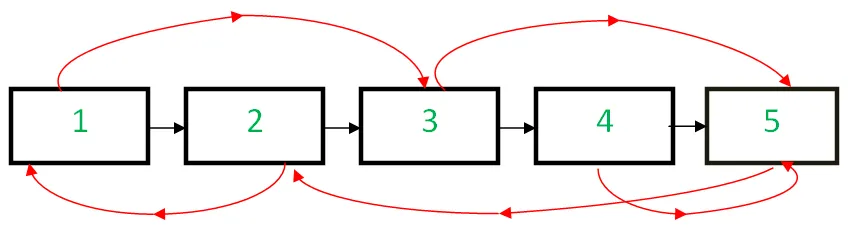
주어진 연결리스트 크기의 N 각 노드에는 두 개의 링크가 있습니다. 다음 포인터 다음 노드를 가리키고 무작위 포인터 목록의 임의의 노드에. 작업은 O(1) 공간, 즉 추가 공간 없이 이 연결 목록의 복제본을 만드는 것입니다.
예:
입력: 아래 링크리스트의 선두
산출: 원래 목록과 동일한 새 연결 목록입니다.
[예상 접근법] 노드를 제자리에 삽입함으로써 – O(3n) 시간과 O(1) 공간
아이디어는 노드의 복제본을 생성하고 별도의 해시 테이블에 저장하는 대신 원래 노드와 다음 노드 사이에 삽입할 수 있다는 것입니다. 이제 대체 위치에 새 노드가 생깁니다. 이제 노드 X 그 중복은 X->다음 복제본의 임의 포인터는 다음을 가리켜야 합니다. X->임의->다음 (그것은 중복이므로 X->랜덤 ). 따라서 전체 연결 목록을 반복하여 모든 복제된 노드의 임의 포인터를 업데이트한 다음 다시 반복하여 원래 연결 목록과 복제된 연결 목록을 분리합니다.
vlc로 유튜브 다운로드
아이디어를 구현하려면 아래에 언급된 단계를 따르세요.
- 사본 만들기 노드 1 그리고 그 사이에 넣어주세요 노드 1 그리고 노드 2 원래 Linked List에서 복사본을 만듭니다. 노드 2 그리고 그 사이에 넣어주세요 2 nd 그리고 3 rd 노드 등등. N 뒤에 N의 복사본을 추가하세요.일마디
- 무작위 포인터를 업데이트하여 복제 노드를 연결합니다.
- 다음 포인터를 업데이트하여 복제된 연결 목록을 원본 목록에서 분리합니다.
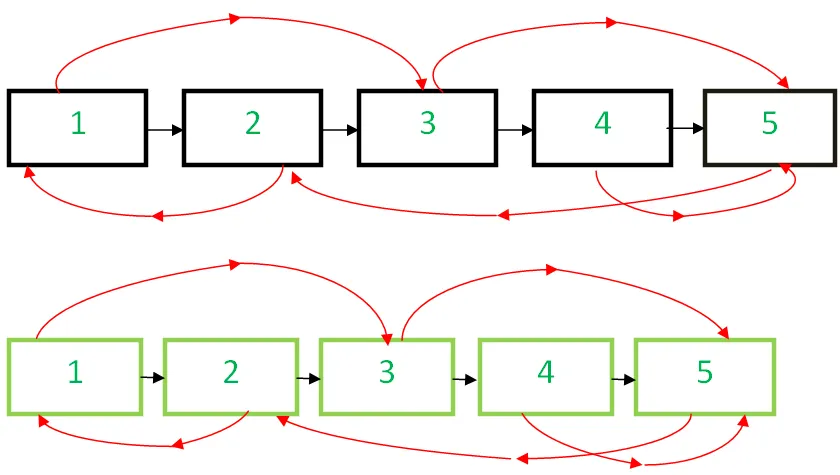
위의 접근 방식을 적용한 경우의 구현은 다음과 같습니다.
C++// C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place #include
// Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { int data; Node next random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.random != null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original and cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + '('); if (head.random != null) { System.out.print(head.random.data); } else { System.out.print('null'); } System.out.print(')'); if (head.next != null) { System.out.print(' -> '); } head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println('Original linked list:'); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList); } }
# Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def clone_linked_list(head): if head is None: return None # Create new nodes and insert them next to # the original nodes curr = head while curr is not None: new_node = Node(curr.data) new_node.next = curr.next curr.next = new_node curr = new_node.next # Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head while curr is not None: if curr.random is not None: curr.next.random = curr.random.next curr = curr.next.next # Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head cloned_head = head.next clone = cloned_head while clone.next is not None: # Update the next nodes of original node # and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next clone.next = clone.next.next # Move pointers of original as well as # cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next clone = clone.next curr.next = None clone.next = None return cloned_head # Function to print the linked list def print_list(head): while head is not None: print(f'{head.data}(' end='') if head.random: print(f'{head.random.data})' end='') else: print('null)' end='') if head.next is not None: print(' -> ' end='') head = head.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print('Original linked list:') print_list(head) # Function call cloned_list = clone_linked_list(head) print('Cloned linked list:') print_list(cloned_list)
// C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int Data; public Node next Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = Random = null; } } class GfG { static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.Data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.Random != null) curr.next.Random = curr.Random.next; curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + '('); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data + ')'); else Console.Write('null)'); if (head.next != null) Console.Write(' -> '); head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } public static void Main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.next.next; head.next.Random = head; head.next.next.Random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.Random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.Random = head.next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine('Original linked list:'); PrintList(head); Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine('Cloned linked list:'); PrintList(clonedList); } }
// JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } function cloneLinkedList(head) { if (head === null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the // original nodes let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { let newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.random !== null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; let clonedHead = head.next; let clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next !== null) { // Update the next nodes of original node and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ''; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + '('; result += head.random ? head.random.data : 'null'; result += ')'; if (head.next !== null) { result += ' -> '; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log('Original linked list:'); printList(head); let clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList);
산출
Original linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
시간 복잡도: O(3n) 연결리스트를 세 번 순회하기 때문입니다.
보조 공간: O(1) 복제된 모든 노드를 원래 연결 목록 자체에 저장하므로 추가 공간이 필요하지 않습니다.