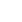
숫자가 주어지면 N 1부터 n까지의 각 숫자로 균등하게 나누어지는 가장 작은 수를 찾으세요.
예:
Input : n = 4 Output : 12 Explanation : 12 is the smallest numbers divisible by all numbers from 1 to 4 Input : n = 10 Output : 2520 Input : n = 20 Output : 232792560
주의깊게 관찰해보면 연령 이어야 합니다 1부터 n까지의 숫자의 LCM .
1부터 n까지의 숫자의 LCM을 찾으려면 -
- ans = 1을 초기화합니다.
- i = 1부터 i = n까지 모든 숫자를 반복합니다.
i 번째 반복에서 ans = LCM(1 2 … .. i) . 이 작업은 다음과 같이 쉽게 수행할 수 있습니다. LCM(1 2 …. i) = LCM(an i) .
따라서 i번째 반복에서 우리는 다음을 수행해야 합니다.
ans = LCM(ans i) = ans * i / gcd(ans i) [Using the below property a*b = gcd(ab) * lcm(ab)]
메모 : C++ 코드에서 대답은 long long 제한에서도 정수 제한을 빠르게 초과합니다.
아래는 로직의 구현입니다.
C++
// C++ program to find smallest number evenly divisible by // all numbers 1 to n #include
// Java program to find the smallest number evenly divisible by // all numbers 1 to n class GFG{ static long gcd(long a long b) { if(a%b != 0) return gcd(ba%b); else return b; } // Function returns the lcm of first n numbers static long lcm(long n) { long ans = 1; for (long i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = (ans * i)/(gcd(ans i)); return ans; } // Driver program to test the above function public static void main(String []args) { long n = 20; System.out.println(lcm(n)); } }
# Python program to find the smallest number evenly # divisible by all number 1 to n import math # Returns the lcm of first n numbers def lcm(n): ans = 1 for i in range(1 n + 1): ans = int((ans * i)/math.gcd(ans i)) return ans # main n = 20 print (lcm(n))
// C# program to find smallest number // evenly divisible by // all numbers 1 to n using System; public class GFG{ static long gcd(long a long b) { if(a%b != 0) return gcd(ba%b); else return b; } // Function returns the lcm of first n numbers static long lcm(long n) { long ans = 1; for (long i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = (ans * i)/(gcd(ans i)); return ans; } // Driver program to test the above function static public void Main (){ long n = 20; Console.WriteLine(lcm(n)); } //This code is contributed by akt_mit }
// Javascript program to find the smallest number evenly divisible by // all numbers 1 to n function gcd(a b) { if(a%b != 0) return gcd(ba%b); else return b; } // Function returns the lcm of first n numbers function lcm(n) { let ans = 1; for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans = (ans * i)/(gcd(ans i)); return ans; } // function call let n = 20; console.log(lcm(n));
// Note: This code is not working on GFG-IDE // because gmp libraries are not supported // PHP program to find smallest number // evenly divisible by all numbers 1 to n // Function returns the lcm // of first n numbers function lcm($n) { $ans = 1; for ($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++) $ans = ($ans * $i) / (gmp_gcd(strval(ans) strval(i))); return $ans; } // Driver Code $n = 20; echo lcm($n); // This code is contributed by mits ?> 산출
232792560
시간 복잡도: O(n log2n) C++에서 _gcd(ab)의 복잡성은 log2n이고 이는 루프에서 n번 실행되기 때문입니다.
보조 공간: O(1)
위의 솔루션은 단일 입력에 대해 잘 작동합니다. 그러나 입력이 여러 개인 경우 에라토스테네스의 체를 사용하여 모든 소인수를 저장하는 것이 좋습니다. Sieve 기반 접근 방식은 아래 기사를 참조하세요.
접근 방식 : [사용 에라토스테네스의 체 ]
보다 효율적인 방법으로 처음 'n' 숫자로 나누어지는 가장 작은 숫자를 찾는 문제를 해결하기 위해 에라토스테네스의 체를 사용하여 'n'까지 소수를 미리 계산할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 이러한 소수를 사용하여 'n'보다 작거나 같은 각 소수의 최고 거듭제곱을 고려함으로써 최소 공배수(LCM)를 보다 효율적으로 계산할 수 있습니다.
단계별 접근 방식:
- 최대 n까지 소수 생성: 에라토스테네스의 체를 사용하여 'n'까지의 모든 소수를 찾아보세요.
- 다음 소수를 사용하여 LCM을 계산합니다. 각 소수에 대해 'n'보다 작거나 같은 소수의 최고 거듭제곱을 결정합니다. 이러한 가장 높은 거듭제곱을 곱하여 LCM을 얻습니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++#include
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class SmallestMultiple { // Function to generate all prime numbers up to n using // the Sieve of Eratosthenes public static List<Integer> sieveOfEratosthenes(int n) { boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { isPrime[i] = true; } int p = 2; while (p * p <= n) { if (isPrime[p]) { for (int i = p * p; i <= n; i += p) { isPrime[i] = false; } } p++; } List<Integer> primeNumbers = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { if (isPrime[i]) { primeNumbers.add(i); } } return primeNumbers; } // Function to find the smallest number divisible by all // numbers from 1 to n public static long smallestMultiple(int n) { List<Integer> primes = sieveOfEratosthenes(n); long lcm = 1; for (int prime : primes) { // Calculate the highest power of the prime that // is <= n int power = 1; while (Math.pow(prime power + 1) <= n) { power++; } lcm *= Math.pow(prime power); } return lcm; } public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 20; System.out.println(smallestMultiple(n)); } }
import math def sieve_of_eratosthenes(n): '''Generate all prime numbers up to n.''' is_prime = [True] * (n + 1) p = 2 while (p * p <= n): if (is_prime[p] == True): for i in range(p * p n + 1 p): is_prime[i] = False p += 1 prime_numbers = [p for p in range(2 n + 1) if is_prime[p]] return prime_numbers def smallest_multiple(n): '''Find the smallest number divisible by all numbers from 1 to n.''' primes = sieve_of_eratosthenes(n) lcm = 1 for prime in primes: # Calculate the highest power of the prime that is <= n power = 1 while prime ** (power + 1) <= n: power += 1 lcm *= prime ** power return lcm # Example usage: n = 20 print(smallest_multiple(n))
// Function to generate all prime numbers up to n using the // Sieve of Eratosthenes function sieveOfEratosthenes(n) { let isPrime = new Array(n + 1).fill(true); let p = 2; while (p * p <= n) { if (isPrime[p]) { for (let i = p * p; i <= n; i += p) { isPrime[i] = false; } } p++; } let primeNumbers = []; for (let p = 2; p <= n; p++) { if (isPrime[p]) { primeNumbers.push(p); } } return primeNumbers; } // Function to find the smallest number divisible by all // numbers from 1 to n function smallestMultiple(n) { let primes = sieveOfEratosthenes(n); let lcm = 1; for (let prime of primes) { // Calculate the highest power of the prime that is // <= n let power = 1; while (Math.pow(prime power + 1) <= n) { power++; } lcm *= Math.pow(prime power); } return lcm; } // Example usage: let n = 20; console.log(smallestMultiple(n));
산출
The smallest number divisible by all numbers from 1 to 20 is 232792560
시간 복잡도: O(n로그로그인)
보조 공간: 에)
