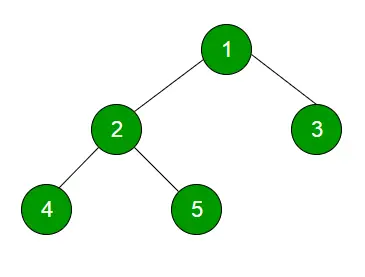
레벨 순서 순회 기술은 다음 레벨을 통과하기 전에 동일한 레벨에 존재하는 모든 노드를 완전히 탐색하도록 트리를 탐색하는 방법으로 정의됩니다.
예:
권장 연습 레벨 순서 순회 사용해 보세요!입력:
산출:
1
23
넷 다섯
레벨 오더 순회는 어떻게 작동하나요?
레벨 순서 탐색의 주요 아이디어는 더 높은 레벨의 노드로 이동하기 전에 낮은 레벨의 모든 노드를 탐색하는 것입니다. 이 작업은 다음 방법 중 하나로 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 순진한 것(트리의 높이를 찾고 각 레벨을 순회하며 해당 레벨의 노드를 인쇄)
- 큐를 효율적으로 사용합니다.
레벨 순서 순회(순진한 접근 방식):
찾다 키 나무의. 그런 다음 각 레벨에 대해 현재 높이를 유지하여 재귀 함수를 실행합니다. 노드의 수준이 일치할 때마다 해당 노드를 인쇄합니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->데이터<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, 레벨 - 1); printCurrentLevel(루트->오른쪽, 레벨 - 1); } } // 트리의 '높이'를 계산합니다. // 루트 노드에서 가장 먼 리프 노드까지 가장 긴 경로를 따라 // 노드 수를 계산합니다. int height(node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; else { // 각 하위 트리의 높이를 계산합니다. int lheight = height(node->left); int rhight = 높이(노드->오른쪽); // 더 큰 것을 사용합니다. if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (오른쪽 높이 + 1); } } } // 주어진 데이터와 // NULL 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 포인터를 사용하여 // 새 노드를 할당하는 도우미 함수입니다. node* newNode(int data) { node* Node = new node(); 노드->데이터 = 데이터; 노드->왼쪽 = NULL; 노드->오른쪽 = NULL; 반환(노드); } // 드라이버 코드 int main() { node* root = newNode(1); 루트->왼쪽 = newNode(2); 루트->오른쪽 = newNode(3); 루트->왼쪽->왼쪽 = newNode(4); 루트->왼쪽->오른쪽 = newNode(5); 시합<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> 씨 // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->데이터); else if (레벨> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, 레벨 - 1); printCurrentLevel(루트->오른쪽, 레벨 - 1); } } // 트리의 '높이'를 계산합니다 -- 루트 노드에서 // 가장 먼 리프 노드까지 가장 긴 경로를 따라 // 노드 수 int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) 0을 반환합니다. else { // 각 하위 트리의 높이를 계산합니다. int lheight = height(node->left); int rhight = 높이(노드->오른쪽); // 더 큰 것을 사용합니다. if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); 그렇지 않으면 반환(오른쪽 높이 + 1); } } // 주어진 데이터와 NULL 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 포인터를 사용하여 // 새 노드를 할당하는 도우미 함수입니다. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 노드->데이터 = 데이터; 노드->왼쪽 = NULL; 노드->오른쪽 = NULL; 반환(노드); } // 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); 루트->왼쪽 = newNode(2); 루트->오른쪽 = newNode(3); 루트->왼쪽->왼쪽 = newNode(4); 루트->왼쪽->오른쪽 = newNode(5); printf('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 탐색은
'); printLevelOrder(루트); 0을 반환합니다. }> 자바 // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>높이) 반환 (l높이 + 1); 그렇지 않으면 반환(오른쪽 높이 + 1); } } // 현재 레벨의 노드를 인쇄합니다. void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (레벨 == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (레벨> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, 레벨 - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, 레벨 - 1); } } // 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = 새 노드(1); tree.root.left = 새 노드(2); tree.root.right = 새 노드(3); tree.root.left.left = 새 노드(4); tree.root.left.right = 새 노드(5); System.out.println('레벨 순서 탐색' + '이진 트리는 '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> 파이썬 # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # 트리의 높이를 계산합니다. # 루트 노드에서 가장 먼 리프까지 가장 긴 경로를 따라 # 노드 수 node def height(node): if node is None: return 0 else: # 각 하위 트리의 높이를 계산합니다. lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # lheight> rheight: return이면 더 큰 값을 사용합니다. lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 탐색은 -') printLevelOrder(root) # 이 코드는 Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)이 기여했습니다.> 씨# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>높이) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (오른쪽 높이 + 1); } } } // 현재 레벨의 노드를 인쇄합니다. public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (레벨 == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (레벨> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, 레벨 - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, 레벨 - 1); } } // 드라이버 코드 public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = 새 노드(1); tree.root.left = 새 노드(2); tree.root.right = 새 노드(3); tree.root.left.left = 새 노드(4); tree.root.left.right = 새 노드(5); Console.WriteLine('레벨 순서 탐색 ' + '이진 트리는 '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // 이 코드는 Shrikant13이 제공한 것입니다.> 자바스크립트 // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>높이) 반환 (l높이 + 1); 그렇지 않으면 반환(오른쪽 높이 + 1); } } // 현재 레벨의 노드를 인쇄합니다. function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (레벨 == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (레벨> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, 레벨 - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, 레벨 - 1); } } // 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 root = new Node(1); root.left = 새 노드(2); root.right = 새 노드(3); root.left.left = 새 노드(4); root.left.right = 새 노드(5); console.log('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 탐색은 '); printLevelOrder(); // 이 코드는 Umadevi9616이 제공한 것입니다.> 산출
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
시간 복잡도: O(N), 여기서 N은 기울어진 트리의 노드 수입니다.
보조 공간: O(1) 재귀 스택을 고려하는 경우 사용되는 공간은 O(N)입니다.
데이터 베이스
다음을 사용한 레벨 순서 순회 대기줄
더 높은 수준의 노드보다 먼저 낮은 수준의 노드를 방문해야 합니다. 이 아이디어는 대기열의 아이디어와 매우 유사합니다. 대기열에서 더 낮은 수준의 노드를 푸시합니다. 임의의 노드를 방문하면 대기열에서 해당 노드를 팝하고 해당 노드의 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다.
이렇게 하면 더 높은 수준의 노드보다 낮은 수준의 노드를 먼저 방문하게 됩니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queue큐; // 루트를 대기열에 넣고 높이를 초기화합니다. q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // 대기열의 앞부분을 인쇄하고 대기열에서 제거합니다. Node* node = q.front(); 시합<< node->데이터<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->왼쪽 != NULL) q.push(node->left); // 오른쪽 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다. if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // 새 트리 노드를 생성하는 유틸리티 함수 Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; 임시->데이터 = 데이터; 온도->왼쪽 = 온도->오른쪽 = NULL; 복귀온도; } // 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 int main() { // 위 다이어그램에 표시된 이진 트리를 만듭니다. Node* root = newNode(1); 루트->왼쪽 = newNode(2); 루트->오른쪽 = newNode(3); 루트->왼쪽->왼쪽 = newNode(4); 루트->왼쪽->오른쪽 = newNode(5); 시합<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> 씨 // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->데이터); // 왼쪽 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다. if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // 오른쪽 자식을 대기열에 추가합니다. if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // 노드를 대기열에서 빼고 temp_node로 만듭니다. temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // 유틸리티 함수 struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* Rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *앞 = *뒤 = 0; 반환 대기열; } void enQueue(struct node** queue, int* Rear, struct node* new_node) { queue[*rear] = new_node; (*뒤)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** queue, int* front) { (*front)++; 반환 대기열[*앞 - 1]; } // 주어진 데이터와 NULL 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 포인터를 사용하여 // 새 노드를 할당하는 도우미 함수입니다. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); 노드->데이터 = 데이터; 노드->왼쪽 = NULL; 노드->오른쪽 = NULL; 반환(노드); } // 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); 루트->왼쪽 = newNode(2); 루트->오른쪽 = newNode(3); 루트->왼쪽->왼쪽 = newNode(4); 루트->왼쪽->오른쪽 = newNode(5); printf('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 탐색은
'); printLevelOrder(루트); 0을 반환합니다. }> 자바 // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queue대기열 = 새로운 LinkedList(); queue.add(루트); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll()은 현재 헤드를 제거합니다. 노드 tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // 왼쪽 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다. if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // 오른쪽 자식을 큐에 넣습니다. if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // 바이너리 트리 생성 및 // 노드 입력 BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = 새 노드(1); tree_level.root.left = 새 노드(2); tree_level.root.right = 새 노드(3); tree_level.root.left.left = 새 노드(4); tree_level.root.left.right = 새 노드(5); System.out.println('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 탐색은 - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> 파이썬 # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # 대기열의 앞 부분을 인쇄하고 # 대기열에서 제거합니다. print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # node.left가 None이 아닌 경우 왼쪽 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다. queue.append(node.left) # node.right가 None이 아닌 경우 오른쪽 자식을 큐에 넣습니다. queue.append(node.right) # 위 함수를 테스트하기 위한 드라이버 프로그램 if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('이진 트리의 레벨 순서 순회는 - ') printLevelOrder(root) # 이 코드는 Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)이 제공한 것입니다.> 씨# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queue대기열 = 새 대기열(); queue.Enqueue(root); while (queue.Count != 0) { 노드 tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // 왼쪽 자식을 대기열에 넣습니다. if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // 오른쪽 자식을 큐에 넣습니다. if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // 드라이버 코드 public static void Main() { // 바이너리 트리 생성 및 // 노드 입력 BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = 새 노드(1); tree_level.root.left = 새 노드(2); tree_level.root.right = 새 노드(3); tree_level.root.left.left = 새 노드(4); tree_level.root.left.right = 새 노드(5); Console.WriteLine('레벨 순서 탐색 ' + '이진 트리는 - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // PrinciRaj1992가 제공한 이 코드> 자바스크립트 class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> 산출
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
시간 복잡도: O(N) 여기서 N은 이진 트리의 노드 수입니다.
보조 공간: O(N) 여기서 N은 이진 트리의 노드 수입니다.