'라는 단어 트라이 '라는 단어에서 발췌한 것입니다. 검색 '. Trie는 문자열 세트를 저장하는 정렬된 트리 기반 데이터 구조입니다. 각 노드의 알파벳 문자 수와 동일한 포인터 수를 갖습니다. 단어의 접두사를 사용하여 사전에서 단어를 검색할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 모든 문자열이 문자 ''로 구성된다고 가정하면 ㅏ ' 에게 ' 와 함께 '는 영어 알파벳에서 각 트라이 노드는 최대 26 포인트들.
Trie는 디지털 트리 또는 접두사 트리라고도 합니다. Trie의 노드 위치에 따라 해당 노드가 연결되는 키가 결정됩니다.
문자열 집합에 대한 Trie의 속성:
- 트리의 루트 노드는 항상 널 노드를 나타냅니다.
- 노드의 각 하위 항목은 알파벳순으로 정렬됩니다.
- 각 노드는 최대 26 어린이(A~Z).
- 각 노드(루트 제외)는 알파벳 한 글자를 저장할 수 있습니다.
아래 다이어그램은 종, 곰, 보어, 배트, 공, 스톱, 스톡 및 스택에 대한 트리 표현을 보여줍니다.
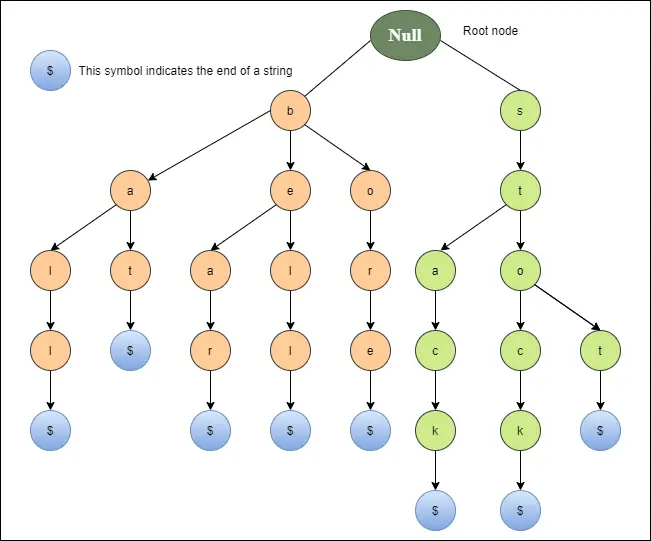
Trie의 기본 동작
Trie에는 세 가지 작업이 있습니다.
- 노드 삽입
- 노드 검색
- 노드 삭제
Trie에 노드 삽입
첫 번째 작업은 트리에 새 노드를 삽입하는 것입니다. 구현을 시작하기 전에 다음 사항을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
- 입력된 키(단어)의 모든 문자가 Trie_node에 개별적으로 삽입됩니다. 하위 항목은 Trie 노드의 다음 레벨을 가리킨다는 점에 유의하세요.
- 키 문자 배열은 하위 항목의 인덱스 역할을 합니다.
- 현재 노드에 이미 현재 문자에 대한 참조가 있는 경우 현재 노드를 해당 참조 노드로 설정합니다. 그렇지 않으면 새 노드를 만들고 문자를 현재 문자와 동일하게 설정하고 이 새 노드로 현재 노드를 시작합니다.
- 문자 길이는 트라이의 깊이를 결정합니다.
Trie에 새 노드 삽입 구현
public class Data_Trie { private Node_Trie root; public Data_Trie(){ this.root = new Node_Trie(); } public void insert(String word){ Node_Trie current = root; int length = word.length(); for (int x = 0; x <length; x++){ char l="word.charAt(x);" node_trie node="current.getNode().get(L);" if (node="=" null){ (); current.getnode().put(l, node); } current="node;" current.setword(true); < pre> <h3>Searching a node in Trie</h3> <p>The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie. The implementation of the searching operation is shown below.</p> <p>Implementation of search a node in the Trie</p> <pre> class Search_Trie { private Node_Trie Prefix_Search(String W) { Node_Trie node = R; for (int x = 0; x <w.length(); x++) { char curletter="W.charAt(x);" if (node.containskey(curletter)) node="node.get(curLetter);" } else return null; node; public boolean search(string w) node_trie !="null" && node.isend(); < pre> <h3>Deletion of a node in the Trie</h3> <p>The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.</li> <li>If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.</li> </ol> <p> <strong>Implementation of delete a node in the Trie</strong> </p> <pre> public void Node_delete(String W) { Node_delete(R, W, 0); } private boolean Node_delete(Node_Trie current, String W, int Node_index) { if (Node_index == W.length()) { if (!current.isEndOfWord()) { return false; } current.setEndOfWord(false); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } char A = W.charAt(Node_index); Node_Trie node = current.getChildren().get(A); if (node == null) { return false; } boolean Current_Node_Delete = Node_delete(node, W, Node_index + 1) && !node.isEndOfWord(); if (Current_Node_Delete) { current.getChildren().remove(A); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } return false; } </pre> <h2>Applications of Trie</h2> <p> <strong>1. Spell Checker</strong> </p> <p>Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.</p> <p>Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.</p> <p> <strong>2. Auto-complete</strong> </p> <p>Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.</p> <ul> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> <li>We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.</li> <li>As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>3. Browser history</strong> </p> <p>It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.</p> <h2>Advantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.</li> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> </ol> <h2>Disadvantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It requires more memory to store the strings.</li> <li>It is slower than the hash table.</li> </ol> <h2>Complete program in C++</h2> <pre> #include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - 'a'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" '�') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf('%c ', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf('search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf('not found
'); else printf('found!
'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" 'oh'); 'way'); 'bag'); 'can'); search(flag, 'ohh'); 'ways'); print_trie(flag); printf('
'); printf('deleting 'hello'...
'); 'can'...
'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;></pre></w.length();></pre></length;> 트라이의 응용
1. 맞춤법 검사기
맞춤법 검사는 3단계 프로세스로 이루어집니다. 먼저 사전에서 해당 단어를 찾아 가능한 제안을 생성한 다음 원하는 단어가 맨 위에 오도록 제안 단어를 정렬합니다.
Trie는 단어를 사전에 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. 맞춤법 검사기는 데이터 구조에서 단어를 검색하여 가장 효율적인 방법으로 쉽게 적용할 수 있습니다. trie를 사용하면 사전에서 단어를 쉽게 볼 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 관련 단어나 제안 모음을 포함하는 알고리즘을 구축하는 것도 간단합니다.
2. 자동 완성
자동 완성 기능은 텍스트 편집기, 모바일 애플리케이션 및 인터넷에서 널리 사용됩니다. 다음과 같은 이유로 단어를 완성하기 위한 대체 단어를 찾는 간단한 방법을 제공합니다.
- 노드의 키를 기준으로 항목의 알파벳순 필터를 제공합니다.
- 우리는 사용자가 입력한 문자열을 나타내는 노드를 얻기 위해서만 포인터를 추적합니다.
- 입력을 시작하자마자 입력을 완료하려고 시도합니다.
3. 브라우저 기록
또한 브라우저에서 URL을 완성하는 데에도 사용됩니다. 브라우저는 귀하가 방문한 웹사이트의 URL 기록을 유지합니다.
트라이의 장점
- 해시 테이블이나 이진 검색 트리보다 더 빠르게 문자열을 삽입하고 검색할 수 있습니다.
- 노드의 키를 기준으로 항목의 알파벳순 필터를 제공합니다.
트라이의 단점
- 문자열을 저장하려면 더 많은 메모리가 필요합니다.
- 해시 테이블보다 느립니다.
C++로 작성된 완전한 프로그램
#include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - \'a\'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" \'�\') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - \'a\'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf(\'%c \', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf(\'search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf(\'not found
\'); else printf(\'found!
\'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" \'oh\'); \'way\'); \'bag\'); \'can\'); search(flag, \'ohh\'); \'ways\'); print_trie(flag); printf(\'
\'); printf(\'deleting \'hello\'...
\'); \'can\'...
\'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;> 