Java의 TreeMap은 구현에 사용됩니다. 지도 인터페이스 AbstractMap 클래스와 함께 NavigableMap이 있습니다. 맵은 키의 자연스러운 순서에 따라 정렬됩니다. 비교기 사용되는 생성자에 따라 지도 생성 시 제공됩니다. 이는 키-값 쌍을 정렬하고 저장하는 효율적인 방법임이 입증되었습니다. 트리맵에 의해 유지되는 저장 순서는 명시적 비교자에 관계없이 다른 정렬된 맵과 마찬가지로 같음과 일치해야 합니다. 여러 스레드에서 동시에 맵에 액세스하고 스레드 중 하나 이상이 맵을 구조적으로 수정하는 경우 외부에서 동기화해야 한다는 점에서 트리맵 구현은 동기화되지 않습니다.
Java의 TreeMap은 java.util.SortedMap 인터페이스의 구체적인 구현입니다. 이는 키-값 쌍의 정렬된 컬렉션을 제공합니다. 여기서 키는 자연 순서 또는 생성자에 전달된 사용자 지정 비교기에 따라 정렬됩니다.
TreeMap은 자체 균형 이진 검색 트리 유형인 Red-Black 트리를 사용하여 구현됩니다. 이는 평균 시간 복잡도 O(log n)로 요소 추가, 제거 및 검색과 같은 일반적인 작업에 효율적인 성능을 제공합니다.
다음은 TreeMap 클래스를 사용하는 방법에 대한 예입니다.
자바
import> java.util.Map;> import> java.util.TreeMap;> public> class> Main {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args) {> >Map treeMap =>new> TreeMap();> >// Adding elements to the tree map> >treeMap.put(>'A'>,>1>);> >treeMap.put(>'C'>,>3>);> >treeMap.put(>'B'>,>2>);> >// Getting values from the tree map> >int> valueA = treeMap.get(>'A'>);> >System.out.println(>'Value of A: '> + valueA);> >// Removing elements from the tree map> >treeMap.remove(>'B'>);> >// Iterating over the elements of the tree map> >for> (String key : treeMap.keySet()) {> >System.out.println(>'Key: '> + key +>', Value: '> + treeMap.get(key));> >}> >}> }> |
>
>산출
Value of A: 1 Key: A, Value: 1 Key: C, Value: 3>
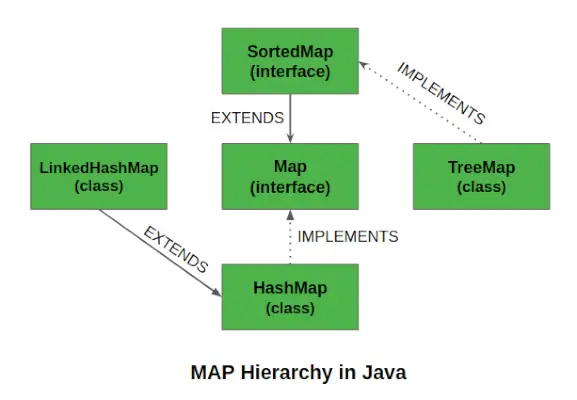
트리맵의 특징
트리맵의 몇 가지 중요한 기능은 다음과 같습니다.
- 이 수업은 자바 컬렉션 뼈대.
- 클래스가 구현합니다. 지도 인터페이스 NavigableMap , SortedMap 포함하고 AbstractMap 클래스를 확장합니다.
- Java의 TreeMap은 Map과 같은 null 키를 허용하지 않으므로 NullPointerException이 발생합니다. 그러나 여러 null 값이 다른 키와 연결될 수 있습니다.
- 이 클래스와 해당 뷰의 메서드에서 반환된 항목 쌍은 생성 당시 매핑의 스냅샷을 나타냅니다. Entry.setValue 메소드를 지원하지 않습니다.
이제 앞으로 나아가서 동기화된 TreeMap에 대해 논의하겠습니다. TreeMap의 구현은 동기화되지 않습니다. 이는 여러 스레드가 동시에 트리 집합에 액세스하고 스레드 중 적어도 하나가 집합을 수정하는 경우 외부에서 동기화되어야 함을 의미합니다. 이는 일반적으로 Collections.synchronizedSortedMap 메소드를 사용하여 수행됩니다. 이는 세트에 대한 실수로 비동기화 액세스를 방지하기 위해 생성 시 수행하는 것이 가장 좋습니다. 이는 다음과 같이 수행할 수 있습니다.
SortedMap m = Collections.synchronizedSortedMap(new TreeMap(...));>
괴짜 여러분, 이제 TreeMap이 내부적으로 어떻게 작동하는지 궁금하시겠죠?
키 세트와 값을 가져오는 동안 TreeMap의 메서드는 본질적으로 실패하지 않는 Iterator를 반환합니다. 따라서 동시 수정은 ConcurrentModificationException을 발생시킵니다. TreeMap은 레드-블랙 트리 데이터 구조를 기반으로 합니다.
트리의 각 노드에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 3개의 변수( K 키=키, V 값=값, 부울 색상=색상 )
- 3개의 참고문헌( 왼쪽 항목 = 왼쪽, 오른쪽 항목 = 오른쪽, 상위 항목 = 상위 )
TreeMap의 생성자
TreeMap을 생성하려면 TreeMap 클래스의 객체를 생성해야 합니다. TreeMap 클래스는 TreeMap을 생성할 수 있는 다양한 생성자로 구성됩니다. 이 클래스에서 사용할 수 있는 생성자는 다음과 같습니다.
- 트리맵()
- TreeMap(비교기 구성 요소)
- 트리맵(Map M)
- 트리맵(SortedMap sm)
다음과 같이 모든 생성자를 구현하는 것과 함께 개별적으로 논의하겠습니다.
생성자 1: 트리맵()
이 생성자는 키의 자연 순서를 사용하여 정렬되는 빈 트리맵을 작성하는 데 사용됩니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the Default Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // TreeMapImplementation> public> class> GFG {> >// Method 1> >// To show TreeMap constructor> >static> void> Example1stConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >tree_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >tree_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >tree_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap() constructor:
'>);> >// Calling constructor> >Example1stConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
TreeMap using TreeMap() constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> 생성자 2: TreeMap(비교기 구성 요소)
이 생성자는 요소에 정렬 순서의 외부 사양이 필요한 빈 TreeMap 개체를 만드는 데 사용됩니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using Comparator Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Class 1> // Helper class representing Student> class> Student {> >// Attributes of a student> >int> rollno;> >String name, address;> >// Constructor> >public> Student(>int> rollno, String name, String address)> >{> >// This keyword refers to current object itself> >this>.rollno = rollno;> >this>.name = name;> >this>.address = address;> >}> >// Method of this class> >// To print student details> >public> String toString()> >{> >return> this>.rollno +>' '> +>this>.name +>' '> >+>this>.address;> >}> }> // Class 2> // Helper class - Comparator implementation> class> Sortbyroll>implements> Comparator {> >// Used for sorting in ascending order of> >// roll number> >public> int> compare(Student a, Student b)> >{> >return> a.rollno - b.rollno;> >}> }> // Class 3> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Calling constructor inside main()> >static> void> Example2ndConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(> >new> Sortbyroll());> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>111>,>'bbbb'>,>'london'>),>2>);> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>131>,>'aaaa'>,>'nyc'>),>3>);> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>121>,>'cccc'>,>'jaipur'>),>1>);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(Comparator)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example2ndConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
TreeMap using TreeMap(Comparator) constructor: TreeMap: {111 bbbb london=2, 121 cccc jaipur=1, 131 aaaa nyc=3}> 생성자 3: 트리맵(Map M)
이 생성자는 키의 자연 순서를 사용하여 정렬되는 지정된 맵 M의 항목으로 TreeMap을 초기화하는 데 사용됩니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the Default Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> public> class> TreeMapImplementation {> >// Method 1> >// To illustrate constructor> >static> void> Example3rdConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty HashMap> >Map hash_map> >=>new> HashMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >hash_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >hash_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >hash_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >hash_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >hash_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Creating the TreeMap using the Map> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(hash_map);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(Map)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example3rdConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
TreeMap using TreeMap(Map) constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> 생성자 4: 트리맵(SortedMap sm)
이 생성자는 주어진 정렬 맵과 동일한 순서로 저장될 주어진 정렬 맵의 항목으로 TreeMap을 초기화하는 데 사용됩니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the SortedMap Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // TreeMapImplementation> public> class> GFG {> >// Method> >// To show TreeMap(SortedMap) constructor> >static> void> Example4thConstructor()> >{> >// Creating a SortedMap> >SortedMap sorted_map> >=>new> ConcurrentSkipListMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >sorted_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >sorted_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >sorted_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >sorted_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >sorted_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Creating the TreeMap using the SortedMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(sorted_map);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(SortedMap)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example4thConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
TreeMap using TreeMap(SortedMap) constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> TreeMap 클래스의 메서드
| 방법 | 수행된 작업 |
|---|---|
| 분명한() | 이 메서드는 이 TreeMap에서 모든 매핑을 제거하고 맵을 지웁니다. |
| 클론() | 이 메서드는 이 TreeMap의 얕은 복사본을 반환합니다. |
| containKey(객체 키) | 이 맵에 지정된 키에 대한 매핑이 포함되어 있으면 true를 반환합니다. |
| containValue(객체 값) | 이 맵이 하나 이상의 키를 지정된 값에 매핑하는 경우 true를 반환합니다. |
| 엔트리셋() | 이 지도에 포함된 매핑의 집합 보기를 반환합니다. |
| 첫 번째 키() | 현재 정렬된 맵에 있는 첫 번째(가장 낮은) 키를 반환합니다. |
| get(객체 키) | 이 맵이 지정된 키를 매핑하는 값을 반환합니다. |
| headMap(객체 키_값) | 이 메소드는 매개변수 key_value보다 엄격하게 작은 지도 부분의 뷰를 반환합니다. |
| 키세트() | 이 메서드는 트리맵에 포함된 키의 Set 보기를 반환합니다. |
| 마지막키() | 현재 정렬된 맵에 있는 마지막(가장 높은) 키를 반환합니다. |
| put(객체 키, 객체 값) | 이 메소드는 지도에 매핑을 삽입하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| putAll(지도 맵) | 지정된 맵의 모든 매핑을 이 맵에 복사합니다. |
| 제거(객체 키) | 존재하는 경우 이 TreeMap에서 이 키에 대한 매핑을 제거합니다. |
| 크기() | 이 맵의 키-값 매핑 수를 반환합니다. |
| subMap((K startKey, K endKey) | 이 메소드는 키 범위가 startKey(포함)부터 endKey(제외)까지인 이 맵의 일부를 반환합니다. |
| 값() | 이 맵에 포함된 값의 컬렉션 뷰를 반환합니다. |
구현: 아래의 다음 프로그램은 TreeMap을 생성, 삽입 및 탐색하는 방법을 더 잘 보여줍니다.
삽화:
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Operations in TreeMap> // Such as Creation, insertion> // searching, and traversal> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // Implementation of TreeMap> public> class> GFG {> >// Declaring a TreeMap> >static> TreeMap tree_map;> >// Method 1> >// To create TreeMap> >static> void> create()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >tree_map =>new> TreeMap();> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap successfully'> >+>' created'>);> >}> >// Method 2> >// To Insert values in the TreeMap> >static> void> insert()> >{> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >tree_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >tree_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >tree_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'
Elements successfully'> >+>' inserted in the TreeMap'>);> >}> >// Method 3> >// To search a key in TreeMap> >static> void> search(>int> key)> >{> >// Checking for the key> >System.out.println(>'
Is key ''> + key> >+>'' present? '> >+ tree_map.containsKey(key));> >}> >// Method 4> >// To search a value in TreeMap> >static> void> search(String value)> >{> >// Checking for the value> >System.out.println(>'
Is value ''> + value> >+>'' present? '> >+ tree_map.containsValue(value));> >}> >// Method 5> >// To display the elements in TreeMap> >static> void> display()> >{> >// Displaying the TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'
Displaying the TreeMap:'>);> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 6> >// To traverse TreeMap> >static> void> traverse()> >{> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'
Traversing the TreeMap:'>);> >for> (Map.Entry e :> >tree_map.entrySet())> >System.out.println(e.getKey() +>' '> >+ e.getValue());> >}> >// Method 6> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Calling above defined methods inside main()> >// Creating a TreeMap> >create();> >// Inserting the values in the TreeMap> >insert();> >// Search key '50' in the TreeMap> >search(>50>);> >// Search value 'Geeks' in the TreeMap> >search(>'Geeks'>);> >// Display the elements in TreeMap> >display();> >// Traversing the TreeMap> >traverse();> >}> }> |
>
>산출
TreeMap successfully created Elements successfully inserted in the TreeMap Is key '50' present? false Is value 'Geeks' present? true Displaying the TreeMap: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You} Traversing the TreeMap: 10 Geeks 15 4 20 Geeks 25 Welcomes 30 You> TreeMap에서 다양한 작업 수행
Java 1.5에 Generic이 도입된 이후에는 TreeMap에 저장할 수 있는 객체 유형을 제한하는 것이 가능해졌습니다. 이제 TreeMap에서 자주 사용되는 몇 가지 작업을 수행하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
작업 1: 요소 추가
TreeMap에 요소를 추가하려면 put() 메소드를 사용할 수 있습니다. 그러나 삽입 순서는 TreeMap에 유지되지 않습니다. 내부적으로 모든 요소에 대해 키를 비교하고 오름차순으로 정렬합니다.
예
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Addition of Elements> // in TreeMap using put() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Default Initialization of a TreeMap> >TreeMap tm1 =>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in TreeMap> >// using put() method> >tm1.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm1.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >tm1.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// Initialization of a TreeMap using Generics> >TreeMap tm2> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in TreeMap> >// again using put() method> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>3>),>'Geeks'>);> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>2>),>'For'>);> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>1>),>'Geeks'>);> >// Printing the elements of both TreeMaps> >// Map 1> >System.out.println(tm1);> >// Map 2> >System.out.println(tm2);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks} {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}> 작업 2: 요소 변경
요소를 추가한 후 요소를 변경하려면 put() 메서드를 사용하여 요소를 다시 추가하면 됩니다. 트리맵의 요소는 키를 사용하여 인덱싱되므로 변경하려는 키에 대해 업데이트된 값을 삽입하기만 하면 키 값을 변경할 수 있습니다.
예
자바
// Java program to Illustrate Updation of Elements> // in TreeMap using put() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in Map> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// Print all current elements in map> >System.out.println(tm);> >// Inserting the element at specified> >// corresponding to specified key> >tm.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >// Printing the updated elements of Map> >System.out.println(tm);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks} {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}> 작업 3: 요소 제거
TreeMap에서 요소를 제거하려면 Remove() 메서드를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 메소드는 키 값을 가져와 맵에 키가 있는 경우 이 트리맵에서 키에 대한 매핑을 제거합니다.
예
자바
Java의 csv 파일에서 읽기
// Java program to Illustrate Removal of Elements> // in TreeMap using remove() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>4>,>'For'>);> >// Printing all elements of Map> >System.out.println(tm);> >// Removing the element corresponding to key> >tm.remove(>4>);> >// Printing updated TreeMap> >System.out.println(tm);> >}> }> |
>
>산출
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For} {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}> 작업 4: TreeMap을 통한 반복
맵을 반복하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다. 가장 유명한 방법은 for-each 루프 그리고 열쇠를 얻으세요. 키 값은 다음을 사용하여 찾습니다. getValue() 메소드 .
예
자바
// Java Program to Illustrate Iterating over TreeMap> // using> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// For-each loop for traversal over Map> >// via entrySet() Method> >for> (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) {> >int> key = (>int>)mapElement.getKey();> >// Finding the value> >String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();> >// Printing the key and value> >System.out.println(key +>' : '> + value);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>산출
1 : Geeks 2 : For 3 : Geeks>
트리맵의 장점:
- 정렬 순서: TreeMap은 키의 자연 순서 또는 생성자에 전달된 사용자 정의 Comparator를 기반으로 요소의 정렬 순서를 제공합니다. 이는 특정 순서로 요소를 검색해야 하는 상황에서 유용합니다.
- 예측 가능한 반복 순서: TreeMap의 요소는 정렬된 순서로 저장되므로 반복 중에 요소가 반환되는 순서를 예측할 수 있으므로 특정 순서로 요소를 처리하는 알고리즘을 더 쉽게 작성할 수 있습니다.
- 검색 성능: TreeMap은 Map 인터페이스의 효율적인 구현을 제공하므로 로그 시간에 요소를 검색할 수 있으므로 요소를 빠르게 검색해야 하는 검색 알고리즘에 유용합니다.
- 자체 균형(Self-balancing): TreeMap은 자체 균형 이진 검색 트리 유형인 Red-Black 트리를 사용하여 구현됩니다. 이는 요소 추가, 제거, 검색은 물론 요소의 정렬된 순서 유지를 위한 효율적인 성능을 제공합니다.
트리맵의 단점:
- 요소 삽입 속도가 느림: TreeMap에 요소를 삽입하는 것은 일반 맵에 요소를 삽입하는 것보다 느릴 수 있습니다. 왜냐하면 TreeMap은 해당 요소의 정렬된 순서를 유지해야 하기 때문입니다.
- 키 제한사항: TreeMap의 키는 java.lang.Comparable 인터페이스를 구현해야 하거나 사용자 정의 Comparator를 제공해야 합니다. 이 인터페이스를 구현하지 않는 사용자 정의 키를 사용해야 하는 경우 이는 제한사항이 될 수 있습니다.
참고 도서:
Maurice Naftalin과 Philip Wadler의 Java 컬렉션. 이 책은 TreeMap을 포함하여 Java 컬렉션 프레임워크에 대한 포괄적인 개요를 제공합니다.
David Flanagan이 쓴 Java in 간단히 말해서. 이 책은 TreeMap을 포함한 Java의 핵심 기능에 대한 빠른 참조를 제공합니다.
Maurice Naftalin과 Philip Wadler가 작성한 Java Generics 및 컬렉션. 이 책은 TreeMap을 포함하여 Java의 제네릭과 컬렉션에 대한 포괄적인 가이드를 제공합니다.
