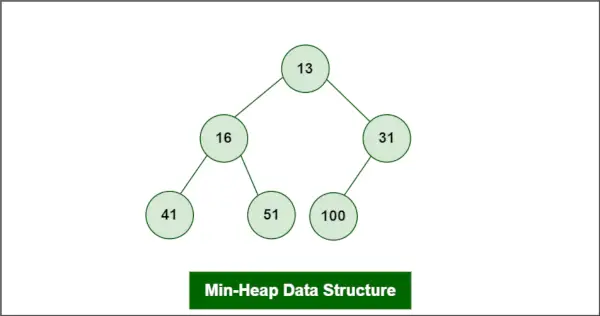
ㅏ 최소 힙 의 유형으로 정의됩니다. 힙 데이터 구조는 데이터 정렬, 검색 및 구성을 비롯한 다양한 목적으로 컴퓨터 과학에서 일반적으로 사용되는 이진 트리 유형입니다.
자바 문자열의 값
최소 힙 소개 - 데이터 구조 및 알고리즘 튜토리얼
최소 힙의 목적 및 사용 사례:
- 우선순위 대기열 구현: 힙 데이터 구조의 주요 용도 중 하나는 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 것입니다.
- Dijkstra의 알고리즘 : Dijkstra 알고리즘은 그래프에서 두 노드 사이의 최단 경로를 찾는 최단 경로 알고리즘입니다. 최소 힙은 소스 노드로부터 가장 가까운 거리에 있는 방문하지 않은 노드를 추적하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 정렬: 최소 힙은 요소 컬렉션을 오름차순으로 효율적으로 정렬하는 정렬 알고리즘으로 사용될 수 있습니다.
- 중앙값 결과: 최소 힙을 사용하면 숫자 스트림의 중앙값을 효율적으로 찾을 수 있습니다. 하나의 최소 힙을 사용하여 숫자의 더 큰 절반을 저장하고 하나의 최대 힙을 사용하여 더 작은 절반을 저장할 수 있습니다. 중앙값은 최소 힙의 루트가 됩니다.
다양한 언어의 최소 힙 데이터 구조:
1. C++의 최소 힙
최소 힙은 다음을 사용하여 구현할 수 있습니다. 우선순위_큐 표준 템플릿 라이브러리(STL)의 컨테이너입니다. 그만큼 우선순위_큐 컨테이너는 각 요소에 연관된 우선순위가 있는 대기열과 같은 데이터 구조에 요소를 저장하는 방법을 제공하는 컨테이너 어댑터 유형입니다.
통사론 :
C++ priority_queue < int, vector , 보다 큰 > 최소H;>
2. Java의 최소 힙
Java에서는 다음을 사용하여 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있습니다. 우선순위 대기열 수업 java.util 패키지 . PriorityQueue 클래스는 각 요소에 연관된 우선순위가 있는 대기열과 같은 데이터 구조에 요소를 저장하는 방법을 제공하는 우선순위 대기열입니다.
통사론 :
자바 PriorityQueue minHeap = 새로운 PriorityQueue ();>
삼. Python의 최소 힙
Python에서는 다음을 사용하여 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있습니다. 힙 힙 구현을 위한 기능을 제공하는 모듈입니다. 구체적으로, 힙 모듈은 힙 데이터 구조를 생성하고 조작하는 방법을 제공합니다.
통사론:
파이썬 heap = [] heapify(heap)>
4. C#의 최소 힙
C#에서는 다음의 PriorityQueue 클래스를 사용하여 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있습니다. System.Collections.Generic 네임스페이스 . PriorityQueue 클래스는 각 요소에 연관된 우선순위가 있는 대기열과 같은 데이터 구조에 요소를 저장하는 방법을 제공하는 우선순위 대기열입니다.
통사론:
씨# var minHeap = new PriorityQueue ();>
5. JavaScript의 최소 힙
최소 힙은 모든 노드가 해당 하위 노드보다 작거나 같은 값을 갖는 이진 트리입니다. JavaScript에서는 배열을 사용하여 최소 힙을 구현할 수 있습니다. 여기서 첫 번째 요소는 루트 노드를 나타내고 노드의 하위 항목은 인덱스를 나타냅니다. 나 인덱스에 위치 2i+1 그리고 2i+2.
통사론:
자바스크립트 const minHeap = new MinHeap();>
최소 힙과 최대 힙의 차이점:
|
| 최소 힙 | 최대 힙 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 최소 힙에서 루트 노드에 있는 키는 모든 하위 노드에 있는 키보다 작거나 같아야 합니다. | Max-Heap에서 루트 노드에 있는 키는 모든 하위 노드에 있는 키보다 크거나 같아야 합니다. |
| 2. | 최소 힙에서는 최소 키 요소가 루트에 존재합니다. 문자열과 비교 | Max-Heap에서는 최대 키 요소가 루트에 존재합니다. |
| 삼. | 최소 힙은 오름차순 우선순위를 사용합니다. | Max-Heap은 내림차순 우선순위를 사용합니다. |
| 4. | Min-Heap을 구성할 때 가장 작은 요소가 우선순위를 갖습니다. | Max-Heap 구성에서는 가장 큰 요소가 우선순위를 갖습니다. |
| 5. | 최소 힙에서는 가장 작은 요소가 힙에서 가장 먼저 팝됩니다. | Max-Heap에서는 가장 큰 요소가 힙에서 가장 먼저 팝됩니다. |
최소 힙 데이터 구조의 내부 구현:
ㅏ 최소 힙은 일반적으로 배열로 표시됩니다. .
- 루트 요소는 다음 위치에 있습니다. 도착[0] .
- 임의의 i번째 노드에 대해 도착[i] :
- 도착[(i -1) / 2] 부모 노드를 반환합니다.
- Arr[(2 * i) + 1] 왼쪽 자식 노드를 반환합니다.
- Arr[(2 * i) + 2] 오른쪽 자식 노드를 반환합니다.
최소 힙의 내부 구현에는 3가지 주요 단계가 필요합니다.
- 삽입 : 최소 힙에 요소를 삽입하려면 먼저 요소를 배열 끝에 추가한 다음 올바른 위치에 올 때까지 요소를 상위 요소와 반복적으로 교체하여 힙 속성을 조정합니다.
- 삭제 : 최소 힙에서 최소 요소를 제거하려면 먼저 루트 노드를 배열의 마지막 요소와 바꾸고, 마지막 요소를 제거한 다음, 요소가 배열에 포함될 때까지 가장 작은 자식 요소와 반복적으로 교체하여 힙 속성을 조정합니다. 올바른 위치.
- 힙파이 : heapify 작업을 사용하면 정렬되지 않은 배열에서 최소 힙을 만들 수 있습니다.
최소 힙 데이터 구조에 대한 작업 및 구현:
다음은 힙 데이터 구조에서 수행할 수 있는 몇 가지 일반적인 작업입니다.
1. 최소 힙 데이터 구조에 삽입 :
삭제에 대해 위에서 설명한 것과 유사한 접근 방식에 따라 요소를 힙에 삽입할 수 있습니다. 아이디어는 다음과 같습니다.
- 최소 힙의 삽입 작업에는 다음 단계가 포함됩니다.
- 힙 끝, 트리의 마지막 수준에서 사용 가능한 다음 위치에 새 요소를 추가합니다.
- 새 요소를 상위 요소와 비교합니다. 상위 요소가 새 요소보다 크면 교체하세요.
- 상위 요소가 새 요소보다 작거나 같을 때까지 또는 새 요소가 트리 루트에 도달할 때까지 2단계를 반복합니다.
- 이제 새 요소는 최소 힙에서 올바른 위치에 있으며 힙 속성이 충족됩니다.
삽화:
힙이 다음과 같이 최소 힙이라고 가정합니다.
최소 힙에 삽입
최소 힙에 삽입 작업 구현:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; // Function to insert a new element into the min-heap void insert_min_heap(vector & heap, int value) { // 힙 끝에 새 요소를 추가합니다. heap.push_back(value); // 마지막 요소의 인덱스를 가져옵니다. int index = heap.size() - 1; // 새 요소를 상위 요소와 비교하고 필요한 경우 // 교체합니다. while (index> 0 && heap[(index - 1) / 2]> heap[index]) { swap(heap[index], heap[(index - 1) / 2]); // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. // index = (index - 1) / 2; } } // insert_min_heap 함수를 테스트하는 기본 함수 int main() { 벡터 더미; int 값[] = { 10, 7, 11, 5, 4, 13 }; int n = sizeof(값) / sizeof(값[0]); for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { insert_min_heap(heap, values[i]); cout << 'Inserted ' << values[i] << ' into the min-heap: '; for (int j = 0; j < heap.size(); j++) { cout << heap[j] << ' '; } cout << endl; } return 0; }>
자바 import java.util.*; public class GFG { // Function to insert a new element into the min-heap public static void insertMinHeap(int[] heap, int size, int value) { // Add the new element to the end of the heap heap[size] = value; // Get the index of the last element int index = size; // Compare the new element with its parent and swap // if necessary while (index>0 && 힙[(인덱스 - 1) / 2]> 힙[인덱스]) { swap(힙, 인덱스, (인덱스 - 1) / 2); // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. // index = (index - 1) / 2; } } // 배열의 두 요소를 바꾸는 함수 public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = 온도; } // insertMinHeap 함수를 테스트하기 위한 기본 함수 public static void main(String[] args) { int[] heap = new int[6]; int[] 값 = { 10, 7, 11, 5, 4, 13 }; 정수 크기 = 0; for (int i = 0; i< values.length; i++) { insertMinHeap(heap, size, values[i]); size++; System.out.print('Inserted ' + values[i] + ' into the min-heap: '); for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { System.out.print(heap[j] + ' '); } System.out.println(); } } }> 파이썬3 def insert_min_heap(heap, value): # Add the new element to the end of the heap heap.append(value) # Get the index of the last element index = len(heap) - 1 # Compare the new element with its parent and swap if necessary while index>0 및 heap[(index - 1) // 2]> heap[index]: heap[index], heap[(index - 1) // 2] = heap[(index - 1) // 2], heap[ index] # 트리를 현재 요소의 상위로 이동 index = (index - 1) // 2 heap = [] 값 = [10, 7, 11, 5, 4, 13] for value in value: insert_min_heap( 힙, 값) print(f'최소 힙에 {값}을(를) 삽입했습니다: {힙}')> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Program { // Function to insert a new element into the min-heap static void InsertMinHeap(List heap, int value) { // 힙 끝에 새 요소를 추가합니다. heap.Add(value); // 마지막 요소의 인덱스를 가져옵니다. int index = heap.Count - 1; // 새 요소를 상위 요소와 비교하고 // 필요한 경우 교체합니다. while (index> 0 && heap[(index - 1) / 2]> heap[index]) { int temp = heap[index]; 힙[인덱스] = 힙[(인덱스 - 1) / 2]; 힙[(인덱스 - 1) / 2] = 임시; // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. // index = (index - 1) / 2; } } // InsertMinHeap 함수를 테스트하기 위한 메인 함수 public static void Main() { List 힙 = 새 목록 (); int[] 값 = { 10, 7, 11, 5, 4, 13 }; foreach(값의 int 값) { InsertMinHeap(힙, 값); Console.Write('최소 힙에 ' + 값 + '를 삽입함: '); foreach(힙의 int 요소) { Console.Write(요소 + ' '); } Console.WriteLine(); } } }> 자바스크립트 function insertMinHeap(heap, value) { heap.push(value); let index = heap.length - 1; let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); while (index>0 && heap[parentIndex]> heap[index]) { [heap[index], heap[parentIndex]] = [heap[parentIndex], heap[index]]; 인덱스 = 부모 인덱스; parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); } } // 사용 예 const heap = []; const 값 = [10, 7, 11, 5, 4, 13]; for (값의 상수 값) { insertMinHeap(힙, 값); console.log(`최소 힙에 ${value}를 삽입했습니다: ${heap}`); }> 산출
Inserted 10 into the min-heap: 10 Inserted 7 into the min-heap: 7 10 Inserted 11 into the min-heap: 7 10 11 Inserted 5 into the min-heap: 5 7 11 10 Inserted 4 into the min-heap: 4 5 11 10 7 Inser...>
시간 복잡도: O(log(n)) ( 여기서 n은 힙에 요소가 없습니다. )
보조 공간: 에)
2. 최소 힙 데이터 구조에서 삭제 :
최소 힙에서 가장 작은 요소(루트)를 제거합니다. 루트는 힙의 마지막 요소로 대체되고, 부모가 두 자식보다 작아지거나 새 루트가 리프 노드에 도달할 때까지 새 루트를 가장 작은 자식으로 교체하여 힙 속성이 복원됩니다.
- 삭제할 루트 또는 요소를 마지막 요소로 바꿉니다.
- 힙에서 마지막 요소를 삭제합니다.
- 이제 마지막 요소가 루트 노드 위치에 배치됩니다. 따라서 힙 속성을 따르지 않을 수도 있습니다. 따라서 루트 위치에 있는 마지막 노드를 힙화한다.
삽화 :
자바에서 난수를 생성하는 방법
힙이 다음과 같이 최소 힙이라고 가정합니다.
최소 힙 데이터 구조
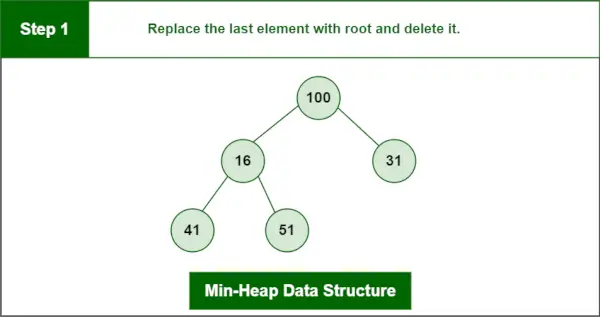
삭제할 요소는 루트, 즉 13입니다.
프로세스 :
마지막 요소는 100입니다.
1 단계: 마지막 요소를 루트로 바꾸고 삭제합니다.
최소 힙 데이터 구조
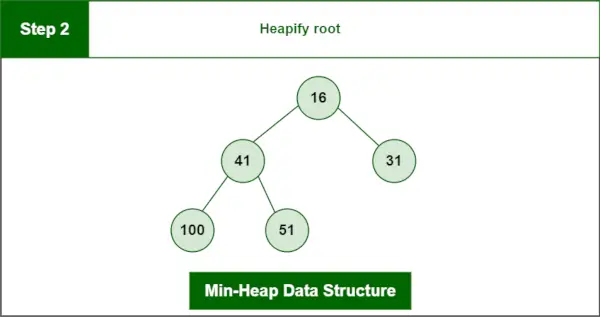
2 단계 : 뿌리를 쌓으세요.
최종 힙:
최소 힙 데이터 구조
최소 힙에서 삭제 작업 구현:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; // Function to insert a new element into the min-heap void insert_min_heap(vector & heap, int value) { // 힙 끝에 새 요소를 추가합니다. heap.push_back(value); // 마지막 요소의 인덱스를 가져옵니다. int index = heap.size() - 1; // 새 요소를 상위 요소와 비교하고 필요한 경우 // 교체합니다. while (index> 0 && heap[(index - 1) / 2]> heap[index]) { swap(heap[index], heap[(index - 1) / 2]); // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. // index = (index - 1) / 2; } } // 최소 힙에서 노드를 삭제하는 함수 void delete_min_heap(벡터 & heap, int value) { // 삭제할 요소의 인덱스를 찾습니다. int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i< heap.size(); i++) { if (heap[i] == value) { index = i; break; } } // If the element is not found, return if (index == -1) { return; } // Replace the element to be deleted with the last // element heap[index] = heap[heap.size() - 1]; // Remove the last element heap.pop_back(); // Heapify the tree starting from the element at the // deleted index while (true) { int left_child = 2 * index + 1; int right_child = 2 * index + 2; int smallest = index; if (left_child < heap.size() && heap[left_child] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = left_child; } if (right_child < heap.size() && heap[right_child] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = right_child; } if (smallest != index) { swap(heap[index], heap[smallest]); index = smallest; } else { break; } } } // Main function to test the insert_min_heap and // delete_min_heap functions int main() { vector 더미; int 값[] = { 13, 16, 31, 41, 51, 100 }; int n = sizeof(값) / sizeof(값[0]); for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { insert_min_heap(heap, values[i]); } cout << 'Initial heap: '; for (int j = 0; j < heap.size(); j++) { cout << heap[j] << ' '; } cout << endl; delete_min_heap(heap, 13); cout << 'Heap after deleting 13: '; for (int j = 0; j < heap.size(); j++) { cout << heap[j] << ' '; } cout << endl; return 0; }>
자바 import java.util.*; public class GFG { // Function to insert a new element into the min-heap public static void insertMinHeap(List heap, int value) { // 힙 끝에 새 요소를 추가합니다. heap.add(value); // 마지막 요소의 인덱스를 가져옵니다. int index = heap.size() - 1; // 새 요소를 상위 요소와 비교하고 // 필요한 경우 교체합니다. while (index> 0 && heap.get((index - 1) / 2)> heap.get(index)) { Collections.swap(heap, index, (색인 - 1) / 2); // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. // index = (index - 1) / 2; } } // 최소 힙에서 노드를 삭제하는 함수 public static void deleteMinHeap(List heap, int value) { // 삭제할 요소의 인덱스를 찾습니다. int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i< heap.size(); i++) { if (heap.get(i) == value) { index = i; break; } } // If the element is not found, return if (index == -1) { return; } // Replace the element to be deleted with the last // element heap.set(index, heap.get(heap.size() - 1)); // Remove the last element heap.remove(heap.size() - 1); // Heapify the tree starting from the element at the // deleted index while (true) { int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; int smallest = index; if (leftChild < heap.size() && heap.get(leftChild) < heap.get(smallest)) { smallest = leftChild; } if (rightChild < heap.size() && heap.get(rightChild) < heap.get(smallest)) { smallest = rightChild; } if (smallest != index) { Collections.swap(heap, index, smallest); index = smallest; } else { break; } } } // Main function to test the insertMinHeap and // deleteMinHeap functions public static void main(String[] args) { List 힙 = 새로운 ArrayList (); int[] 값 = { 13, 16, 31, 41, 51, 100 }; int n = 값.길이; for (int i = 0; i< n; i++) { insertMinHeap(heap, values[i]); } System.out.print('Initial heap: '); for (int j = 0; j < heap.size(); j++) { System.out.print(heap.get(j) + ' '); } System.out.println(); deleteMinHeap(heap, 13); System.out.print('Heap after deleting 13: '); for (int j = 0; j < heap.size(); j++) { System.out.print(heap.get(j) + ' '); } System.out.println(); } }> 파이썬3 def insert_min_heap(heap, value): heap.append(value) index = len(heap) - 1 while index>0 및 heap[(index - 1) // 2]> heap[index]: heap[index], heap[(index - 1) // 2] = heap[(index - 1) // 2], heap[ index] index = (index - 1) // 2 def delete_min_heap(heap, value): index = -1 for i in range(len(heap)): if heap[i] == value: index = i break if index == -1: heap[index] = heap[-1] heap.pop() 반환 while True: left_child = 2 * 인덱스 + 1 right_child = 2 * 인덱스 + 2 가장 작은 = index if left_child< len(heap) and heap[left_child] < heap[smallest]: smallest = left_child if right_child < len(heap) and heap[right_child] < heap[smallest]: smallest = right_child if smallest != index: heap[index], heap[smallest] = heap[smallest], heap[index] index = smallest else: break heap = [] values = [13, 16, 31, 41, 51, 100] for value in values: insert_min_heap(heap, value) print('Initial heap:', heap) delete_min_heap(heap, 13) print('Heap after deleting 13:', heap)> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class MinHeap { private List 힙 = 새 목록 (); 공개 무효 삽입(int value) { heap.Add(value); int 인덱스 = heap.Count - 1; while (index> 0 && heap[(index - 1) / 2]> heap[index]) { Swap(index, (index - 1) / 2); 인덱스 = (인덱스 - 1) / 2; } } 공개 무효 삭제(int value) { int index = heap.IndexOf(value); if (색인 == -1) { 반환; } 힙[인덱스] = 힙[힙.카운트 - 1]; heap.RemoveAt(heap.Count - 1); while (true) { int leftChild = 2 * 인덱스 + 1; int rightChild = 2 * 인덱스 + 2; int 가장 작은 = 인덱스; if(왼쪽자식< heap.Count && heap[leftChild] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = leftChild; } if (rightChild < heap.Count && heap[rightChild] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = rightChild; } if (smallest != index) { Swap(index, smallest); index = smallest; } else { break; } } } private void Swap(int i, int j) { int temp = heap[i]; heap[i] = heap[j]; heap[j] = temp; } public void Print() { for (int i = 0; i < heap.Count; i++) { Console.Write(heap[i] + ' '); } Console.WriteLine(); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MinHeap heap = new MinHeap(); int[] values = { 13, 16, 31, 41, 51, 100 }; for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) { heap.Insert(values[i]); } Console.Write('Initial heap: '); heap.Print(); heap.Delete(13); Console.Write('Heap after deleting 13: '); heap.Print(); } }> 자바스크립트 function insertMinHeap(heap, value) { // Add the new element to the end of the heap heap.push(value); // Get the index of the last element let index = heap.length - 1; // Compare the new element with its parent and swap if necessary for (let flr = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); index>0 && 힙[flr]> 힙[인덱스]; flr = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2)) { [heap[index], heap[flr]] = [ heap[flr], heap[index], ]; // 현재 요소의 부모로 트리를 위로 이동합니다. index = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); } } function deleteMinHeap(heap, value) { // 삭제할 요소의 인덱스를 찾습니다. let index = -1; for (나는 = 0이라고 하자; 나는< heap.length; i++) { if (heap[i] == value) { index = i; break; } } // If the element is not found, return if (index == -1) { return; } // Replace the element to be deleted with the last element heap[index] = heap[heap.length - 1]; // Remove the last element heap.pop(); // Heapify the tree starting from the element at the deleted index while (true) { let left_child = 2 * index + 1; let right_child = 2 * index + 2; let smallest = index; if (left_child < heap.length && heap[left_child] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = left_child; } if (right_child < heap.length && heap[right_child] < heap[smallest]) { smallest = right_child; } if (smallest != index) { [heap[index], heap[smallest]] = [heap[smallest], heap[index]]; index = smallest; } else { break; } } } // Main function to test the insertMinHeap and deleteMinHeap functions let heap = []; let values = [13, 16, 31, 41, 51, 100]; for (let i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { insertMinHeap(heap, values[i]); } console.log('Initial heap: ' + heap.join(' ')); deleteMinHeap(heap, 13); console.log('Heap after deleting 13: ' + heap.join(' '));> 산출
Initial heap: 13 16 31 41 51 100 Heap after deleting 13: 16 41 31 100 51>
시간 복잡도 : O(log n) 여기서 n은 힙에 요소가 없습니다.
보조 공간: 에)
3. 최소 힙 데이터 구조에 대한 Peek 작업:
최소 요소(즉, 힙의 루트)에 액세스하려면 루트 노드의 값이 반환됩니다. 최소 힙에서 엿보기의 시간 복잡도는 O(1)입니다.
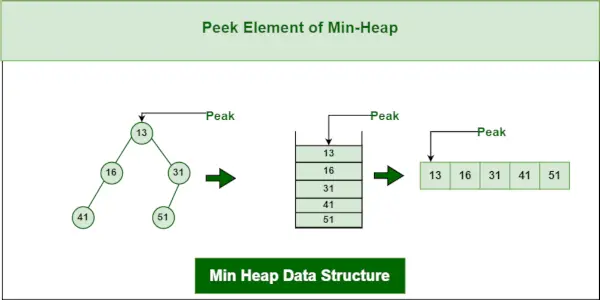
최소 힙 데이터 구조
Min-Heap에서 Peek 작업 구현:
C++ #include #include #include using namespace std; int main() { // Create a max heap with some elements using a // priority_queue priority_queue , 보다 큰 > 최소힙; minHeap.push(9); minHeap.push(8); minHeap.push(7); minHeap.push(6); minHeap.push(5); minHeap.push(4); minHeap.push(3); minHeap.push(2); minHeap.push(1); // 피크 요소(즉, 가장 큰 요소)를 가져옵니다. int peakElement = minHeap.top(); // 피크 요소를 인쇄합니다. cout<< 'Peak element: ' << peakElement << std::endl; return 0; }> 자바 import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class GFG { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a max heap with some elements using a // PriorityQueue PriorityQueue minHeap = 새로운 PriorityQueue(); minHeap.add(9); minHeap.add(8); minHeap.add(7); minHeap.add(6); minHeap.add(5); minHeap.add(4); minHeap.add(3); minHeap.add(2); minHeap.add(1); // 피크 요소(즉, 가장 큰 요소)를 가져옵니다. int peakElement = minHeap.peek(); // 피크 요소를 인쇄합니다. System.out.println('피크 요소: ' + peakElement); } }> 파이썬3 import heapq # Create a min heap with some elements using a list min_heap = [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] heapq.heapify(min_heap) # Get the peak element (i.e., the smallest element) peak_element = heapq.nsmallest(1, min_heap)[0] # Print the peak element print('Peak element:', peak_element)> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class GFG { public static void Main() { // Create a min heap with some elements using a // PriorityQueue var minHeap = new PriorityQueue (); minHeap.Enqueue(9); minHeap.Enqueue(8); minHeap.Enqueue(7); minHeap.Enqueue(6); minHeap.Enqueue(5); minHeap.Enqueue(4); minHeap.Enqueue(3); minHeap.Enqueue(2); minHeap.Enqueue(1); // 피크 요소(즉, 가장 작은 요소)를 가져옵니다. int peakElement = minHeap.Peek(); // 피크 요소를 인쇄합니다. Console.WriteLine('피크 요소: ' + peakElement); } }> 자바스크립트 const PriorityQueue = require('fast-priority-queue'); // Create a min heap with some elements using a PriorityQueue const minHeap = new PriorityQueue((a, b) =>a-b); minHeap.add(9); minHeap.add(8); minHeap.add(7); minHeap.add(6); minHeap.add(5); minHeap.add(4); minHeap.add(3); minHeap.add(2); minHeap.add(1); // 피크 요소(즉, 가장 작은 요소)를 가져옵니다. const peakElement = minHeap.peek(); // 피크 요소를 인쇄합니다. console.log(`피크 요소: ${peakElement}`);> 산출
Peak element: 1>
시간 복잡도 : 배열이나 목록을 사용하여 구현된 최소 힙에서 피크 요소는 항상 힙의 루트에 위치하므로 상수 시간 O(1)에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
이진 트리를 사용하여 구현된 최소 힙에서 피크 요소는 항상 트리의 루트에 위치하므로 O(1) 시간 내에 액세스할 수도 있습니다.
보조 공간: 에)
4. 최소 힙 데이터 구조에 대한 힙화 작업:
heapify 작업을 사용하면 정렬되지 않은 배열에서 최소 힙을 만들 수 있습니다. 이는 리프가 아닌 마지막 노드에서 시작하여 모든 노드가 힙 속성을 충족할 때까지 버블다운 작업을 반복적으로 수행하여 수행됩니다.
Min Heap에서의 Heapify 연산
Min-Heap에서 Heapify 작업 구현:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; void minHeapify(vector &arr, int i, int n) { int 최소 = i; int l = 2*i + 1; int r = 2*i + 2; 만약 (l< n && arr[l] < arr[smallest]) smallest = l; if (r < n && arr[r] < arr[smallest]) smallest = r; if (smallest != i) { swap(arr[i], arr[smallest]); minHeapify(arr, smallest, n); } } int main() { vector 도착 = {10, 5, 15, 2, 20, 30}; 시합<< 'Original array: '; for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << ' '; // Perform heapify operation on min-heap for (int i = arr.size()/2 - 1; i>= 0; i--) minHeapify(arr, i, arr.size()); 시합<< '
Min-Heap after heapify operation: '; for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << ' '; return 0; }>
자바 // Java code of Heapify operation in Min-Heap import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class Main { // Function to maintain the min-heap property of the heap rooted at index 'i' public static void minHeapify(List arr, int i, int n) { // 루트가 처음에 가장 작은 요소라고 가정합니다. int maximum = i; // 현재 노드의 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 자식의 인덱스를 계산합니다. int l = 2 * i + 1; int r = 2 * i + 2; // 왼쪽 자식과 현재 가장 작은 자식을 비교합니다. if (l< n && arr.get(l) < arr.get(smallest)) smallest = l; // Compare the right child with the current smallest if (r < n && arr.get(r) < arr.get(smallest)) smallest = r; // If the current node is not the smallest, swap it with the smallest child if (smallest != i) { int temp = arr.get(i); arr.set(i, arr.get(smallest)); arr.set(smallest, temp); // Recursively heapify the subtree rooted at the smallest child minHeapify(arr, smallest, n); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a list representing the array List arr = Arrays.asList(10, 5, 15, 2, 20, 30); System.out.print('원본 배열: '); // (int i = 0; i에 대한 원래 배열을 인쇄합니다.< arr.size(); i++) System.out.print(arr.get(i) + ' '); // Perform heapify operation on the min-heap // Start from the last non-leaf node and go up to the root of the tree for (int i = arr.size() / 2 - 1; i>= 0; i--) minHeapify(arr, i, arr.size()); System.out.print('
힙화 작업 후 최소 힙: '); // (int i = 0; i에 대한 힙화 작업 후 최소 힙을 인쇄합니다.< arr.size(); i++) System.out.print(arr.get(i) + ' '); } }> 파이썬 def minHeapify(arr, i, n): smallest = i left = 2 * i + 1 right = 2 * i + 2 if left < n and arr[left] < arr[smallest]: smallest = left if right < n and arr[right] < arr[smallest]: smallest = right if smallest != i: arr[i], arr[smallest] = arr[smallest], arr[i] minHeapify(arr, smallest, n) if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [10, 5, 15, 2, 20, 30] print('Original array:', arr) # Perform heapify operation on a min-heap for i in range(len(arr) // 2 - 1, -1, -1): minHeapify(arr, i, len(arr)) print('Min-Heap after heapify operation:', arr)> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { // Function to perform the minHeapify operation on a min-heap. static void MinHeapify(List arr, int i, int n) { int 가장 작은 = i; int left = 2 * i + 1; int right = 2 * i + 2; // 왼쪽 자식을 현재 가장 작은 노드와 비교합니다. 만약 (왼쪽< n && arr[left] < arr[smallest]) smallest = left; // Compare the right child with the current smallest node. if (right < n && arr[right] < arr[smallest]) smallest = right; // If the current node is not the smallest // swap it with the smallest child. if (smallest != i) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[smallest]; arr[smallest] = temp; // Recursively call minHeapify on the affected subtree. MinHeapify(arr, smallest, n); } } static void Main(string[] args) { List arr = 새 목록 { 10, 5, 15, 2, 20, 30 }; Console.Write('원본 배열: '); foreach (arr의 int num) Console.Write(num + ' '); // 최소 힙에 대해 힙화 작업을 수행합니다. for (int i = arr.Count / 2 - 1; i>= 0; i--) MinHeapify(arr, i, arr.Count); Console.Write('
힙화 작업 후 최소 힙: '); foreach (arr의 int num) Console.Write(num + ' '); } }> 자바스크립트 // Define a function to perform min-heapify operation on an array function minHeapify(arr, i, n) { let smallest = i; let l = 2 * i + 1; let r = 2 * i + 2; // Check if left child is smaller than the current smallest element if (l < n && arr[l] < arr[smallest]) smallest = l; // Check if right child is smaller than the current smallest element if (r < n && arr[r] < arr[smallest]) smallest = r; // If the smallest element is not the current element, swap them if (smallest !== i) { [arr[i], arr[smallest]] = [arr[smallest], arr[i]]; minHeapify(arr, smallest, n); } } // Main function function main() { const arr = [10, 5, 15, 2, 20, 30]; // Print the original array console.log('Original array: ' + arr.join(' ')); // Perform heapify operation on the min-heap for (let i = Math.floor(arr.length / 2) - 1; i>= 0; i--) minHeapify(arr, i, arr.length); // 힙화 작업 후 최소 힙을 인쇄합니다. console.log('힙화 작업 후 최소 힙: ' + arr.join(' ')); } // 메인 함수를 호출하여 프로세스를 시작합니다. main();> 산출
Original array: 10 5 15 2 20 30 Min-Heap after heapify operation: 2 5 15 10 20 30>
최소 힙에서 heapify의 시간 복잡도는 O(n)입니다.
병렬 처리
5. 최소 힙 데이터 구조에 대한 검색 작업:
최소 힙에서 요소를 검색하려면 힙을 나타내는 배열에 대해 선형 검색을 수행할 수 있습니다. 그러나 선형 탐색의 시간 복잡도는 O(n)이므로 효율적이지 않습니다. 따라서 검색은 최소 힙에서 일반적으로 사용되는 작업이 아닙니다.
다음은 다음을 사용하여 최소 힙에서 요소를 검색하는 방법을 보여주는 예제 코드입니다. 표준::찾기() :
C++ #include using namespace std; int main() { priority_queue , 보다 큰 > 최소힙; // 최대 힙 예시 min_heap.push(10); min_heap.push(9); min_heap.push(8); min_heap.push(6); min_heap.push(4); int 요소 = 6; // bool을 검색할 요소found = false; // 최소 힙을 임시 큐에 복사하고 // std::priority_queue 요소를 검색합니다. , 보다 큰 > 임시 = min_heap; while (!temp.empty()) { if (temp.top() == 요소) {found = true; 부서지다; } 임시.팝(); } if (발견) { std::cout<< 'Element found in the min heap.' << std::endl; } else { std::cout << 'Element not found in the min heap.' << std::endl; } return 0; }> 자바 import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class GFG { public static void main(String[] args) { PriorityQueue min_heap = 새로운 PriorityQueue(); min_heap.add(3); // 우선순위 큐에 요소를 삽입합니다. min_heap.offer(1); min_heap.offer(4); min_heap.offer(1); min_heap.offer(6); int 요소 = 6; // 부울을 검색할 요소found = false; // 최소 힙을 임시 대기열에 복사하고 // PriorityQueue 요소를 검색합니다. temp = new PriorityQueue(min_heap); while (!temp.isEmpty()) { if (temp.poll() == 요소) {found = true; 부서지다; } } if (found) { System.out.println( '최소 힙에서 요소를 찾았습니다.'); } else { System.out.println( '최소 힙에서 요소를 찾을 수 없습니다.'); } } }> 파이썬3 import heapq min_heap = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10] # example min heap heapq.heapify(min_heap) element = 6 # element to search for found = False # Copy the min heap to a temporary list and search for the element temp = list(min_heap) while temp: if heapq.heappop(temp) == element: found = True break if found: print('Element found in the min heap.') else: print('Element not found in the min heap.')> 씨# using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class GFG { public static void Main() { var minHeap = new PriorityQueue (); // 최소 힙 예시 minHeap.Enqueue(4); minHeap.Enqueue(6); minHeap.Enqueue(8); minHeap.Enqueue(9); minHeap.Enqueue(10); int 요소 = 6; // bool을 검색할 요소found = false; // 최소 힙을 임시 대기열에 복사하고 // 요소를 검색합니다. var temp = new PriorityQueue (최소힙); while (temp.Count> 0) { if (temp.Peek() == 요소) {found = true; 부서지다; } temp.Dequeue(); } if (found) { Console.WriteLine( '최소 힙에서 요소를 찾았습니다.'); } else { Console.WriteLine( '최소 힙에서 요소를 찾을 수 없습니다.'); } } }> 자바스크립트 // Example min heap let minHeap = new PriorityQueue(); minHeap.enqueue(4); minHeap.enqueue(6); minHeap.enqueue(8); minHeap.enqueue(9); minHeap.enqueue(10); let element = 6; // Element to search for let found = false; // Copy the min heap to a temporary queue and search for the element let temp = new PriorityQueue(minHeap); while (temp.size()>0) { if (temp.peek() == 요소) {found = true; 부서지다; } temp.dequeue(); } if (found) { console.log('최소 힙에서 요소를 찾았습니다.'); } else { console.log('최소 힙에서 요소를 찾을 수 없습니다.'); }> 산출
Element found in the min heap.>
복잡성 분석 :
그만큼 시간 복잡도 이 프로그램의 O(n 로그 n) , 어디 N 우선순위 큐의 요소 수입니다.
삽입 연산의 시간 복잡도는 다음과 같습니다. O(로그 n) 최악의 경우에는 힙 속성을 유지해야 하기 때문입니다. 검색 작업에는 우선순위 큐를 임시 큐에 복사한 다음 임시 큐를 순회하는 작업이 포함됩니다. O(n 로그 n) 최악의 경우에는 각 요소를 복사하여 대기열에서 꺼내야 하고 각 작업에 대해 우선순위 대기열을 다시 작성해야 하기 때문입니다.
그만큼 공간 복잡도 프로그램의 에) 저장하기 때문에 N 우선 순위 큐의 요소를 사용하여 임시 큐를 생성합니다. N 강요.
최소 힙 데이터 구조의 응용:
- 힙 정렬: 최소 힙은 시간 복잡도가 O(nlogn)인 효율적인 정렬 알고리즘인 힙 정렬 알고리즘의 핵심 구성 요소로 사용됩니다.
- 우선순위 대기열: 최소값을 갖는 요소가 항상 루트에 있는 최소 힙 데이터 구조를 사용하여 우선순위 큐를 구현할 수 있습니다.
- Dijkstra의 알고리즘: Dijkstra 알고리즘에서는 최소 힙을 사용하여 시작 정점으로부터 최소 거리에 있는 그래프의 정점을 저장합니다. 최소 거리를 갖는 정점은 항상 힙의 루트에 있습니다.
- 허프만 코딩: 허프만 코딩에서 최소 힙은 주어진 문자 집합에 대한 최적의 접두사 코드를 구축하기 위해 우선순위 대기열을 구현하는 데 사용됩니다.
- K개의 정렬된 배열을 병합합니다. K개의 정렬된 배열이 주어지면 최소 힙 데이터 구조를 사용하여 효율적으로 단일 정렬된 배열로 병합할 수 있습니다.
최소 힙 데이터 구조의 장점:
- 효율적인 삽입 및 삭제 : 최소 힙을 사용하면 O(log n)의 시간 복잡도로 요소를 빠르게 삽입하고 삭제할 수 있습니다. 여기서 n은 힙의 요소 수입니다.
- 최소 요소의 효율적인 검색: 최소 힙의 최소 요소는 항상 힙의 루트에 있으며 O(1) 시간에 검색할 수 있습니다.
- 공간 효율성: 최소 힙은 배열이나 이진 트리를 사용하여 구현할 수 있는 컴팩트한 데이터 구조이므로 공간 효율적입니다.
- 정렬: 최소 힙은 시간 복잡도가 O(n log n)인 힙 정렬과 같은 효율적인 정렬 알고리즘을 구현하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 우선순위 대기열: 최소 힙은 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 데 사용될 수 있으며, 여기서 최소 우선순위를 가진 요소는 O(1) 시간 내에 효율적으로 검색될 수 있습니다.
- 다재: 최소 힙은 그래프 알고리즘, 데이터 압축 및 데이터베이스 시스템을 포함하여 컴퓨터 과학의 여러 응용 프로그램을 가지고 있습니다.
전반적으로 최소 힙은 효율적인 작업, 공간 효율성을 제공하고 컴퓨터 과학에서 여러 응용 프로그램을 제공하는 유용하고 다재다능한 데이터 구조입니다.