ㅏ C++ 우선순위 큐 컨테이너 어댑터의 일종으로, 큐의 첫 번째 요소가 큐의 모든 요소 중 가장 크거나 가장 작으며 요소가 증가하지 않거나 감소하지 않는 순서로 지정되도록 특별히 설계되었습니다. 대기열 요소의 우선순위는 {고정 순서}입니다.
C++ STL에서는 기본적으로 최상위 요소가 항상 가장 큽니다. 상단의 가장 작은 요소로 변경할 수도 있습니다. 우선순위 큐는 최대 힙 상단에 구축되며 배열이나 벡터를 내부 구조로 사용합니다. 간단히 말해서, STL 우선순위 대기열 C++의 구현입니다
날짜 형식.형식 자바
// C++ program to demonstrate the use of priority_queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // driver code> int> main()> {> >int> arr[6] = { 10, 2, 4, 8, 6, 9 };> >// defining priority queue> >priority_queue<>int>>pq;> >// printing array> >cout <<>'Array: '>;> >for> (>auto> i : arr) {> >cout << i <<>' '>;> >}> >cout << endl;> >// pushing array sequentially one by one> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <6; i++) {> >pq.push(arr[i]);> >}> >// printing priority queue> >cout <<>'Priority Queue: '>;> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>산출
Array: 10 2 4 8 6 9 Priority Queue: 10 9 8 6 4 2>
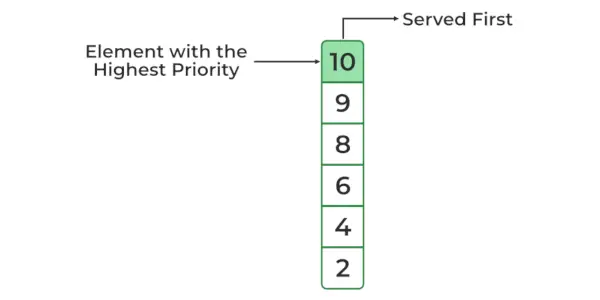
최대 힙 우선순위 큐(기본 구성표)
우선순위 큐에 대한 최소 힙을 만드는 방법은 무엇입니까?
앞에서 본 것처럼 우선순위 큐는 C++에서 기본적으로 최대 힙으로 구현되지만 우선순위 큐를 생성하는 동안 다른 매개변수를 전달하여 최소 힙으로 변경할 수 있는 옵션도 제공합니다.
통사론:
priority_queue gq;>
어디,
- 'int'는 우선순위 큐에 저장하려는 요소 유형입니다. 이 경우 정수입니다. 교체할 수 있습니다 정수 필요한 다른 데이터 유형을 사용하십시오. '벡터'는 이러한 요소를 저장하는 데 사용되는 내부 컨테이너 유형입니다. 표준::우선순위_큐 는 그 자체로 컨테이너가 아니라 컨테이너 채택자입니다. 다른 용기를 포장합니다. 이 예에서는 벡터 , 그러나 front(), push_back() 및 pop_back() 메서드를 지원하는 다른 컨테이너를 선택할 수 있습니다.
- ' 보다 큰 '는 사용자 정의 비교 함수입니다. 이는 우선순위 큐 내에서 요소가 정렬되는 방식을 결정합니다. 이 특정 예에서 더 큰 설정은 최소 힙 . 이는 가장 작은 요소가 대기열의 맨 위에 위치한다는 것을 의미합니다.
최대 힙의 경우 기본값이 이미 최대 힙에 적합하므로 지정할 필요가 없습니다.
예:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate> // min heap for priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> void> showpq(> >priority_queue<>int>, vector<>int>>, 보다 큰<>int>>> 지)> {> >while> (!g.empty()) {> >cout <<>' '> << g.top();> >g.pop();> >}> >cout <<>'
'>;> }> void> showArray(>int>* arr,>int> n)> {> >for> (>int> i = 0; i cout << arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { int arr[6] = { 10, 2, 4, 8, 6, 9 }; priority_queue |
>
>산출
Array: 10 2 4 8 6 9 Priority Queue : 2 4 6 8 9 10>
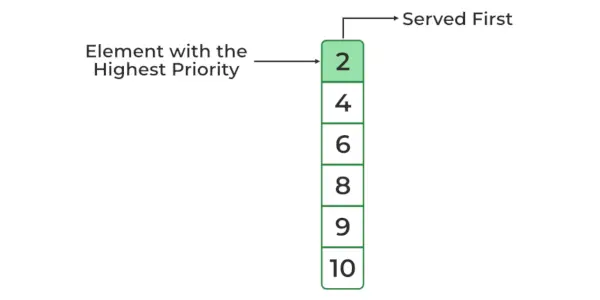
최소 힙 우선순위 큐
메모: 위의 구문은 기억하기 어려울 수 있으므로 숫자 값의 경우 해당 값에 -1을 곱하고 최대 힙을 사용하여 최소 힙의 효과를 얻을 수 있습니다. 교체하여 사용자 정의 정렬 방법을 사용할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 보다 큰 맞춤형 비교기 기능 포함.
우선순위 대기열의 방법
std::priority_queue 클래스의 모든 메소드 목록은 다음과 같습니다.
| 방법 | 정의 |
|---|---|
| 우선순위_큐::비어 있음() | 대기열이 비어 있는지 여부를 반환합니다. |
| 우선순위_큐::크기() | 대기열의 크기를 반환합니다. |
| 우선순위_큐::top() | 대기열의 최상위 요소에 대한 참조를 반환합니다. |
| 우선순위_큐::푸시() | 대기열 끝에 요소 'g'를 추가합니다. |
| 우선순위_큐::팝() | 대기열의 첫 번째 요소를 삭제합니다. |
| 우선순위_큐::스왑() | 크기는 다를 수 있지만 대기열의 유형이 동일해야 하는 경우 두 대기열의 내용을 교환하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| Priority_queue::emplace() | 우선순위 큐 컨테이너에 새 요소를 삽입하는 데 사용됩니다. |
| 우선순위_큐 값_유형 | Priority_queue의 요소로 저장된 개체 유형을 나타냅니다. 이는 템플릿 매개변수의 동의어 역할을 합니다. |
C++의 우선순위 대기열 작업
1. 우선순위 대기열 요소 삽입 및 제거
그만큼 푸시() 메소드는 우선순위 큐에 요소를 삽입하는 데 사용됩니다. 우선순위 큐에서 요소를 제거하려면 팝() 메서드는 우선 순위가 가장 높은 요소를 제거하기 때문에 사용됩니다.
다음은 우선순위 큐의 다양한 기능에 대한 C++ 프로그램입니다.
C++
안드로이드에서 아이폰 이모티콘을 얻는 방법
// C++ Program to demonstrate various> // method/function in Priority Queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Implementation of priority queue> void> showpq(priority_queue<>int>>gq)> {> >priority_queue<>int>>g = gq;> >while> (!g.empty()) {> >cout <<>' '> << g.top();> >g.pop();> >}> >cout <<>'
'>;> }> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>퀴즈;> >// used in inserting the element> >gquiz.push(10);> >gquiz.push(30);> >gquiz.push(20);> >gquiz.push(5);> >gquiz.push(1);> >cout <<>'The priority queue gquiz is : '>;> > >// used for highlighting the element> >showpq(gquiz);> >// used for identifying the size> >// of the priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.size() : '> <<> >gquiz.size();> >// used for telling the top element> >// in priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.top() : '> <<> >gquiz.top();> >// used for popping the element> >// from a priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.pop() : '>;> >gquiz.pop();> >showpq(gquiz);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>산출
The priority queue gquiz is : 30 20 10 5 1 gquiz.size() : 5 gquiz.top() : 30 gquiz.pop() : 20 10 5 1>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
메모 : 위에 표시된 것은 우선순위 큐 초기화 방법 중 하나입니다. 우선순위 큐의 효율적인 초기화에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 여기를 클릭하세요.
2. 우선순위 대기열의 최상위 요소에 액세스하려면
우선순위 큐의 최상위 요소는 다음을 사용하여 액세스할 수 있습니다. 맨 위() 방법.
C++
// C++ program to access the top> // element of priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// create a priority queue of int> >priority_queue<>int>>숫자;> >// add items to priority_queue> >numbers.push(1);> >numbers.push(20);> >numbers.push(7);> >// get the element at the top> >cout <<>'Top element: '> <<> >numbers.top();> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>산출
Top element: 20>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
메모: 우선순위 큐의 최상위 요소에만 액세스할 수 있습니다.
3. 우선순위 대기열이 비어 있는지 확인하려면:
Priority_queue가 비어 있는지 확인하기 위해empty() 메소드를 사용합니다. 이 메서드는 다음을 반환합니다.
- True – 우선순위 큐가 비어 있을 때 반환되며 1로 표현됩니다. False – 우선순위 큐가 비어 있지 않거나 False일 때 생성되며 0으로 표현됩니다.
예:
C++
인공지능과 지능형 에이전트
// C++ program to demonstrate> // Implementation of empty() function> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>pqueueGFG;> >pqueueGFG.push(1);> > >// Priority Queue becomes 1> >// check if it is empty or not> >if> (pqueueGFG.empty())> >{> >cout <<>'Empty or true'>;> >}> >else> >{> >cout <<>'Contains element or False'>;> >}> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>산출
Contains element or False>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
4. 우선순위 큐의 크기를 가져오거나 확인하려면
우선순위 큐의 크기를 결정합니다. 간단히 말해서, 크기() 메서드는 현재 존재하는 요소의 수를 가져오는 데 사용됩니다. 우선순위 대기열 .
다음은 우선순위 큐의 크기를 확인하는 C++ 프로그램입니다.
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the> // size() method of priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// create a priority queue of string> >priority_queue pqueue;> >// add items to priority_queue> >pqueue.push(>'Geeks'>);> >pqueue.push(>'for'>);> >pqueue.push(>'Geeks'>);> >pqueue.push(>'C++'>);> >// get the size of queue> >int> size = pqueue.size();> >cout <<>'Size of the queue: '> << size;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>산출
Size of the queue: 4>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
5. 우선순위 대기열의 내용을 유사한 유형의 다른 대기열로 교환하려면
교환() 함수는 하나의 우선순위 큐의 내용을 동일한 유형, 동일하거나 크기가 다른 다른 우선순위 큐로 교환하는 데 사용됩니다.
다음은 우선순위 큐의 내용을 유사한 유형의 다른 큐와 교환하는 C++ 프로그램입니다.
C++
// CPP program to illustrate> // Implementation of swap() function> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Print elements of priority queue> void> print(priority_queue<>int>>pq)> {> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >cout << endl;> }> int> main()> {> >// priority_queue container declaration> >priority_queue<>int>>pq1;> >priority_queue<>int>>pq2;> >// pushing elements into the 1st priority queue> >pq1.push(1);> >pq1.push(2);> >pq1.push(3);> >pq1.push(4);> >// pushing elements into the 2nd priority queue> >pq2.push(3);> >pq2.push(5);> >pq2.push(7);> >pq2.push(9);> >cout <<>'Before swapping:-'> << endl;> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 1 = '>;> >print(pq1);> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 2 = '>;> >print(pq2);> >// using swap() function to swap elements of priority> >// queues> >pq1.swap(pq2);> >cout << endl <<>'After swapping:-'> << endl;> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 1 = '>;> >print(pq1);> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 2 = '>;> >print(pq2);> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>산출
Before swapping:- Priority Queue 1 = 4 3 2 1 Priority Queue 2 = 9 7 5 3 After swapping:- Priority Queue 1 = 9 7 5 3 Priority Queue 2 = 4 3 2 1>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
6. 우선순위 큐 컨테이너에 새 요소를 배치하려면
엠플레이스() 함수는 우선순위 큐 컨테이너에 새 요소를 삽입하는 데 사용되며, 새 요소는 우선순위에 따라 우선순위 큐에 추가됩니다. 푸시 작업과 유사합니다. 차이점은 emplace() 작업이 객체의 불필요한 복사본을 저장한다는 것입니다.
다음은 우선순위 큐 컨테이너에 새 요소를 배치하는 C++ 프로그램입니다.
C++
// CPP program to illustrate> // Implementation of emplace() function> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>pq;> >pq.emplace(1);> >pq.emplace(2);> >pq.emplace(3);> >pq.emplace(4);> >pq.emplace(5);> >pq.emplace(6);> >// Priority queue becomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6> >// Printing the priority queue> >cout <<>'Priority Queue = '>;> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>산출
Priority Queue = 6 5 4 3 2 1>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
7. Priority_queue의 요소로 저장된 객체의 유형을 표현하려면
Priority_queue :: value_type 메소드는 Priority_queue의 요소로 저장된 객체 유형을 나타내는 C++ STL의 내장 함수입니다. 이는 템플릿 매개변수의 동의어 역할을 합니다.
통사론:
priority_queue::value_type variable_name>
다음은 Priority_queue의 요소로 저장된 객체 유형을 나타내는 C++ 프로그램입니다.
C++
네트워킹 및 유형
// C++ program to illustrate the> // priority_queue :: value_type function> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// declare integer value_type for priority queue> >priority_queue<>int>>::value_type AnInt;> >// declare string value_type for priority queue> >priority_queue::value_type AString;> >// Declares priority_queues> >priority_queue<>int>>q1;> >priority_queue q2;> >// Here AnInt acts as a variable of int data type> >AnInt = 20;> >cout <<>'The value_type is AnInt = '> << AnInt << endl;> >q1.push(AnInt);> >AnInt = 30;> >q1.push(AnInt);> >cout <<>'Top element of the integer priority_queue is: '> ><< q1.top() << endl;> >// here AString acts as a variable of string data type> >AString =>'geek'>;> >cout << endl> ><<>'The value_type is AString = '> << AString> ><< endl;> >q2.push(AString);> >AString =>'for'>;> >q2.push(AString);> >AString =>'geeks'>;> >q2.push(AString);> >cout <<>'Top element of the string priority_queue is: '> ><< q2.top() << endl;> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>산출
The value_type is AnInt = 20 Top element of the integer priority_queue is: 30 The value_type is AString = geek Top element of the string priority_queue is: geeks>
복잡성 분석은 끝을 참조하세요.
모든 작업의 복잡성:
| 행동 양식 | 시간 복잡도 | 보조 공간 |
|---|---|---|
| 우선순위_큐::비어 있음() | 오(1) | 오(1) |
| 우선순위_큐::크기() | 오(1) | 오(1) |
| 우선순위_큐::top() | 오(1) | 오(1) |
| 우선순위_큐::푸시() | 오(로그N) | 오(1) |
| 우선순위_큐::팝() | 오(로그N) | 오(1) 그라이바흐 정규형 |
| 우선순위_큐::스왑() | 오(1) | 에) |
| Priority_queue::emplace() | 오(로그N) | 오(1) |
| 우선순위_큐 값_유형 | 오(1) | 오(1) |
