그만큼 asList() 의 방법 java.util.Arrays 클래스는 지정된 배열이 지원하는 고정 크기 목록을 반환하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 방법은 다음과 같은 역할을 합니다. 배열 기반 API와 컬렉션 기반 API 간의 브리지 , Collection.toArray()와 함께 사용됩니다. 반환된 목록은 직렬화 가능하며 RandomAccess를 구현합니다.
팁: 이는 O(1) 시간에 실행됩니다.
김프 변경 색상
통사론:
public static List asList(T... a)>
매개변수: 이 방법은 배열 List로 변환해야 합니다. 여기서는 ...로 알려져 있습니다. 가변 인자 이는 매개변수의 배열이며 객체 배열 매개변수와 유사하게 작동합니다.
특별 참고 사항: 기본 데이터 유형(int, float 등)의 경우 배열 유형은 래퍼 클래스(Integer,Float 등)여야 합니다. 즉, int a[]를 전달할 수 없지만 Integer a[]를 전달할 수 있습니다. int a[]를 전달하면 이 함수는 List가 아닌 List를 반환합니다. 이 경우 오토박싱이 발생하지 않고 int a[] 자체가 객체로 식별되고 list 대신 int 배열의 List가 반환되기 때문입니다. 이는 다양한 컬렉션 함수에서 오류를 발생시킵니다.
반환 값: 이 메소드는 목록보기 지정된 배열의
예시 1:
자바
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>산출
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
예시 2:
자바
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>산출
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
예시 3:
자바
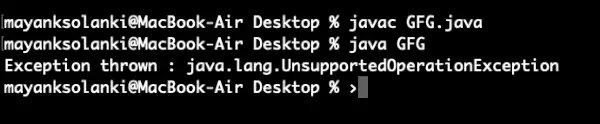
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
문자열을 int로 구문 분석
>
산출: