R-행렬 행과 열로 된 데이터의 2차원 배열입니다.
행렬에서 행은 가로로 이어지는 항목이고 열은 세로로 이어지는 항목입니다. ~ 안에 R 프로그래밍 , 행렬은 2차원의 동종 데이터 구조입니다. 다음은 행렬의 몇 가지 예입니다.
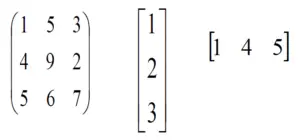
R – 행렬
R에서 행렬 만들기
R에서 행렬을 생성하려면 다음과 같은 함수를 사용해야 합니다. 행렬() .
이에 대한 주장 행렬() 벡터의 요소 집합입니다. 행렬에 포함하려는 행 수와 열 수를 전달해야 합니다.
메모: 기본적으로 행렬은 열 방향 순서로 되어 있습니다.
R-행렬을 생성하는 구문
행렬(데이터, nrow, ncol, byrow, 희미한 이름)
매개변수:
- 데이터 - 입력하려는 값
- 지금 – 아니요. 행
- ncol - 아니요. 열의
- byrow - 논리적 단서, 'true' 값이 행별로 할당되는 경우
- 딤네임 – 행과 열의 이름
예:
mylivecricket.in
아르 자형
# R program to create a matrix> > A =>matrix>(> > ># Taking sequence of elements> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> > ># No of rows> >nrow = 3,> > ># No of columns> >ncol = 3,> > ># By default matrices are in column-wise order> ># So this parameter decides how to arrange the matrix> >byrow =>TRUE> )> > # Naming rows> rownames>(A) =>c>(>'a'>,>'b'>,>'c'>)> > # Naming columns> colnames>(A) =>c>(>'c'>,>'d'>,>'e'>)> > cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: c d e a 1 2 3 b 4 5 6 c 7 8 9>
R에서 특수 행렬 만들기
R에서는 행렬() 함수에 전달된 인수를 사용하여 다양한 유형의 행렬을 생성할 수 있습니다.
1. 모든 행과 열이 단일 상수 'k'로 채워지는 행렬:
이러한 R 행렬을 생성하기 위한 구문은 다음과 같습니다.
통사론: 행렬(k, m, n)
매개변수:
케이: 상수
중: 행 수
N: 열 수
예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Matrix having 3 rows and 3 columns> # filled by a single constant 5> print>(>matrix>(5, 3, 3))> |
>
>산출
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 5 5 5 [2,] 5 5 5 [3,] 5 5 5>
2. 대각선 행렬:
대각행렬은 주대각선 밖의 성분이 모두 0인 행렬이다. 이러한 R 행렬을 생성하기 위한 구문은 다음과 같습니다.
통사론: 진단(k, m, n)
매개변수:
케이: 상수/배열
중: 행 수
N: 열 수
예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Diagonal matrix having 3 rows and 3 columns> # filled by array of elements (5, 3, 3)> print>(>diag>(>c>(5, 3, 3), 3, 3))> |
>
>산출
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 5 0 0 [2,] 0 3 0 [3,] 0 0 3>
삼. 단위 행렬:
주대각선의 모든 요소가 1이고 다른 모든 요소가 0인 단위 행렬입니다. 이러한 R 행렬을 생성하기 위한 구문은 다음과 같습니다.
통사론: 진단(k, m, n)
매개변수:
케이: 1
중: 행 수
N: 열 수
예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # special matrices> # Identity matrix having> # 3 rows and 3 columns> print>(>diag>(1, 3, 3))> |
>
>산출
[,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 0 0 [2,] 0 1 0 [3,] 0 0 1>
4. 매트릭스 지표
매트릭스 메트릭은 귀하가 생성한 매트릭스에 대해 알려줍니다. 행렬의 행 수, 열 수, 차원을 알고 싶을 수도 있습니다.
아래 예는 다음 질문에 답하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 행렬의 차원을 어떻게 알 수 있나요?
- 행렬에 몇 개의 행이 있는지 어떻게 알 수 있나요?
- 행렬에는 몇 개의 열이 있습니까?
- 행렬에는 몇 개의 요소가 있습니까?
예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # matrix metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> cat>(>'Dimension of the matrix:
'>)> print>(>dim>(A))> cat>(>'Number of rows:
'>)> print>(>nrow>(A))> cat>(>'Number of columns:
'>)> print>(>ncol>(A))> cat>(>'Number of elements:
'>)> print>(>length>(A))> # OR> print>(>prod>(>dim>(A)))> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Dimension of the matrix: [1] 3 3 Number of rows: [1] 3 Number of columns: [1] 3 Number of elements: [1] ...>
R-행렬의 요소에 액세스
데이터 프레임에서 따르는 것과 동일한 규칙을 사용하여 R 행렬의 요소에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 따라서 행렬이 있고 배열 사이에 쉼표가 있는 대괄호가 뒤따릅니다.
쉼표 앞의 값은 행에 액세스하는 데 사용되고 쉼표 뒤의 값은 열에 액세스하는 데 사용됩니다. 간단한 R 코드를 사용하여 이를 설명하겠습니다.
행에 액세스 중:
아르 자형
세상 최고의 미소
# R program to illustrate> # access rows in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Accessing first and second row> cat>(>'Accessing first and second row
'>)> print>(A[1:2, ])> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing first and second row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6>
열에 액세스:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # access columns in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Accessing first and second column> cat>(>'Accessing first and second column
'>)> print>(A[, 1:2])> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing first and second column [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 2 [2,] 4 5 [3,] 7 8>
R-행렬 요소에 액세스하는 추가 예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # access an entry in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Accessing 2> print>(A[1, 2])> # Accessing 6> print>(A[2, 3])> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 [1] 2 [1] 6>
R에서 부분행렬에 접근하기:
다음을 사용하여 행렬의 부분행렬에 접근할 수 있습니다. 콜론(:) 운영자.
아르 자형
스크립트 쉘 실행
# R program to illustrate> # access submatrices in a matrix> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> cat>(>'Accessing the first three rows and the first two columns
'>)> print>(A[1:3, 1:2])> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 Accessing the first three rows and the first two columns [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 2 [2,] 4 5 [3...>
R-행렬의 요소 수정
R에서는 직접 할당을 통해 행렬의 요소를 수정할 수 있습니다.
예:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # editing elements in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Editing the 3rd rows and 3rd column element> # from 9 to 30> # by direct assignments> A[3, 3] = 30> cat>(>'After edited the matrix
'>)> print>(A)> |
>
다이애나 메리 블랙커
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After edited the matrix [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 30>
R-행렬 연결
행렬 연결은 기존 R 행렬의 행이나 열을 병합하는 것을 의미합니다.
행 연결:
행렬에 대한 행의 연결은 다음을 사용하여 수행됩니다. r바인드() .
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # concatenation of a row in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Creating another 1x3 matrix> B =>matrix>(> >c>(10, 11, 12),> >nrow = 1,> >ncol = 3> )> cat>(>'The 1x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(B)> # Add a new row using rbind()> C =>rbind>(A, B)> cat>(>'After concatenation of a row:
'>)> print>(C)> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 The 1x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 10 11 12 After concatenation of a row: [,1] [,2] [,3...>
열 연결:
열과 행렬의 연결은 다음을 사용하여 수행됩니다. c바인드() .
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # concatenation of a column in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Creating another 3x1 matrix> B =>matrix>(> >c>(10, 11, 12),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 1,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x1 matrix:
'>)> print>(B)> # Add a new column using cbind()> C =>cbind>(A, B)> cat>(>'After concatenation of a column:
'>)> print>(C)> |
>
>산출
The 3x3 matrix: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 The 3x1 matrix: [,1] [1,] 10 [2,] 11 [3,] 12 After concatenation of a column: [,1] [,2] ...>
치수 불일치: 이 행렬 연결을 수행하기 전에 행렬 간의 차원 일관성을 확인해야 합니다.
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # Dimension inconsistency in metrics concatenation> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'The 3x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(A)> # Creating another 1x3 matrix> B =>matrix>(> >c>(10, 11, 12),> >nrow = 1,> >ncol = 3,> )> cat>(>'The 1x3 matrix:
'>)> print>(B)> # This will give an error> # because of dimension inconsistency> C =>cbind>(A, B)> cat>(>'After concatenation of a column:
'>)> print>(C)> |
>
>
산출:
The 3x3 matrix: [, 1] [, 2] [, 3] [1, ] 1 2 3 [2, ] 4 5 6 [3, ] 7 8 9 The 1x3 matrix: [, 1] [, 2] [, 3] [1, ] 10 11 12 Error in cbind(A, B) : number of rows of matrices must match (see arg 2)>
R-행렬에 행과 열 추가하기
R-행렬에 행을 추가하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다. r바인드() 함수를 사용하고 R-행렬에 열을 추가하려면 사용할 수 있습니다. 결합 () 기능.
행 추가
R-행렬에 행을 추가하는 방법에 대한 아래 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
예:
아르 자형
# Create a 3x3 matrix> number <->matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'Before inserting a new row:
'>)> print>(number)> # New row to be inserted> new_row <->c>(10, 11, 12)># Define the new row> # Inserting the new row at the second position> A <->rbind>(number[1, ], new_row, number[-1, ])> cat>(>'
After inserting a new row:
'>)> print>(number)> |
>
>산출
Before inserting a new row: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After inserting a new row: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,]...>
열 추가
R-행렬에 열을 추가하는 방법에 대한 아래 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
아르 자형
# Create a 3x3 matrix> number <->matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'Before adding a new column:
'>)> print>(number)> # New column to be added> new_column <->c>(10, 11, 12)># Define the new column> # Adding the new column at the end> number <->cbind>(number, new_column)> cat>(>'
After adding a new column:
'>)> print>(number)> |
>
>산출
Before adding a new column: [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After adding a new column: new_column [1,] 1 2 3 10 [2,] 4 5 6 1...>
R-행렬의 행과 열 삭제
행이나 열을 삭제하려면 먼저 해당 행이나 열에 액세스한 다음 해당 행이나 열 앞에 음수 기호를 삽입해야 합니다. 이는 해당 행이나 열을 삭제해야 했음을 나타냅니다.
행 삭제:
아르 자형
이진 트리 자바
# R program to illustrate> # row deletion in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'Before deleting the 2nd row
'>)> print>(A)> # 2nd-row deletion> A = A[-2, ]> cat>(>'After deleted the 2nd row
'>)> print>(A)> |
>
>산출
Before deleting the 2nd row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After deleted the 2nd row [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 7 8 9>
열 삭제:
아르 자형
# R program to illustrate> # column deletion in metrics> # Create a 3x3 matrix> A =>matrix>(> >c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9),> >nrow = 3,> >ncol = 3,> >byrow =>TRUE> )> cat>(>'Before deleting the 2nd column
'>)> print>(A)> # 2nd-row deletion> A = A[, -2]> cat>(>'After deleted the 2nd column
'>)> print>(A)> |
>
>산출
Before deleting the 2nd column [,1] [,2] [,3] [1,] 1 2 3 [2,] 4 5 6 [3,] 7 8 9 After deleted the 2nd column [,1] [,2] [1,] 1 3 [2,] 4 6 [3,] 7 9>
우리는 R-행렬과 새 행과 열 추가, 행과 열 삭제, 행렬 병합 등과 같은 기본 작업에 대해 논의했습니다.
이것이 R의 행렬을 이해하는 데 도움이 되기를 바랍니다. 이제 프로젝트에서 R-행렬을 편안하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
또한 확인하십시오:
- R – 배열
- R – 목록
- R – 튜플
