function to compute LPS array def computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps): len = 0 # length of the previous longest prefix suffix lps[0] = 0 # lps[0] is always 0 i = 1 # the loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1 while i if pat[i] == pat[len]: len += 1 lps[i] = len i += 1 else: # This is tricky. Consider the example. # AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar # to search step. if len != 0: len = lps[len-1] # Also, note that we do not increment i here else: lps[i] = 0 i += 1 # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': txt = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB' pat = 'ABABCABAB' KMPSearch(pat, txt) # This code is contributed by Bhavya Jain> |
>
>
씨#
// C# program for implementation of KMP pattern> // searching algorithm> using> System;> class> GFG {> >void> KMPSearch(>string> pat,>string> txt)> >{> >int> M = pat.Length;> >int> N = txt.Length;> >// Create lps[] that will hold the longest> >// prefix suffix values for pattern> >int>[] lps =>new> int>[M];> >// Index for pat[]> >int> j = 0;> >// Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[]> >// array)> >computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps);> >int> i = 0;> >while> ((N - i)>= (M - j)) {> >if> (pat[j] == txt[i]) {> >j++;> >i++;> >}> >if> (j == M) {> >Console.Write(>'Found pattern '> >+>'at index '> + (i - j));> >j = lps[j - 1];> >}> >// Mismatch after j matches> >else> if> (i // Do not match lps[0..lps[j-1]] characters, // they will match anyway if (j != 0) j = lps[j - 1]; else i = i + 1; } } } void computeLPSArray(string pat, int M, int[] lps) { // Length of the previous longest prefix suffix int len = 0; int i = 1; lps[0] = 0; // The loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1 while (i if (pat[i] == pat[len]) { len++; lps[i] = len; i++; } else // (pat[i] != pat[len]) { // This is tricky. Consider the example. // AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar // to search step. if (len != 0) { len = lps[len - 1]; // Also, note that we do not increment // i here } else // len = 0 { lps[i] = len; i++; } } } } // Driver code public static void Main() { string txt = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB'; string pat = 'ABABCABAB'; new GFG().KMPSearch(pat, txt); } } // This code has been contributed by Amit Khandelwal.> |
>
>
자바스크립트
데이터 링크 계층 프로토콜
> >//Javascript program for implementation of KMP pattern> >// searching algorithm> > >function> computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps)> >{> >// length of the previous longest prefix suffix> >var> len = 0;> >var> i = 1;> >lps[0] = 0;>// lps[0] is always 0> > >// the loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1> >while> (i if (pat.charAt(i) == pat.charAt(len)) { len++; lps[i] = len; i++; } else // (pat[i] != pat[len]) { // This is tricky. Consider the example. // AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar // to search step. if (len != 0) { len = lps[len - 1]; // Also, note that we do not increment // i here } else // if (len == 0) { lps[i] = len; i++; } } } } function KMPSearch(pat,txt) { var M = pat.length; var N = txt.length; // create lps[] that will hold the longest // prefix suffix values for pattern var lps = []; var j = 0; // index for pat[] // Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[] // array) computeLPSArray(pat, M, lps); var i = 0; // index for txt[] while ((N - i)>= (M - j)) { if (pat.charAt(j) == txt.charAt(i)) { j++; 나++; } if (j == M) { document.write('발견된 패턴 ' + '인덱스에서 ' + (i - j) + '
'); j = lps[j - 1]; } // j가 일치한 후 불일치 else if (i // lps[0..lps[j-1]] 문자와 일치하지 않음, // 어쨌든 일치함 if (j != 0) j = lps[j - 1 ]; else i = i + 1; } } var txt = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB'; var pat = 'ABABCABAB'(pat, txt); //이 코드는 shruti456rawal이 제공한 것입니다. |
>
// PHP program for implementation of KMP pattern searching // algorithm // Prints occurrences of txt[] in pat[] function KMPSearch($pat, $txt) { $M = strlen($pat); $N = strlen($txt); // create lps[] that will hold the longest prefix suffix // values for pattern $lps=array_fill(0,$M,0); // Preprocess the pattern (calculate lps[] array) computeLPSArray($pat, $M, $lps); $i = 0; // index for txt[] $j = 0; // index for pat[] while (($N - $i)>= ($M - $j)) { if ($pat[$j] == $txt[$i]) { $j++; $i++; } if ($j == $M) { printf('인덱스 '에서 패턴을 찾았습니다.($i - $j)); $j = $lps[$j - 1]; } // j 이후 불일치 else if ($i<$N && $pat[$j] != $txt[$i]) { // Do not match lps[0..lps[j-1]] characters, // they will match anyway if ($j != 0) $j = $lps[$j - 1]; else $i = $i + 1; } } } // Fills lps[] for given pattern pat[0..M-1] function computeLPSArray($pat, $M, &$lps) { // Length of the previous longest prefix suffix $len = 0; $lps[0] = 0; // lps[0] is always 0 // The loop calculates lps[i] for i = 1 to M-1 $i = 1; while ($i <$M) { if ($pat[$i] == $pat[$len]) { $len++; $lps[$i] = $len; $i++; } else // (pat[i] != pat[len]) { // This is tricky. Consider the example. // AAACAAAA and i = 7. The idea is similar // to search step. if ($len != 0) { $len = $lps[$len - 1]; // Also, note that we do not increment // i here } else // if (len == 0) { $lps[$i] = 0; $i++; } } } } // Driver program to test above function $txt = 'ABABDABACDABABCABAB'; $pat = 'ABABCABAB'; KMPSearch($pat, $txt); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?>>>>산출Found pattern at index 10>시간 복잡도: O(N+M) 여기서 N은 텍스트의 길이이고 M은 찾을 패턴의 길이입니다.
보조 공간: 오(남)